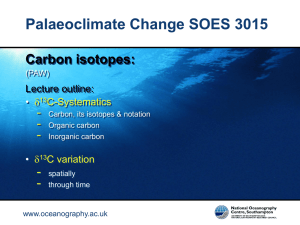
Spore-Forming Plants
... haploid phase. Diploid gives a backup copy of each gene, as a defense against random mutations. Allows a larger, more complex body. 4. Spore, seed and pollen protection and dispersal. How can they be protected, how can the male gametes find the females, and how can new individuals disperse to new lo ...
... haploid phase. Diploid gives a backup copy of each gene, as a defense against random mutations. Allows a larger, more complex body. 4. Spore, seed and pollen protection and dispersal. How can they be protected, how can the male gametes find the females, and how can new individuals disperse to new lo ...
Figure 2-5
... If G > 0, the reverse reaction will tend to occur If G = 0, both reactions will occur at equal rates ...
... If G > 0, the reverse reaction will tend to occur If G = 0, both reactions will occur at equal rates ...
AHSGE Science Vocabulary
... 43. Carbon dioxide- CO2- a by-product of cellular respiration and also the atmospheric gas necessary for photosynthesis 44. Catalyst- substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction 45. Cell-in biology, the smallest unit that can perform all life processes; cells are covered by a membrane a ...
... 43. Carbon dioxide- CO2- a by-product of cellular respiration and also the atmospheric gas necessary for photosynthesis 44. Catalyst- substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction 45. Cell-in biology, the smallest unit that can perform all life processes; cells are covered by a membrane a ...
Chapter 6 Plant structure and function
... carbohydrates. lipids), for construction of new cytoplasm, new cells and new tissues, i.e. growth. 4. Once the first leaves appear in the seedling and start to produce food by photosynthesis, the seedling will become less and less dependent on the stored food. 5. The radicle will start to absorb wat ...
... carbohydrates. lipids), for construction of new cytoplasm, new cells and new tissues, i.e. growth. 4. Once the first leaves appear in the seedling and start to produce food by photosynthesis, the seedling will become less and less dependent on the stored food. 5. The radicle will start to absorb wat ...
Cellular respiration 2
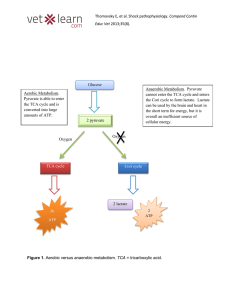
... After glycogen stores are used up the body begins to FAT break down ________ That’s why aerobic exercise must continue for longer than 20 minutes if you want to lose weight! Image from: http://blackmovie.us/movie/Fat.Albert/fat.albert.movie.jpg ...
... After glycogen stores are used up the body begins to FAT break down ________ That’s why aerobic exercise must continue for longer than 20 minutes if you want to lose weight! Image from: http://blackmovie.us/movie/Fat.Albert/fat.albert.movie.jpg ...
Ch 9 Power Point - Cellular Respiration
... • Multiprotein Complex (I, II, III, IV) • Many of the proteins are cytochromes – have a heme group (iron) which accepts protons • NADH and FADH2 enter and release e• e- are passed down the complexes until they reach oxygen (which also picks up 2 H atoms from surrounding solution to form H2O) ...
... • Multiprotein Complex (I, II, III, IV) • Many of the proteins are cytochromes – have a heme group (iron) which accepts protons • NADH and FADH2 enter and release e• e- are passed down the complexes until they reach oxygen (which also picks up 2 H atoms from surrounding solution to form H2O) ...
BL 1021 – Unit 2-3 Plants III
... 2.4 Life Cycle of Flowering Plants • On the stamen (male reproductive organ) of a flower, spores are created by cells undergoing meiosis. These spore cells will undergo mitosis to create multiple cells in the spore. Unlike with human sperm which can accomplish fertilization individually, there is n ...
... 2.4 Life Cycle of Flowering Plants • On the stamen (male reproductive organ) of a flower, spores are created by cells undergoing meiosis. These spore cells will undergo mitosis to create multiple cells in the spore. Unlike with human sperm which can accomplish fertilization individually, there is n ...
Cellular Respiration
... molecules broken down from food and release the chemical energy stored in the chemical bonds of those molecules • The energy that is released from chemical bonds during cellular respiration is stored in molecules of ATP. ...
... molecules broken down from food and release the chemical energy stored in the chemical bonds of those molecules • The energy that is released from chemical bonds during cellular respiration is stored in molecules of ATP. ...
Chapter 8 Lecture Notes - Science Learning Center
... Cell Respiration The overall reaction for cell respiration is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP (this reaction is the reverse of photosynthesis) There are three stages to cell respiration: glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain/oxidative phosphorylation. ...
... Cell Respiration The overall reaction for cell respiration is: C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP (this reaction is the reverse of photosynthesis) There are three stages to cell respiration: glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and electron transport chain/oxidative phosphorylation. ...
In this essay you should have written it as two
... chlorophyll absorbs in the red and blue regions /wavelengths of the visible spectrum accessory pigments absorb in different wavelengths / colours this increases energy absorption over the spectrum/range of light/ range of colours the accessory/others pigments pass energy to chlorophyll a chlorophyll ...
... chlorophyll absorbs in the red and blue regions /wavelengths of the visible spectrum accessory pigments absorb in different wavelengths / colours this increases energy absorption over the spectrum/range of light/ range of colours the accessory/others pigments pass energy to chlorophyll a chlorophyll ...
File
... Lactic acid is a chemical structure made out of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. It is also known as milk acid. Lactate is produced in the body during a chemical reaction, but lactic acid doesn’t form under such simple conditions. During hard exercise when anaerobic respiration occurs with aerobic resp ...
... Lactic acid is a chemical structure made out of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. It is also known as milk acid. Lactate is produced in the body during a chemical reaction, but lactic acid doesn’t form under such simple conditions. During hard exercise when anaerobic respiration occurs with aerobic resp ...
Food and Diet - Ian Dalgleish
... e.g. Glucose, Fructose, Maltose and Sucrose (table sugar) Some can be detected by Benedict's test: ...
... e.g. Glucose, Fructose, Maltose and Sucrose (table sugar) Some can be detected by Benedict's test: ...
Krebs and ETC
... phosphorylation. The phosphate group from succinylCoA is transferred to GDP, forming GTP, which then forms ATP. In step 8, oxaloacetate is formed from malate, which is used as a reactant in step 1. CO2 is released in steps 3 and 4. ...
... phosphorylation. The phosphate group from succinylCoA is transferred to GDP, forming GTP, which then forms ATP. In step 8, oxaloacetate is formed from malate, which is used as a reactant in step 1. CO2 is released in steps 3 and 4. ...
Cycles of Life: EXPLORING BIOLOGY Module 2
... • All organisms require a supply of energy, usually, but not always, from photosynthesis. • Most of the energy entering the biosphere is solar energy trapped by green plants during photosynthesis. • In addition to the production of energetic sugar molecules, photosynthesis also produces the oxygen u ...
... • All organisms require a supply of energy, usually, but not always, from photosynthesis. • Most of the energy entering the biosphere is solar energy trapped by green plants during photosynthesis. • In addition to the production of energetic sugar molecules, photosynthesis also produces the oxygen u ...
Worksheet Plants ANS.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Photosynthesis and storage of food b) What are the two types of leaves? Describe how you would tell one type from another by looking at a plant. Simple leaf, compound leaf. A simple leaf is one full structure, like a maple leaf, a compound leaf is divided into many parts, like a fern. c) Describe th ...
... Photosynthesis and storage of food b) What are the two types of leaves? Describe how you would tell one type from another by looking at a plant. Simple leaf, compound leaf. A simple leaf is one full structure, like a maple leaf, a compound leaf is divided into many parts, like a fern. c) Describe th ...
Words to Pronounce ACIDS: Sulfuric Acid Sulfurous Acid
... Without sufficient levels of these ions, muscle weakness or muscle cramps can occur. 5b. Without energy, compounds would form but never change. However, with energy we get rearrangement and change and therefore life. Energy ultimately comes from the sun. In photosynthesis light pulls apart energy-po ...
... Without sufficient levels of these ions, muscle weakness or muscle cramps can occur. 5b. Without energy, compounds would form but never change. However, with energy we get rearrangement and change and therefore life. Energy ultimately comes from the sun. In photosynthesis light pulls apart energy-po ...
Practice Bypass Answers
... used in grills. Three things are required for a gas grill to ignite: gas, oxygen from the air and a spark. When the grill is turned on, propane is delivered to the igniter, where it reacts with oxygen (burns). The process of burning propane is called combustion. It can be represented by the followin ...
... used in grills. Three things are required for a gas grill to ignite: gas, oxygen from the air and a spark. When the grill is turned on, propane is delivered to the igniter, where it reacts with oxygen (burns). The process of burning propane is called combustion. It can be represented by the followin ...
B2 revision questions
... The process by which all living organisms release energy from organic molecules 1. Glucose and oxygen diffuse from capillaries into respiring cells 2. Carbon dioxide diffuses from respiring cells into capillaries The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentr ...
... The process by which all living organisms release energy from organic molecules 1. Glucose and oxygen diffuse from capillaries into respiring cells 2. Carbon dioxide diffuses from respiring cells into capillaries The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentr ...
Cell Resp. Power Point Brief SV
... 1) ______________________ Phosphorylation: An enzyme transfers a __________ from a substrate (a molecule) to ADP, yielding ATP: ex: 1,3 Bisphosphate glycerate loses a phosphate to ADP-----> ATP 2) ______________________ Phosphorylation: Energy from redox reactions in electrontransport chain is used ...
... 1) ______________________ Phosphorylation: An enzyme transfers a __________ from a substrate (a molecule) to ADP, yielding ATP: ex: 1,3 Bisphosphate glycerate loses a phosphate to ADP-----> ATP 2) ______________________ Phosphorylation: Energy from redox reactions in electrontransport chain is used ...
Protists - TeacherWeb
... ◦ Break down organic matter, provide food for small aquatic animals ◦ Trichonympha – lives in guts of termites Breaks down cellulose in wood for termite to digest ...
... ◦ Break down organic matter, provide food for small aquatic animals ◦ Trichonympha – lives in guts of termites Breaks down cellulose in wood for termite to digest ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.