File - HEENAN SCIENCE
... bonds between carbon and hydrogen atoms in the wax are broken. • The high-energy bonds are replaced by lowenergy bonds between the atoms and oxygen. • The energy of a candle flame is released from electrons. When the electrons in those bonds are shifted from higher energy levels to lower energy leve ...
... bonds between carbon and hydrogen atoms in the wax are broken. • The high-energy bonds are replaced by lowenergy bonds between the atoms and oxygen. • The energy of a candle flame is released from electrons. When the electrons in those bonds are shifted from higher energy levels to lower energy leve ...
3.28.05 - El Camino College
... transport system, they give up energy, which is used to pump H+ from the stroma into the thylakoid space. • Thus, H+ build up in the thylakoid space. • The flow of H+ through an ATP synthase complex back into the stroma drives the chemiosmotic production of ATP. ...
... transport system, they give up energy, which is used to pump H+ from the stroma into the thylakoid space. • Thus, H+ build up in the thylakoid space. • The flow of H+ through an ATP synthase complex back into the stroma drives the chemiosmotic production of ATP. ...
Note 1.3 Carbon Chemistry of Life
... Hydrocarbons - are molecules that are made up of a carbon and hydrogen atoms, such as: methane. Organic molecules - are molecules consisting of a carbon chain, with hydrogen and other atoms (nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur) attached. Carbon has the ability to form the back-bone of large diverse molecul ...
... Hydrocarbons - are molecules that are made up of a carbon and hydrogen atoms, such as: methane. Organic molecules - are molecules consisting of a carbon chain, with hydrogen and other atoms (nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur) attached. Carbon has the ability to form the back-bone of large diverse molecul ...
Biology Review
... What factors could speed up (or slow down) process C? amount of glucose; temperature; pH 2.04 Investigate and describe the structure and function of enzymes and explain their importance in biological systems. What is the function of enzymes in biological systems? Why are they necessary for all bioch ...
... What factors could speed up (or slow down) process C? amount of glucose; temperature; pH 2.04 Investigate and describe the structure and function of enzymes and explain their importance in biological systems. What is the function of enzymes in biological systems? Why are they necessary for all bioch ...
Chloroplasts are the food producers of the cell. The organelles are
... Chloroplasts are the food producers of the cell. The organelles are only found in plant cells and some protists such as algae. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts. Chloroplasts work to convert light energy of the Sun into sugars that can be used by cells. It is like a solar panel that changes sunl ...
... Chloroplasts are the food producers of the cell. The organelles are only found in plant cells and some protists such as algae. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts. Chloroplasts work to convert light energy of the Sun into sugars that can be used by cells. It is like a solar panel that changes sunl ...
No Slide Title
... Pyruvic acid is broken down to ethanol and carbon dioxide. Ex. yeast (used in production of baked ...
... Pyruvic acid is broken down to ethanol and carbon dioxide. Ex. yeast (used in production of baked ...
Biology Review
... o Inorganic Molecules (DO NOT contain carbon) Cellular Energy o Energy for chemical reactions and life processes comes in the form of a molecule called ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and Enzymes speed up the reactions. When chemical bonds form ENERGY is STORED. When chemical bonds break ENERGY is RELE ...
... o Inorganic Molecules (DO NOT contain carbon) Cellular Energy o Energy for chemical reactions and life processes comes in the form of a molecule called ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and Enzymes speed up the reactions. When chemical bonds form ENERGY is STORED. When chemical bonds break ENERGY is RELE ...
Final Exam Study Guide
... FADH2 and then in the ETC, it would be pumped into the intermembrane space of mitochondria to form a proton gradient. Then it will travel through ATP synthase. They may also end up in water. c. Describe the function of the oxygen molecules in cellular respiration they draw the electrons through the ...
... FADH2 and then in the ETC, it would be pumped into the intermembrane space of mitochondria to form a proton gradient. Then it will travel through ATP synthase. They may also end up in water. c. Describe the function of the oxygen molecules in cellular respiration they draw the electrons through the ...
Chemistry of Life
... Section 4: Energy and Metabolism Conservation of Mass – mass is neither created or destroyed, only changed forms Conservation of Energy – energy is neither created or destroyed, only changed forms ...
... Section 4: Energy and Metabolism Conservation of Mass – mass is neither created or destroyed, only changed forms Conservation of Energy – energy is neither created or destroyed, only changed forms ...
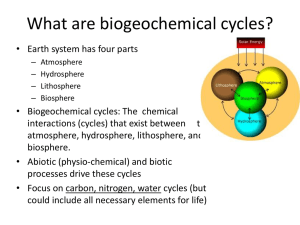
What are biogeochemical cycles?
... • Biogeochemical cycles: The chemical interactions (cycles) that exist between the atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere. • Abiotic (physio-chemical) and biotic processes drive these cycles • Focus on carbon, nitrogen, water cycles (but could include all necessary elements for life) ...
... • Biogeochemical cycles: The chemical interactions (cycles) that exist between the atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere. • Abiotic (physio-chemical) and biotic processes drive these cycles • Focus on carbon, nitrogen, water cycles (but could include all necessary elements for life) ...
Unit 2 Principals of Ecology Chapter 2 Section 2.1 Organisms and
... water molecules are carried to the atmosphere via wind or air currents water droplets condense around dust and are returned to the atmosphere as rain, snow, hail or fog. ...
... water molecules are carried to the atmosphere via wind or air currents water droplets condense around dust and are returned to the atmosphere as rain, snow, hail or fog. ...
Lecture notes for Lecture 3 Chapters 3 (Coping with Environmental
... photosynthetic organisms are able to use are called photosynthetically active radiation. For example, the most common sorts of photosynthetic pigments are the chlorophylls. Chlorophylls absorb lights in the blue and in the red and orange wavelengths (see slide 28). They reflect wavelengths in the gr ...
... photosynthetic organisms are able to use are called photosynthetically active radiation. For example, the most common sorts of photosynthetic pigments are the chlorophylls. Chlorophylls absorb lights in the blue and in the red and orange wavelengths (see slide 28). They reflect wavelengths in the gr ...
chapter 5 study guide
... Trace the path of a nitrogen atom through the nitrogen cycle o What are the major reservoirs of the nitrogen cycle? o Which are sources and which are sinks? o Why is the nitrogen cycle important to plants and animals? o How are humans influencing the nitrogen cycle? o What is the role of bacteria in ...
... Trace the path of a nitrogen atom through the nitrogen cycle o What are the major reservoirs of the nitrogen cycle? o Which are sources and which are sinks? o Why is the nitrogen cycle important to plants and animals? o How are humans influencing the nitrogen cycle? o What is the role of bacteria in ...
Enzyme Worksheet
... Proteins are made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen (CHON). Nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus (CHON P). The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper ...
... Proteins are made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen (CHON). Nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus (CHON P). The four main classes of organic compounds (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids) that are essential to the proper ...
Plant Kingdom2011
... • Multicellular, eukaryotic, cell walls made of cellulose, and carry out photosynthesis in structures called chloroplasts using a pigment called chlorophyll. ...
... • Multicellular, eukaryotic, cell walls made of cellulose, and carry out photosynthesis in structures called chloroplasts using a pigment called chlorophyll. ...
Algae • TYPES OF LIVING (plants and animals)
... • Pelagic – live up in the water column , away from the bottom. • Planktonic – Drifting and floating organisms that move with wind and currents. Many ...
... • Pelagic – live up in the water column , away from the bottom. • Planktonic – Drifting and floating organisms that move with wind and currents. Many ...
Aquatic Plants PowerPoint
... They are food for the fish and other tiny animals. They provide shelter for fish to hide from predators. Some add beauty with their bright colors and unusual shapes. They help provide oxygen for the animals in the water. ...
... They are food for the fish and other tiny animals. They provide shelter for fish to hide from predators. Some add beauty with their bright colors and unusual shapes. They help provide oxygen for the animals in the water. ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.