Operating Systems Lab Manual (2003 Credit System)
... CPU scheduling algorithms: To calculate the turnaround time and waiting time of each process along with average turnaround and waiting times using the following scheduling algorithms. ...
... CPU scheduling algorithms: To calculate the turnaround time and waiting time of each process along with average turnaround and waiting times using the following scheduling algorithms. ...
GNoC - Technion - Electrical Engineering
... Complete-exchange periodic traffic pattern. No buffering, deflecting or dropping packets. Equal propagation times and capacity on links. Equal packet sizes. Shortest routing. ...
... Complete-exchange periodic traffic pattern. No buffering, deflecting or dropping packets. Equal propagation times and capacity on links. Equal packet sizes. Shortest routing. ...
RAL Tier 1a
... • Maui scheduler has been in production for last 3 months. • Allows extremely flexible scheduling with many features. But …. – Not all of it works – we have done much work with developers for fixes. – Major problem – MAUI schedules on wall clock time – not CPU time. Had to bodge it!! ...
... • Maui scheduler has been in production for last 3 months. • Allows extremely flexible scheduling with many features. But …. – Not all of it works – we have done much work with developers for fixes. – Major problem – MAUI schedules on wall clock time – not CPU time. Had to bodge it!! ...
Win32 Programming
... We’ve got thread basics worked out… But it’s very helpful to understand how the OS deals with thread scheduling This lesson, we’ll work on scheduling threads – understanding how each one gets executed on the machine ...
... We’ve got thread basics worked out… But it’s very helpful to understand how the OS deals with thread scheduling This lesson, we’ll work on scheduling threads – understanding how each one gets executed on the machine ...
Production and Operations Management: Manufacturing and Services
... Management (OM) is defined as the design, operation, and improvement of the systems that create and deliver the firm’s primary products and services ...
... Management (OM) is defined as the design, operation, and improvement of the systems that create and deliver the firm’s primary products and services ...
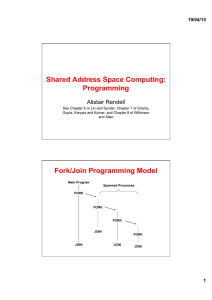
Shared Address Space Computing: Programming Fork/Join
... – Ability to mask access to memory, I/O or communication by having another thread execute in the meantime (but how quickly can execution switch between threads?) ...
... – Ability to mask access to memory, I/O or communication by having another thread execute in the meantime (but how quickly can execution switch between threads?) ...
1up
... – Ability to mask access to memory, I/O or communication by having another thread execute in the meantime (but how quickly can execution switch between threads?) ...
... – Ability to mask access to memory, I/O or communication by having another thread execute in the meantime (but how quickly can execution switch between threads?) ...
Template for project specification
... 1. A military base controls some remote devices whose feedback and reaction time is critical. The devices are managed through some software programs. Each program receives a signal from the device, elaborates the signal and must reply within a certain time. Criteria: Since feedback and reaction is c ...
... 1. A military base controls some remote devices whose feedback and reaction time is critical. The devices are managed through some software programs. Each program receives a signal from the device, elaborates the signal and must reply within a certain time. Criteria: Since feedback and reaction is c ...
ppt version
... In the Resource Aware Scheduling, it is mentioned that it has workload sensitive form of admission control. How does it actually measure whether a given thread is near to complete ? ...
... In the Resource Aware Scheduling, it is mentioned that it has workload sensitive form of admission control. How does it actually measure whether a given thread is near to complete ? ...
Chapter 13
... Parallel – old and new run together Direct cutover (or plunge) – replace the old system with new Pilot – introduce to a small are of the organization Phased – introduce in stages ...
... Parallel – old and new run together Direct cutover (or plunge) – replace the old system with new Pilot – introduce to a small are of the organization Phased – introduce in stages ...
CS 411 – Operating Systems II
... 3. Explain why synchronization is necessary for a concurrent processes scenario, and design synchronization solutions (ABET Outcomes: A, J) 4. Apply appropriate algorithms to avoid deadlock for given concurrent processes (ABET Outcomes: A, B, C, I, J) 5. Explain the strengths and weaknesses of sever ...
... 3. Explain why synchronization is necessary for a concurrent processes scenario, and design synchronization solutions (ABET Outcomes: A, J) 4. Apply appropriate algorithms to avoid deadlock for given concurrent processes (ABET Outcomes: A, B, C, I, J) 5. Explain the strengths and weaknesses of sever ...
Processes and Threads
... A Race Condition may occur when Two or more processes want to access a shared resource at same time and the result depends upon who runs when. ...
... A Race Condition may occur when Two or more processes want to access a shared resource at same time and the result depends upon who runs when. ...
Path Scheduling on Digital Microfluidic Biochips
... Resource-constrained scheduling of operations into time-steps Time-step ~ scheduling unit, usually 1s or 2s ...
... Resource-constrained scheduling of operations into time-steps Time-step ~ scheduling unit, usually 1s or 2s ...
Threads in Java
... Timed Waiting: sleeping for a specific amount of time Blocked: waiting for resources Terminated: thread is complete ...
... Timed Waiting: sleeping for a specific amount of time Blocked: waiting for resources Terminated: thread is complete ...
Windows XP - British Columbia Institute of Technology
... – Traditionally via motherboard with multiple processor slots – Multiple processors are now incorporated into single packages containing multiple ‘cores’ • Single core, dual core, quad core, etc.. – Individual processes, threads can run simultaneously on each processor/core ...
... – Traditionally via motherboard with multiple processor slots – Multiple processors are now incorporated into single packages containing multiple ‘cores’ • Single core, dual core, quad core, etc.. – Individual processes, threads can run simultaneously on each processor/core ...
BeOS-by-Robert-Robinson-2005
... Levels 100-120: reserved for real-time threads. Time-sharing threads are scheduled according to their priority number and a logarithmic scale of 2. • So a thread with a priority number greater by 2 is four times as likely to be chosen to execute. ...
... Levels 100-120: reserved for real-time threads. Time-sharing threads are scheduled according to their priority number and a logarithmic scale of 2. • So a thread with a priority number greater by 2 is four times as likely to be chosen to execute. ...
PL , OS and OOPS Concept - Banking Solutions , Nagpur
... Crating and deleting both the files and directives. Other functions of Operating system Allocating space for files Keeping backup securing easy access to file Input-output management ...
... Crating and deleting both the files and directives. Other functions of Operating system Allocating space for files Keeping backup securing easy access to file Input-output management ...
SOLUTION
... c. Allot a longer amount of time to processes deserving higher priority, in other words, have two or more quantums possible in the round-robin scheme. (Adaptive quantums for each process. A higher priority process can use up to 2/3/4/etc.) Question 4 [8 marks]. Explain the differences in how much th ...
... c. Allot a longer amount of time to processes deserving higher priority, in other words, have two or more quantums possible in the round-robin scheme. (Adaptive quantums for each process. A higher priority process can use up to 2/3/4/etc.) Question 4 [8 marks]. Explain the differences in how much th ...
Columbia University Department of Computer Science
... Thread overhead less; more useful processing ...
... Thread overhead less; more useful processing ...
CPU Scheduling
... Scheduling (as an Optimization task): How to best order the ready queue for efficiency purposes. CPU utilization: % of time CPU in use Throughput: # of jobs completed per time unit Turnaround Time: wall clock time required to complete a job Waiting Time: amount of time process is ready but waiting t ...
... Scheduling (as an Optimization task): How to best order the ready queue for efficiency purposes. CPU utilization: % of time CPU in use Throughput: # of jobs completed per time unit Turnaround Time: wall clock time required to complete a job Waiting Time: amount of time process is ready but waiting t ...
The following is reprinted from European Journal of Operational
... A.V. Naik, A. Baveja, R. Batta, and P. Caulkins, “Scheduling crackdowns on illicit drug markets,” pp. 231-250, ©1996, with permission from Elsevier. Abstract: This paper presents an analytical approach for scheduling crackdowns on street-corner drug markets. The crackdown scheduling problem is shown ...
... A.V. Naik, A. Baveja, R. Batta, and P. Caulkins, “Scheduling crackdowns on illicit drug markets,” pp. 231-250, ©1996, with permission from Elsevier. Abstract: This paper presents an analytical approach for scheduling crackdowns on street-corner drug markets. The crackdown scheduling problem is shown ...
CS 354 (Park) Midterm Oct. 19 (Mon.), 2015
... current (i.e., old) process that is context switched out, and retoring the state of the (new) process that is context switched in. What is the sequence of steps performed—specify what each step does in words (i.e., no need to write assembly code)—to save the state of the old process? Restoring the s ...
... current (i.e., old) process that is context switched out, and retoring the state of the (new) process that is context switched in. What is the sequence of steps performed—specify what each step does in words (i.e., no need to write assembly code)—to save the state of the old process? Restoring the s ...
January 2010 Preliminary Exams Computer Operating Systems (Questions 1-4)
... Describe how and the OS schedules read/write head of the disk. Explain the need for such scheduling. Describe LOOK and C-LOOK disk scheduling algorithms. Give an example of read/write head scheduling using these two algorithms. One of the algorithms results in less read/write head movement. Name whi ...
... Describe how and the OS schedules read/write head of the disk. Explain the need for such scheduling. Describe LOOK and C-LOOK disk scheduling algorithms. Give an example of read/write head scheduling using these two algorithms. One of the algorithms results in less read/write head movement. Name whi ...