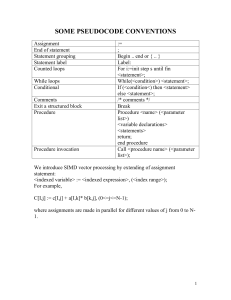
Click Here
... that are popular in scientific applications, such as discrete time Markov chains, the Poisson process, continuous time Markov processes, renewal processes, queuing models, and Brownian motion. ...
... that are popular in scientific applications, such as discrete time Markov chains, the Poisson process, continuous time Markov processes, renewal processes, queuing models, and Brownian motion. ...
Lecture OS - University of Wisconsin
... Applicable to any number of processes on either a single processor or multiple processors sharing main memory It is simple and therefore easy to verify It can be used to support multiple critical sections Disadvantages Busy-waiting consumes processor time Starvation is possible when a pr ...
... Applicable to any number of processes on either a single processor or multiple processors sharing main memory It is simple and therefore easy to verify It can be used to support multiple critical sections Disadvantages Busy-waiting consumes processor time Starvation is possible when a pr ...
Colin Roby and Jaewook Kim - WindowsThread
... Detect the cpu core topology – how many real hardware threads exist Detect the relationship between the hardware threads such as sharing data caches or sharing instructions set ...
... Detect the cpu core topology – how many real hardware threads exist Detect the relationship between the hardware threads such as sharing data caches or sharing instructions set ...
HVAC-Aware Occupancy Scheduling
... too little is destroyed the effect of a large neighborhood is lost and if too much is destroyed then the approach turns into repeated re-optimisation. Another important decision is whether the repair step should be optimal or not. An optimal repair will be slower than a heuristic, but may potentiall ...
... too little is destroyed the effect of a large neighborhood is lost and if too much is destroyed then the approach turns into repeated re-optimisation. Another important decision is whether the repair step should be optimal or not. An optimal repair will be slower than a heuristic, but may potentiall ...
Scheduling Algorithms
... Default_oss describes the default location of requested objects (default RR strategy). Target_oss represents the storage server calculated based on this MLML scheduling algorithm. If the target_oss and the default_oss are not the same server, we then need to consider whether it is worth of sche ...
... Default_oss describes the default location of requested objects (default RR strategy). Target_oss represents the storage server calculated based on this MLML scheduling algorithm. If the target_oss and the default_oss are not the same server, we then need to consider whether it is worth of sche ...
495-210
... allocation ones and finally hybrid scheduling. In the first group, the capacities for each resource are known and the determination of the activities over time must be determined (Flow-shop and Job-shop problems belong to this class). In resource allocation problems the demand is known and the alloc ...
... allocation ones and finally hybrid scheduling. In the first group, the capacities for each resource are known and the determination of the activities over time must be determined (Flow-shop and Job-shop problems belong to this class). In resource allocation problems the demand is known and the alloc ...
Thread Basics
... can – static and global variables can be modified at any time by other threads, leading to all sorts of interesting race conditions Your thread function must return a DWORD ...
... can – static and global variables can be modified at any time by other threads, leading to all sorts of interesting race conditions Your thread function must return a DWORD ...
threads
... Haskell and The Poor Man’s Concurrency Monad are a promising solution for highperformance, massively-concurrent networking ...
... Haskell and The Poor Man’s Concurrency Monad are a promising solution for highperformance, massively-concurrent networking ...
Chapter
... O.S describe a process by means of a description table known as process control block (PCB) PCB contains all the information related to to the whole life cycle of a process like process identification, owner, process status, description of the allocated address space and so on. Different O.S u ...
... O.S describe a process by means of a description table known as process control block (PCB) PCB contains all the information related to to the whole life cycle of a process like process identification, owner, process status, description of the allocated address space and so on. Different O.S u ...
A Priority Based Job Scheduling Algorithm in Cloud Computing
... one the tasks performed in order to gain maximum profit. Different types of job scheduling algorithms have been applied on different types of data workloads. And results are measured with different performance parameters to evaluate the performance. Job-scheduling algorithms are developed to accompl ...
... one the tasks performed in order to gain maximum profit. Different types of job scheduling algorithms have been applied on different types of data workloads. And results are measured with different performance parameters to evaluate the performance. Job-scheduling algorithms are developed to accompl ...
deadlock
... First process scans, then tries to write to CD Second process locks the CD first, then tries to scan Both processes block! This is called a deadlock. ...
... First process scans, then tries to write to CD Second process locks the CD first, then tries to scan Both processes block! This is called a deadlock. ...
PPT - School of Computer Science
... GUI-based applications: closely tied to a singly-threaded event handler, but relies on other concurrent services – also improves performance. Component-based software: Large granularity components belonging to a single system can compute semi-autonomously in a collaborative context. Mobile Code: Can ...
... GUI-based applications: closely tied to a singly-threaded event handler, but relies on other concurrent services – also improves performance. Component-based software: Large granularity components belonging to a single system can compute semi-autonomously in a collaborative context. Mobile Code: Can ...
i ≠ 1 - The Department of Computer Science
... Heisenbugs, corrupt states, leaked resources are common… Correct and faultless SW is hard ...
... Heisenbugs, corrupt states, leaked resources are common… Correct and faultless SW is hard ...
P2P Streaming 1H2007 - University of Wales, Newport
... Simple scheduler • Packet is scheduled or re-scheduled whenever • notification is received ...
... Simple scheduler • Packet is scheduled or re-scheduled whenever • notification is received ...
mecce 101 analytical foundations for communication engineering
... What is the probability that (i) there are exactly 2 arrivals in the first 15 minutes (ii) there are at least 2 arrivals in the first 20 minutes (iii) Probability of ( at least one arrival in the first 15 minutes / there are exactly 2 arrivals in the first 15 minutes) ...
... What is the probability that (i) there are exactly 2 arrivals in the first 15 minutes (ii) there are at least 2 arrivals in the first 20 minutes (iii) Probability of ( at least one arrival in the first 15 minutes / there are exactly 2 arrivals in the first 15 minutes) ...
on page 2-2
... sets of data. These are, in general, good candidates for thread types. When data is present in the system in sequential blocks, only one instance of the thread type is required. If the same operation is performed on separate sets of data simultaneously, multiple threads of the same type can coexist ...
... sets of data. These are, in general, good candidates for thread types. When data is present in the system in sequential blocks, only one instance of the thread type is required. If the same operation is performed on separate sets of data simultaneously, multiple threads of the same type can coexist ...
IS C362/ IS F372 (Operating Systems) Assign
... 100, it executes a new program (assume /usr/bin/prog1.exe) and passes the integer data item ...
... 100, it executes a new program (assume /usr/bin/prog1.exe) and passes the integer data item ...
Click Here
... This course introduces stochastic processes as models for a variety of phenomena in sciences. Following a brief review of basic concepts in probability the course will introduce stochastic processes that are popular in scientific applications, such as discrete time Markov chains, the Poisson process ...
... This course introduces stochastic processes as models for a variety of phenomena in sciences. Following a brief review of basic concepts in probability the course will introduce stochastic processes that are popular in scientific applications, such as discrete time Markov chains, the Poisson process ...
Introduction (cont)
... The component of a computer that can run a program is called a processor Static body of the text of the code which is to be executed by processor is called a program Dynamic execution of a program by the processor is called a process (instruction stream, thread of execution). When multiple processes ...
... The component of a computer that can run a program is called a processor Static body of the text of the code which is to be executed by processor is called a program Dynamic execution of a program by the processor is called a process (instruction stream, thread of execution). When multiple processes ...
Chapter 7 - Process Synchronization
... mechanisms to ensure the orderly execution of cooperating processes – Synchronization itself requires some form of communication Chapter 7 -3 ...
... mechanisms to ensure the orderly execution of cooperating processes – Synchronization itself requires some form of communication Chapter 7 -3 ...
Processes
... Uniprogramming - Only one process at a time Multiprogramming 1. Multiple process at a time 2. Which process gets physical resources of machine? ...
... Uniprogramming - Only one process at a time Multiprogramming 1. Multiple process at a time 2. Which process gets physical resources of machine? ...
Solutions
... (b) Construct a numerical example with two flows to illustrate WFQ’s superiority to NFQ. Solution: • (a) The “max” in WFQ’s definition of virtual finishing time, in essence queues a particular session’s traffic behind itself. Since NFQ does not have the max, a session can send an arbitrarily large a ...
... (b) Construct a numerical example with two flows to illustrate WFQ’s superiority to NFQ. Solution: • (a) The “max” in WFQ’s definition of virtual finishing time, in essence queues a particular session’s traffic behind itself. Since NFQ does not have the max, a session can send an arbitrarily large a ...