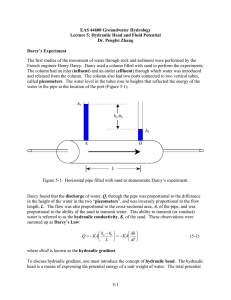
Lecture 5
... In deriving the above expression for hydraulic head we have ignored the fact that moving fluid tends to remain in motion due to its kinetic energy (Ek). This energy is equal to one-half the product of the fluid mass (m) and the square of the fluid velocity (v): Ek = ...
... In deriving the above expression for hydraulic head we have ignored the fact that moving fluid tends to remain in motion due to its kinetic energy (Ek). This energy is equal to one-half the product of the fluid mass (m) and the square of the fluid velocity (v): Ek = ...
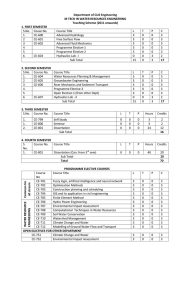
Department of Civil Engineering M TECH IN WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING
... Historical profile on world water resources development, global water resources, hydrologic cycle, watershed, zoning, watershed management, interrelation of water resources with other natural resources and the environment, concept of sustainable water resources development. Water quality and water p ...
... Historical profile on world water resources development, global water resources, hydrologic cycle, watershed, zoning, watershed management, interrelation of water resources with other natural resources and the environment, concept of sustainable water resources development. Water quality and water p ...
Length and Flow Rate
... Since this equation applies to non-turbulent flow, it may not perfectly model the situation studied. For the head of water used in this investigation, the velocity of the water flowing through the tube is relatively high, therefore some turbulence may be expected. Reynolds number2 can be used to dis ...
... Since this equation applies to non-turbulent flow, it may not perfectly model the situation studied. For the head of water used in this investigation, the velocity of the water flowing through the tube is relatively high, therefore some turbulence may be expected. Reynolds number2 can be used to dis ...
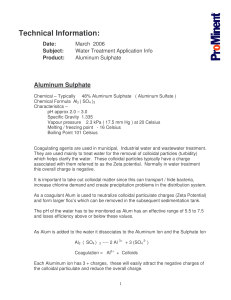
Tech Info Aluminum Sulphate - ProMinent
... which helps clarify the water. These colloidal particles typically have a charge associated with them referred to as the Zeta potential. Normally in water treatment this overall charge is negative. It is important to take out colloidal matter since this can transport / hide bacteria, increase chlori ...
... which helps clarify the water. These colloidal particles typically have a charge associated with them referred to as the Zeta potential. Normally in water treatment this overall charge is negative. It is important to take out colloidal matter since this can transport / hide bacteria, increase chlori ...
Rethinking the water cycle
... substances that were formerly only regarded as contaminants. For instance, ammonia removed from water can be used in the production of ammonium sulfate fertilizer, rather than simply discarded. Our ability to reuse water. We are witnessing significant improvements in membrane-based treatments that s ...
... substances that were formerly only regarded as contaminants. For instance, ammonia removed from water can be used in the production of ammonium sulfate fertilizer, rather than simply discarded. Our ability to reuse water. We are witnessing significant improvements in membrane-based treatments that s ...
All About Aqueducts
... waterway system ran below ground. Channels bored through rock, or dug below the surface carried water where it was convenient and possible. Of the approximately 260 miles in the aqueduct system, only 30 miles consisted of the visible, mammoth arched structures. The aqueducts were built only to carry ...
... waterway system ran below ground. Channels bored through rock, or dug below the surface carried water where it was convenient and possible. Of the approximately 260 miles in the aqueduct system, only 30 miles consisted of the visible, mammoth arched structures. The aqueducts were built only to carry ...
L-14 Fluids - 3 - University of Iowa Physics
... • The buoyant force is always there whether the object floats or not • The object will float if the buoyant force is big enough to support the object’s weight • The object will displace just enough water so that the buoyant force = its weight • If the object is completely submerged, and the weight o ...
... • The buoyant force is always there whether the object floats or not • The object will float if the buoyant force is big enough to support the object’s weight • The object will displace just enough water so that the buoyant force = its weight • If the object is completely submerged, and the weight o ...
State of groundwater in the coastal cities of Bangladesh and
... • Peoples participation, awareness education and applied research is necessary and it should be included in national urban water development program to maintain drinking water quality, supply and management in the coastal cities in Bangladesh. ...
... • Peoples participation, awareness education and applied research is necessary and it should be included in national urban water development program to maintain drinking water quality, supply and management in the coastal cities in Bangladesh. ...
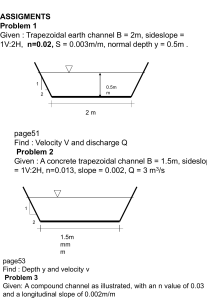
1 Pipe Sizing Part 1: Friction Loss Basics
... The faster the water molecules move against one another, the more friction there is – just like when you rub your hands together to make them warm: The faster you move them, the warmer your hands get. Again, this is friction. ...
... The faster the water molecules move against one another, the more friction there is – just like when you rub your hands together to make them warm: The faster you move them, the warmer your hands get. Again, this is friction. ...
Ground Water
... – Water table can be lowered by pumping, a process known as drawdown – Water may rise to a level above the top of a confined aquifer, producing an artesian well ...
... – Water table can be lowered by pumping, a process known as drawdown – Water may rise to a level above the top of a confined aquifer, producing an artesian well ...
Read the Mid-Project Preliminary Research Report
... Overview of Methods and Procedures A laboratory approach is being used to investigate the flow and nitrate-N reducing properties of agricultural residue-based biofilter media—corn cobs, corn stover, and barley straw—compared to wood chips. PVC pipe columns (6-in. dia. by 19 in. long) were packed wit ...
... Overview of Methods and Procedures A laboratory approach is being used to investigate the flow and nitrate-N reducing properties of agricultural residue-based biofilter media—corn cobs, corn stover, and barley straw—compared to wood chips. PVC pipe columns (6-in. dia. by 19 in. long) were packed wit ...
JWET Sample Paper
... The Society promotes the diffusion of the newer knowledge and information in areas concerning the water environment by holding seminars and lectures. The Society accepts commissions for information collection, investigations and research. Such commissions serve to fulfill of the Society's social res ...
... The Society promotes the diffusion of the newer knowledge and information in areas concerning the water environment by holding seminars and lectures. The Society accepts commissions for information collection, investigations and research. Such commissions serve to fulfill of the Society's social res ...
29006_L14
... the weight of the fluid which it displaces. Anything less dense than water will float in water water weighs 10N/liter each liter of displaced water provides 10 N of buoyant force –helium balloons: (density of He = 0.18 kg/m3) –hot air balloons: the density of hot air is lower than the density o ...
... the weight of the fluid which it displaces. Anything less dense than water will float in water water weighs 10N/liter each liter of displaced water provides 10 N of buoyant force –helium balloons: (density of He = 0.18 kg/m3) –hot air balloons: the density of hot air is lower than the density o ...
Physics 123 Fluid Mechanics Review
... (b) The difference in height between the mouth and the surface gets larger as so the flow rate will decrease. (It is harder to pull the water up a larger distance.) 7. (a) We apply the continuity equation: ...
... (b) The difference in height between the mouth and the surface gets larger as so the flow rate will decrease. (It is harder to pull the water up a larger distance.) 7. (a) We apply the continuity equation: ...
How Can You Save Water? Don`t ignore leaks! Dust suppression
... Saving water is part of being a responsible contractor – it makes financial and environmental sense. Society and our clients now expect companies to avoid wasting water. Currently you could pay up to £4.85 per cubic meter for your mains water and wastewater disposal and the cost of water is likely t ...
... Saving water is part of being a responsible contractor – it makes financial and environmental sense. Society and our clients now expect companies to avoid wasting water. Currently you could pay up to £4.85 per cubic meter for your mains water and wastewater disposal and the cost of water is likely t ...
L-14 Fluids [3] - University of Iowa Physics
... • The pressure in a moving fluid is less than the pressure in a fluid at rest! Æ this is Bernoulli's principle. • Where a fluid moves faster its pressure is lower, where it moves slower, its pressure is higher. • As we will see, this is the principle that allows airplanes to fly ...
... • The pressure in a moving fluid is less than the pressure in a fluid at rest! Æ this is Bernoulli's principle. • Where a fluid moves faster its pressure is lower, where it moves slower, its pressure is higher. • As we will see, this is the principle that allows airplanes to fly ...
[] Chapter 14b
... Two cups are filled to the same level with water. One of the two cups has plastic balls floating in it. If the density of the plastic balls is less than that of ice, which of the two cups ...
... Two cups are filled to the same level with water. One of the two cups has plastic balls floating in it. If the density of the plastic balls is less than that of ice, which of the two cups ...
The water cycle and energy transformations
... Flow rate depends on: • Potential difference • “resistance” (or “conductance”) ...
... Flow rate depends on: • Potential difference • “resistance” (or “conductance”) ...
Notes - Physical Properties of Seawater
... How Unique is Water? • Water is one of only 3 naturally occurring liquids (mercury and ammonia) • Only substance occurring naturally that exists in all 3 states – solid, liquid, and gas – on Earth’s surface • Extremely large liquid range (0oC - 100oC) • Expands, becomes less dense as a solid ...
... How Unique is Water? • Water is one of only 3 naturally occurring liquids (mercury and ammonia) • Only substance occurring naturally that exists in all 3 states – solid, liquid, and gas – on Earth’s surface • Extremely large liquid range (0oC - 100oC) • Expands, becomes less dense as a solid ...
pretest_posttest - Understanding Science Using NOS
... 1. Water is essential for life. Its special properties make water the single most important molecule in plant life. Which of the following properties of water enables it to move from the roots to the leaves of plants? A. Water expands as it freezes. B. Water is an excellent solvent. C. Water exhibit ...
... 1. Water is essential for life. Its special properties make water the single most important molecule in plant life. Which of the following properties of water enables it to move from the roots to the leaves of plants? A. Water expands as it freezes. B. Water is an excellent solvent. C. Water exhibit ...
Water Transport in Plants
... – High temp = lots of transpiration water can raise 75cm per minute – Low temperature = transpiration rate slower ...
... – High temp = lots of transpiration water can raise 75cm per minute – Low temperature = transpiration rate slower ...
Earth Systems Review Test 3
... 8. What determines whether water on Earth’s surface will seep into the ground or become runoff? Whether the pores in the ground can take water in 9. What happens to surface water when it evaporates? It stays in the clouds 10. What separates one watershed from another? A divide (watershed is a strea ...
... 8. What determines whether water on Earth’s surface will seep into the ground or become runoff? Whether the pores in the ground can take water in 9. What happens to surface water when it evaporates? It stays in the clouds 10. What separates one watershed from another? A divide (watershed is a strea ...












![L-14 Fluids [3] - University of Iowa Physics](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015391226_1-fdc5124b593c632cc9a0ec2ed3f4cea6-300x300.png)
![[] Chapter 14b](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008122839_1-6d9fbc58632d0d5ee395cbb7289d87a1-300x300.png)





