2. Plant Production Systems
... (b) Photosynthesis requires oxygen and its rate depends on the oxygen concentration. (c) Photosynthesis requires water and its availability effects photosynthetic rate. (d) Light intensity influences photosynthetic rate. ...
... (b) Photosynthesis requires oxygen and its rate depends on the oxygen concentration. (c) Photosynthesis requires water and its availability effects photosynthetic rate. (d) Light intensity influences photosynthetic rate. ...
Respiratory System
... • Most cells utilize cellular respiration to convert the chemical energy stored in nutrient macromolecules to the chemical energy utilized by cells ATP • This process is an oxidation reaction a steady supply of oxygen is required to combust glucose to carbon dioxide and water ...
... • Most cells utilize cellular respiration to convert the chemical energy stored in nutrient macromolecules to the chemical energy utilized by cells ATP • This process is an oxidation reaction a steady supply of oxygen is required to combust glucose to carbon dioxide and water ...
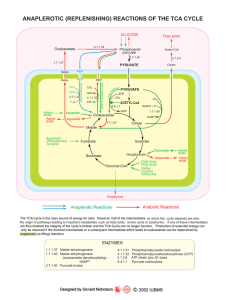
anaplerotic (replenishing) reactions of the tca cycle - Sigma
... The TCA Cycle is the main source of energy for cells. However, half of the intermediates on which the cycle depends are also the origin of pathways leading to important metabolites such as fatty acids , amino acids or porphyrins. If any of these intermediates are thus diverted the integrity of the c ...
... The TCA Cycle is the main source of energy for cells. However, half of the intermediates on which the cycle depends are also the origin of pathways leading to important metabolites such as fatty acids , amino acids or porphyrins. If any of these intermediates are thus diverted the integrity of the c ...
MCAS And Final Review Packet 2014
... 10. What kind of organisms carry out cellular respiration? All living things 11. Label this simple diagram to illustrate how carbon dioxide, water, glucose, and oxygen are used in the process of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in a plant. CO2 and H2O go into the chloroplast and C6H12O6 + O2 ...
... 10. What kind of organisms carry out cellular respiration? All living things 11. Label this simple diagram to illustrate how carbon dioxide, water, glucose, and oxygen are used in the process of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in a plant. CO2 and H2O go into the chloroplast and C6H12O6 + O2 ...
APDC Unit IV Biochem
... organic compounds (carbs, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids) by their structural formulas The cellular functions of all 4 organic compounds The 4 structural levels of proteins Water properties ...
... organic compounds (carbs, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids) by their structural formulas The cellular functions of all 4 organic compounds The 4 structural levels of proteins Water properties ...
Metabolism
... occurs in the cytoplasm of all cells. This process does not require oxygen. It is therefore referred to as an anaerobic process. ...
... occurs in the cytoplasm of all cells. This process does not require oxygen. It is therefore referred to as an anaerobic process. ...
Solomon chapter 8 practice AP bio test sept 2015
... Protons are pumped out of the mitochondria by the complexes of the electron transport chain. The proton gradient established during electron transport is a form of potential energy. The electron transport chain can be found in the mitochondria of aerobic bacteria and other cells. The movement of pro ...
... Protons are pumped out of the mitochondria by the complexes of the electron transport chain. The proton gradient established during electron transport is a form of potential energy. The electron transport chain can be found in the mitochondria of aerobic bacteria and other cells. The movement of pro ...
Respiration
... isolated environment for the mitochondrion. This membrane also adjusts the metabolites entering and leaving the mitochondrion. The inner membrane is folded up a lot to increase the surface area for attachment of ETC. These infolds are called cristae. Attaching to the cristae are many stalked particl ...
... isolated environment for the mitochondrion. This membrane also adjusts the metabolites entering and leaving the mitochondrion. The inner membrane is folded up a lot to increase the surface area for attachment of ETC. These infolds are called cristae. Attaching to the cristae are many stalked particl ...
patternsinnature
... cholesterol, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, phospholipids and proteins. These structures in turn all have a specialised function. These functions account for the movement of some substances into and out of cells. - The phospholipid bilayer acts as a barrier to ions, polar substances and large molecul ...
... cholesterol, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, phospholipids and proteins. These structures in turn all have a specialised function. These functions account for the movement of some substances into and out of cells. - The phospholipid bilayer acts as a barrier to ions, polar substances and large molecul ...
Section 3-3
... 2. Elements, chemical compounds, and other forms of matter are passed from one organism to another and from one part of the biosphere to another through biogeochemical cycles. 3. Matter can cycle through the biosphere because biological systems do not use up matter, they transform it. 4. Biogeochemi ...
... 2. Elements, chemical compounds, and other forms of matter are passed from one organism to another and from one part of the biosphere to another through biogeochemical cycles. 3. Matter can cycle through the biosphere because biological systems do not use up matter, they transform it. 4. Biogeochemi ...
CHAPTER - 6 LIFE PROCESSES
... In the mouth :- the food is broken down into smaller particles by the teeth and mixed with saliva from the salivary glands. Saliva contains the enzyme salivary amylase which converts starch into sugar. Then the food passes through the oesophagus into the stomach. In the stomach :- the gastric gland ...
... In the mouth :- the food is broken down into smaller particles by the teeth and mixed with saliva from the salivary glands. Saliva contains the enzyme salivary amylase which converts starch into sugar. Then the food passes through the oesophagus into the stomach. In the stomach :- the gastric gland ...
Muscle cramps! - WordPress.com
... During exercise, more ATP energy needs to be produced to keep the body regulated, which also results in the need for more oxygen. The most ATP is actually produced by the electron transport chain, the last step of cellular respiration. The final electron acceptor is oxygen, as it creates a pull for ...
... During exercise, more ATP energy needs to be produced to keep the body regulated, which also results in the need for more oxygen. The most ATP is actually produced by the electron transport chain, the last step of cellular respiration. The final electron acceptor is oxygen, as it creates a pull for ...
Biology 3 summary an..
... 4. Comparison of cost (dialysis more expensive long term) [1], lifestyle restrictions e.g. diet with dialysis [1], independent after transplant [1], low availability of transplant [1], donated kidney may be rejected / immunosuppressant drugs required [1] 5. Glucose enters the blood from digestive sy ...
... 4. Comparison of cost (dialysis more expensive long term) [1], lifestyle restrictions e.g. diet with dialysis [1], independent after transplant [1], low availability of transplant [1], donated kidney may be rejected / immunosuppressant drugs required [1] 5. Glucose enters the blood from digestive sy ...
Producers, Consumers, and Decomposers
... of photosynthesis is central to sustaining life on Earth. The survival of every ecosystem is dependent on the producers. Without producers capturing the energy from the sun and turning it into glucose, an ecosystem could not exist. On land, plants are the dominant producers. Phytoplankton, tiny phot ...
... of photosynthesis is central to sustaining life on Earth. The survival of every ecosystem is dependent on the producers. Without producers capturing the energy from the sun and turning it into glucose, an ecosystem could not exist. On land, plants are the dominant producers. Phytoplankton, tiny phot ...
Biology Unit 3 revision
... 4. Comparison of cost (dialysis more expensive long term) [1], lifestyle restrictions e.g. diet with dialysis [1], independent after transplant [1], low availability of transplant [1], donated kidney may be rejected / immunosuppressant drugs required [1] 5. Glucose enters the blood from digestive sy ...
... 4. Comparison of cost (dialysis more expensive long term) [1], lifestyle restrictions e.g. diet with dialysis [1], independent after transplant [1], low availability of transplant [1], donated kidney may be rejected / immunosuppressant drugs required [1] 5. Glucose enters the blood from digestive sy ...
Summary - Shavington High School
... 4. Comparison of cost (dialysis more expensive long term) [1], lifestyle restrictions e.g. diet with dialysis [1], independent after transplant [1], low availability of transplant [1], donated kidney may be rejected / immunosuppressant drugs required [1] 5. Glucose enters the blood from digestive sy ...
... 4. Comparison of cost (dialysis more expensive long term) [1], lifestyle restrictions e.g. diet with dialysis [1], independent after transplant [1], low availability of transplant [1], donated kidney may be rejected / immunosuppressant drugs required [1] 5. Glucose enters the blood from digestive sy ...
4.2 Cellular Respiration - Dr Rob's A
... This involves the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain The respiratory substrate is usually glucose but others can be used. Oxygen is also needed for cellular respiration to go to completion and produced the maximum amount of ATP ...
... This involves the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain The respiratory substrate is usually glucose but others can be used. Oxygen is also needed for cellular respiration to go to completion and produced the maximum amount of ATP ...
ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN, OXIDATIVE
... Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (1,3BPG), Succinyl-CoA, etc. ...
... Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (1,3BPG), Succinyl-CoA, etc. ...
Secondary growth increases the girth of woody plants
... roots, stems, and leaves Plants absorb water and minerals from soil through roots Plants absorb the sun’s energy and carbon dioxide from the air through shoots (stems and leaves) Plant roots depend on shoots for carbohydrates produced via photosynthesis Plant shoots depend on roots for water ...
... roots, stems, and leaves Plants absorb water and minerals from soil through roots Plants absorb the sun’s energy and carbon dioxide from the air through shoots (stems and leaves) Plant roots depend on shoots for carbohydrates produced via photosynthesis Plant shoots depend on roots for water ...
File
... ATP is continuously made at the same time as it is being used up, so there is no need for humans to have a vast store of ATP Phosphorylation is an enzyme controlled process by which a phosphate group is added to a molecule Phosphorylation also occurs when the phosphate and energy are transferred fro ...
... ATP is continuously made at the same time as it is being used up, so there is no need for humans to have a vast store of ATP Phosphorylation is an enzyme controlled process by which a phosphate group is added to a molecule Phosphorylation also occurs when the phosphate and energy are transferred fro ...
Nutrition and Metabolism (Chap 4)
... 2. Anoxygenic phototrophy Capture of light energy and production of ATP in the absence of O2. Anaerobic green and purple bacteria and heliobacteria (use reduced sulfur compounds like H2S as a source of electrons) Only PSI - (photons excite bacteriochlorophyll and are cycled back through a seri ...
... 2. Anoxygenic phototrophy Capture of light energy and production of ATP in the absence of O2. Anaerobic green and purple bacteria and heliobacteria (use reduced sulfur compounds like H2S as a source of electrons) Only PSI - (photons excite bacteriochlorophyll and are cycled back through a seri ...
Microbial Metabolism
... 2. Anoxygenic phototrophy • Capture of light energy and production of ATP in the absence of O2. • Anaerobic green and purple bacteria and heliobacteria (use reduced sulfur compounds like H2S as a source of electrons) • Only PSI - (photons excite bacteriochlorophyll and are cycled back through a seri ...
... 2. Anoxygenic phototrophy • Capture of light energy and production of ATP in the absence of O2. • Anaerobic green and purple bacteria and heliobacteria (use reduced sulfur compounds like H2S as a source of electrons) • Only PSI - (photons excite bacteriochlorophyll and are cycled back through a seri ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.