Atomic Emission Spectra, Electron Configuration, Periodicity
... are able to “jump” to higher energy levels in the atom. We call this an electron’s excited state. The excited state is, however, unstable and the electron soon falls back to its original, lower energy position in the atom, we call this its ground state. As it travels back towards its ground state it ...
... are able to “jump” to higher energy levels in the atom. We call this an electron’s excited state. The excited state is, however, unstable and the electron soon falls back to its original, lower energy position in the atom, we call this its ground state. As it travels back towards its ground state it ...
Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
... A.The suffix –ase is used to identify the specific enzymesubstrate pairing. B.The bonding sites of enzymes to substrates fit like pieces in a ...
... A.The suffix –ase is used to identify the specific enzymesubstrate pairing. B.The bonding sites of enzymes to substrates fit like pieces in a ...
Krebs Cycle - ScienceFolks
... The Krebs cycle itself actually begins when acetyl-CoA combines with a four-carbon molecule called OAA (oxaloacetate) (see Figure 1.1). This produces citric acid, which has six carbon atoms. This is why the Krebs cycle is also called the citric acid cycle. After citric acid forms, it goes through a ...
... The Krebs cycle itself actually begins when acetyl-CoA combines with a four-carbon molecule called OAA (oxaloacetate) (see Figure 1.1). This produces citric acid, which has six carbon atoms. This is why the Krebs cycle is also called the citric acid cycle. After citric acid forms, it goes through a ...
No Slide Title
... A.1. Design, analyze, or carry out simple investigations and formulate appropriate conclusions based on data obtained or provided. A.1.B Identify general distinctions among organisms that support classifying some things as plants, some as animals, and some that do not fit neatly into either group. B ...
... A.1. Design, analyze, or carry out simple investigations and formulate appropriate conclusions based on data obtained or provided. A.1.B Identify general distinctions among organisms that support classifying some things as plants, some as animals, and some that do not fit neatly into either group. B ...
1030ExamI
... 62. If a high-energy "donor" molecule physically transfers a phosphate group to ADP, this is called: A. Substrate-level phosphorylation B. Photosynthesis C. Oxidative phosphorylation D. Electron transport E. Glycolysis 63. Only a small amount of ATP is produced during glycolysis because most of the ...
... 62. If a high-energy "donor" molecule physically transfers a phosphate group to ADP, this is called: A. Substrate-level phosphorylation B. Photosynthesis C. Oxidative phosphorylation D. Electron transport E. Glycolysis 63. Only a small amount of ATP is produced during glycolysis because most of the ...
Enzymes Notes - The Lesson Locker
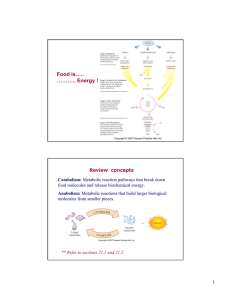
... broken down in the presence of oxygen to carbon dioxide and water. e. Anabolic pathways consume energy to build complicated molecules from simpler compounds. i. The synthesis of protein from amino acids is an example of an anabolic pathway. f. The energy released by catabolic pathways can be stored ...
... broken down in the presence of oxygen to carbon dioxide and water. e. Anabolic pathways consume energy to build complicated molecules from simpler compounds. i. The synthesis of protein from amino acids is an example of an anabolic pathway. f. The energy released by catabolic pathways can be stored ...
Chapter 19
... - From the 8 electrons and 7 H+: - 6 electrons are transferred to 3 NAD+ along with 3 H+ - 2 electrons are transferred to Q along with 2 H+ - 2 H+ are released per cycle. The two CO2 molecules do NOT come directly from the acetyl group added to CoA ...
... - From the 8 electrons and 7 H+: - 6 electrons are transferred to 3 NAD+ along with 3 H+ - 2 electrons are transferred to Q along with 2 H+ - 2 H+ are released per cycle. The two CO2 molecules do NOT come directly from the acetyl group added to CoA ...
Harvesting Electrons from the Citric Acid Cycle
... Harvesting electrons from the citric acid cycle - Enzymes of the cycle are in the mitochondria of eukaryotes - Energy of the oxidation reactions is largely conserved as reducing power (stored electrons) - Coenzymes reduced: NAD+ FAD ...
... Harvesting electrons from the citric acid cycle - Enzymes of the cycle are in the mitochondria of eukaryotes - Energy of the oxidation reactions is largely conserved as reducing power (stored electrons) - Coenzymes reduced: NAD+ FAD ...
Life on Earth Revision Notes
... Habitat is where an organism lives. Community consists of all the animals/plants living in one area. Population is one particular species. Ecosystem is made up of living (community) and non living (habitat) parts. Biomes are large ecosystems. There are 9 biomes worldwide dependent on the climate (te ...
... Habitat is where an organism lives. Community consists of all the animals/plants living in one area. Population is one particular species. Ecosystem is made up of living (community) and non living (habitat) parts. Biomes are large ecosystems. There are 9 biomes worldwide dependent on the climate (te ...
Slides - Websupport1
... As soon as glucose is inside the cell, a phosphate is added to carbon number 6, and the new molecule is called glucose 6 phosphate. This reaction is called phosphorylation and it requires one ATP, enzyme ...
... As soon as glucose is inside the cell, a phosphate is added to carbon number 6, and the new molecule is called glucose 6 phosphate. This reaction is called phosphorylation and it requires one ATP, enzyme ...
Untitled
... air. These are called stoma and they take in carbon dioxide from the air. After the plant breathes in carbon dioxide, and the water travels through the veins to the cells, it reaches something called chloroplasts. Photosynthesis takes place in the plant’s chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are inside the pl ...
... air. These are called stoma and they take in carbon dioxide from the air. After the plant breathes in carbon dioxide, and the water travels through the veins to the cells, it reaches something called chloroplasts. Photosynthesis takes place in the plant’s chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are inside the pl ...
Energy
... As starvation continues, the brain and other tissues are able to switch over to producing up to 50% of their ATP from catabolizing ketone bodies instead of glucose. By the 40th day of starvation, metabolism has stabilized at the use of about 25 g of protein and 180 g of fat each day. So long as adeq ...
... As starvation continues, the brain and other tissues are able to switch over to producing up to 50% of their ATP from catabolizing ketone bodies instead of glucose. By the 40th day of starvation, metabolism has stabilized at the use of about 25 g of protein and 180 g of fat each day. So long as adeq ...
Glycolysis Questions
... Using the diagram provided and page 65-66, answer the following questions. 1. Where does glycolysis occur? ...
... Using the diagram provided and page 65-66, answer the following questions. 1. Where does glycolysis occur? ...
Final Answer Key
... (8 pts) Answer the following questions a) What type of reaction does the coenzyme NAD+ help facilitate? Please be specific (type of functional groups or compounds and give a specific reaction name. ...
... (8 pts) Answer the following questions a) What type of reaction does the coenzyme NAD+ help facilitate? Please be specific (type of functional groups or compounds and give a specific reaction name. ...
Glycolysis - Fairfield Public Schools
... In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration Each NADH (the reduced fo ...
... In cellular respiration, glucose and other organic molecules are broken down in a series of steps Electrons from organic compounds are usually first transferred to NAD+, a coenzyme As an electron acceptor, NAD+ functions as an oxidizing agent during cellular respiration Each NADH (the reduced fo ...
The World Within An Ecosystem
... The raw materials needed by plants to produce their own food -with the energy from the Sun - are water and carbon dioxide. The products produced are food (sugars) and oxygen, which is released back into the atmosphere. The food making process is called photosynthesis. The Importance of Photosynthesi ...
... The raw materials needed by plants to produce their own food -with the energy from the Sun - are water and carbon dioxide. The products produced are food (sugars) and oxygen, which is released back into the atmosphere. The food making process is called photosynthesis. The Importance of Photosynthesi ...
Transpiration
... cells allow for gas exchange. Mesophyll cells (both palisade and spongy) are packed with chloroplasts, and this is where photosynthesis actually occurs. Epidermis also lines the lower area of the leaf (as does the cuticle). The leaf also has tiny holes within the epidermis called stomata (H). Specia ...
... cells allow for gas exchange. Mesophyll cells (both palisade and spongy) are packed with chloroplasts, and this is where photosynthesis actually occurs. Epidermis also lines the lower area of the leaf (as does the cuticle). The leaf also has tiny holes within the epidermis called stomata (H). Specia ...
AP BIOLOGY – CHAPTER 7 Cellular Respiration Outline
... b. Per glucose, 10 NADH and two FADH2 molecules provide electrons and H+ ions to electron transport system. c. For each NADH formed within the mitochondrion, three ATP are produced. d. For each FADH2 formed by Krebs cycle, two ATP result since FADH2 delivers electrons after NADH. e. For each NADH fo ...
... b. Per glucose, 10 NADH and two FADH2 molecules provide electrons and H+ ions to electron transport system. c. For each NADH formed within the mitochondrion, three ATP are produced. d. For each FADH2 formed by Krebs cycle, two ATP result since FADH2 delivers electrons after NADH. e. For each NADH fo ...
18 Pyruvate to Acetyl-CoA to Krebs Cycle A/P
... Pyruvate is one of most important intermediate forms of the breakdown of high energy macromolecules (such as sugar, lipid, and protein). Pyruvate can be converted to lactic acid in bacteria and man when oxygen is in short supply or not available. The build up of lactic acid causes some interesting e ...
... Pyruvate is one of most important intermediate forms of the breakdown of high energy macromolecules (such as sugar, lipid, and protein). Pyruvate can be converted to lactic acid in bacteria and man when oxygen is in short supply or not available. The build up of lactic acid causes some interesting e ...
Plants
... • 2) Stems- support UPRIGHT growth, transport WATER up from the roots through a special kind of vascular tissue called XYLEM, and FOOD down to the rest of the plant through another ...
... • 2) Stems- support UPRIGHT growth, transport WATER up from the roots through a special kind of vascular tissue called XYLEM, and FOOD down to the rest of the plant through another ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.