THE CITRIC ACID CYCLE
... 1. Two carbon atoms enter the cycle in the condensation of an acetyl unit (from acetyl CoA) with oxaloacetate. Two carbon atoms leave the cycle in the form of CO2 in the successive decarboxylations catalyzed by: ...
... 1. Two carbon atoms enter the cycle in the condensation of an acetyl unit (from acetyl CoA) with oxaloacetate. Two carbon atoms leave the cycle in the form of CO2 in the successive decarboxylations catalyzed by: ...
The Respiratory System
... Sound is made in larynx, and that is where pitch and volume are controlled. The strength of expiration from the lungs also contributes to loudness. A thin-walled, cartilaginous tube that carries air from the larynx to the lungs and bronchi. Spongy, saclike respiratory organs that remove carbon dioxi ...
... Sound is made in larynx, and that is where pitch and volume are controlled. The strength of expiration from the lungs also contributes to loudness. A thin-walled, cartilaginous tube that carries air from the larynx to the lungs and bronchi. Spongy, saclike respiratory organs that remove carbon dioxi ...
Unit 2 – pupil notes
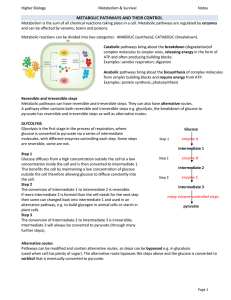
... Some of the proteins in the plasma membrane are ENZYMES that catalyse some metabolic processes. For example, ATP synthase, present in the membrane of mitochondria, chloroplasts and prokaryotes, catalyses the synthesis of ATP. Multi-enzyme complexes ensure that steps in a metabolic pathway occur in t ...
... Some of the proteins in the plasma membrane are ENZYMES that catalyse some metabolic processes. For example, ATP synthase, present in the membrane of mitochondria, chloroplasts and prokaryotes, catalyses the synthesis of ATP. Multi-enzyme complexes ensure that steps in a metabolic pathway occur in t ...
Krebs Cycle - 2008 BIOCHEM 201
... • Function of citric acid cycle is to oxidize organic molecules under aerobic conditions. • 8 reactions in the Krebs cycle • Pyruvate is degraded to CO2. • 1 GTP (ATP in bacteria) and 1 FADH2 are produced during one turn of the cycle. • 3 NADH are produced during one turn of the cycle. • NADH and FA ...
... • Function of citric acid cycle is to oxidize organic molecules under aerobic conditions. • 8 reactions in the Krebs cycle • Pyruvate is degraded to CO2. • 1 GTP (ATP in bacteria) and 1 FADH2 are produced during one turn of the cycle. • 3 NADH are produced during one turn of the cycle. • NADH and FA ...
North Carolina Test of Biology
... A strand of DNA with the sequence AAC AAG CCC undergoes a mutation, and the first A is changed to a C. How will this mutation affect the amino acid sequence? One amino acid will change. ...
... A strand of DNA with the sequence AAC AAG CCC undergoes a mutation, and the first A is changed to a C. How will this mutation affect the amino acid sequence? One amino acid will change. ...
Oh Say Can You Seed - Alabama Ag In The Classroom
... Tell students that the bean they have investigated is a part of a plant. Every flowering plant has six parts and their bean is one of them. Ask students to hypothesize which plant part they think the bean might be and explain why. (It is the seed) Instruct students to discuss the three different par ...
... Tell students that the bean they have investigated is a part of a plant. Every flowering plant has six parts and their bean is one of them. Ask students to hypothesize which plant part they think the bean might be and explain why. (It is the seed) Instruct students to discuss the three different par ...
CHAPTER 39
... In transcriptional regulation, transcription factors bind directly to specific regions of DNA and control the transcription of specific genes. ○ In the case of phytochrome-induced de-etiolation, several transcription factors are activated by phosphorylation, some through the cyclic GMP pathway, whil ...
... In transcriptional regulation, transcription factors bind directly to specific regions of DNA and control the transcription of specific genes. ○ In the case of phytochrome-induced de-etiolation, several transcription factors are activated by phosphorylation, some through the cyclic GMP pathway, whil ...
aerobic respiration
... ↑ surface area of inner membrane, which ↑ capacity to generate ATP Matrix Contains 100s of enzymes which oxidize pyruvate and fatty acids, and control the Krebs cycle ...
... ↑ surface area of inner membrane, which ↑ capacity to generate ATP Matrix Contains 100s of enzymes which oxidize pyruvate and fatty acids, and control the Krebs cycle ...
Classifying Ornamental Plants
... is written as Picea pungens var. glauca or Picea pungens glauca. ...
... is written as Picea pungens var. glauca or Picea pungens glauca. ...
Chemistry IGCSE
... filter it. We then take the filtrate and evaporate some of it water to get the most concentrated sample. Then we are ready to do the experiment. When dealing with ethanol in concentrating the sample. We have to heat it in a water bath because it is flammable. And when we use it a solvent in chromato ...
... filter it. We then take the filtrate and evaporate some of it water to get the most concentrated sample. Then we are ready to do the experiment. When dealing with ethanol in concentrating the sample. We have to heat it in a water bath because it is flammable. And when we use it a solvent in chromato ...
MS-SCI-LS-Unit 1 -- Chapter 4- Cell Processes and Energy
... equation. The products-one molecule of a sugar and six molecules of oxygen-are on the right side of the equation. An arrow, which you can read as ((yields;' connects the raw materials to the products. Light energy, which is necessary for the chemical reaction to occur, is written above the arrow. Wh ...
... equation. The products-one molecule of a sugar and six molecules of oxygen-are on the right side of the equation. An arrow, which you can read as ((yields;' connects the raw materials to the products. Light energy, which is necessary for the chemical reaction to occur, is written above the arrow. Wh ...
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
... There are three major ways in which different cells handle pyruvic acid produced by glycolysis. These are lactic acid fermentation, alcoholic fermentation and aerobic respiration. Fermentation takes place under anaerobic conditions in many prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes. For the complete oxi ...
... There are three major ways in which different cells handle pyruvic acid produced by glycolysis. These are lactic acid fermentation, alcoholic fermentation and aerobic respiration. Fermentation takes place under anaerobic conditions in many prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes. For the complete oxi ...
Chapter 16 Citric Acid Cycle
... Cycle is nice 1 oxaloacetate can oxidized infinite # of acetate 4, 5, & 6C intermediates serve both and sources for synthesis of other compounds, and a ways to bring in other compound for oxidation In eukaryote entire cycle and the subsequent oxidative phosphorylation take place in mitochondria in p ...
... Cycle is nice 1 oxaloacetate can oxidized infinite # of acetate 4, 5, & 6C intermediates serve both and sources for synthesis of other compounds, and a ways to bring in other compound for oxidation In eukaryote entire cycle and the subsequent oxidative phosphorylation take place in mitochondria in p ...
maintaining a balance
... Identify the role of enzymes in metabolism, describe their chemical composition and use a simple model to describe their specificity on substrates. Things to consider: - What does identify mean? - What does describe mean? - Understand what you are going to write before you write your answer down. Al ...
... Identify the role of enzymes in metabolism, describe their chemical composition and use a simple model to describe their specificity on substrates. Things to consider: - What does identify mean? - What does describe mean? - Understand what you are going to write before you write your answer down. Al ...
Detoxification of ammonia and biosynthesis of urea
... The liver takes up the alanine and converts it back into pyruvate by transamination. The glutamate formed in the liver is deaminated and ammonia is utilized in urea cycle. ...
... The liver takes up the alanine and converts it back into pyruvate by transamination. The glutamate formed in the liver is deaminated and ammonia is utilized in urea cycle. ...
electron transport chain
... with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
... with no release of CO2 • Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce ...
MIKROBIOLOGI DASAR
... Degradation of organic matter is influenced by nutrients present in the environment, abiotic conditions (pH, oxidation-reduction potential, O2, osmotic conditions), and the microbial community present c. Microbial degradation of complex organic material occurs when microbes use these molecules for g ...
... Degradation of organic matter is influenced by nutrients present in the environment, abiotic conditions (pH, oxidation-reduction potential, O2, osmotic conditions), and the microbial community present c. Microbial degradation of complex organic material occurs when microbes use these molecules for g ...
1. 植物 苔 Ice nucleation captures water: lichen Fungus provides UV
... Plants rise above flooding: peatland plants Glassiness protects plants in drought: blue gem plant Pollen coat prevents dehydration: plants Hairs prevent evaporation: arid zone plants Bulk prevents moisture loss: cushion plants Tightly packed stems insulate against cold: cushion plants Weak leaves d ...
... Plants rise above flooding: peatland plants Glassiness protects plants in drought: blue gem plant Pollen coat prevents dehydration: plants Hairs prevent evaporation: arid zone plants Bulk prevents moisture loss: cushion plants Tightly packed stems insulate against cold: cushion plants Weak leaves d ...
Plant Hormones
... Fruit ripening. Senescence and abscission. Interference with auxin transport. Inhibition of stem elongation Positive feedback mechanisms amplify responses in organisms. Amplification occurs when the stimulus is further activated which, initiates an additional response that produces system change. ...
... Fruit ripening. Senescence and abscission. Interference with auxin transport. Inhibition of stem elongation Positive feedback mechanisms amplify responses in organisms. Amplification occurs when the stimulus is further activated which, initiates an additional response that produces system change. ...
review - bio21.bas.bg
... melts at 157–159 oC. It is moderately soluble in water and very soluble in polar organic solvents. The pH of saturated aqueous SA is 2.4; pKa of SA is 2.98, logKow = 2.26. SA could be actively transported, metabolized, or conjugated and it could also translocate rapidly from the point of initial app ...
... melts at 157–159 oC. It is moderately soluble in water and very soluble in polar organic solvents. The pH of saturated aqueous SA is 2.4; pKa of SA is 2.98, logKow = 2.26. SA could be actively transported, metabolized, or conjugated and it could also translocate rapidly from the point of initial app ...
7 | cellular respiration
... GLUT proteins, and it can no longer leave the cell because the negatively charged phosphate will not allow it to cross the hydrophobic interior of the plasma membrane. Step 2. In the second step of glycolysis, an isomerase converts glucose-6-phosphate into one of its isomers, fructose-6-phosphate. A ...
... GLUT proteins, and it can no longer leave the cell because the negatively charged phosphate will not allow it to cross the hydrophobic interior of the plasma membrane. Step 2. In the second step of glycolysis, an isomerase converts glucose-6-phosphate into one of its isomers, fructose-6-phosphate. A ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.