0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5
... Your graduate student friends are working on a new transistor structure made out of carbon nanotubes*. Sure, it’s not silicon, but these devices that function like normal MOSFETs. They want to put their device into the RTL circuit (like in Problem 3) as shown below, in which a PMOS carbon nanotube t ...
... Your graduate student friends are working on a new transistor structure made out of carbon nanotubes*. Sure, it’s not silicon, but these devices that function like normal MOSFETs. They want to put their device into the RTL circuit (like in Problem 3) as shown below, in which a PMOS carbon nanotube t ...
File
... transistors are designed to afford the greatest common-emitter current gain, βF, in forward-active mode. If this is the case, the collector–emitter current is approximately proportional to the base current, but many times larger, for small base current variations. • Saturation: With both junctions f ...
... transistors are designed to afford the greatest common-emitter current gain, βF, in forward-active mode. If this is the case, the collector–emitter current is approximately proportional to the base current, but many times larger, for small base current variations. • Saturation: With both junctions f ...
semiconductor
... A semiconductor is a material which has electrical conductivity between that of a conductor such as copper and an insulator such as glass. The conductivity of a semiconductor increases with increasing temperature, behavior opposite to that of a metal. Semiconductors can display a range of useful pro ...
... A semiconductor is a material which has electrical conductivity between that of a conductor such as copper and an insulator such as glass. The conductivity of a semiconductor increases with increasing temperature, behavior opposite to that of a metal. Semiconductors can display a range of useful pro ...
1296 MHz AMPLIFIER Measured at 1296 MHz : NF
... drain current – typ. + 0,59V on the gate to give 60 mA drain current. If the gate is put to ground potential the current will drop to a few microamperes of leakage current. This is more like biasing a bipolar transistor ! Therefore we have the possibility to make a simple resistor bias as well as bu ...
... drain current – typ. + 0,59V on the gate to give 60 mA drain current. If the gate is put to ground potential the current will drop to a few microamperes of leakage current. This is more like biasing a bipolar transistor ! Therefore we have the possibility to make a simple resistor bias as well as bu ...
Experiment 9 – Bipolar Junction Transistor Amplifier
... 1. What is the nominal value of C1? Calculate its impedance at 10 kHz. Then wire in C1. 2. Connect a 10 kHz sine wave from the FG to the amplifier input. Initially set the input signal, vi, for a peak-to-peak (p-p) value of about 300 mV. Display the output signal vO1 and compare it to the input sig ...
... 1. What is the nominal value of C1? Calculate its impedance at 10 kHz. Then wire in C1. 2. Connect a 10 kHz sine wave from the FG to the amplifier input. Initially set the input signal, vi, for a peak-to-peak (p-p) value of about 300 mV. Display the output signal vO1 and compare it to the input sig ...
Document
... Point b is the point in which Vin is larger than the Vc again. The capacitor resumes the charging again until it reaches point c (= point a) Repeating the discharging from point a to point b and the charging from point b to point c, we obtain the following waveform.(it is much smooth than the wav ...
... Point b is the point in which Vin is larger than the Vc again. The capacitor resumes the charging again until it reaches point c (= point a) Repeating the discharging from point a to point b and the charging from point b to point c, we obtain the following waveform.(it is much smooth than the wav ...
biasing
... VBB is the base supply voltage, which is used to forward-bias the base-emitter junction. RB is used to provide the desired value of base current. VCC is the collector supply voltage, which provides the reverse-bias voltage required for the collector-base junction. The collector resistor, RC, ...
... VBB is the base supply voltage, which is used to forward-bias the base-emitter junction. RB is used to provide the desired value of base current. VCC is the collector supply voltage, which provides the reverse-bias voltage required for the collector-base junction. The collector resistor, RC, ...
Series Voltage Regulators
... Although the Zener diode makes a reasonable voltage regulator, there are still minor variations in O/P voltage as the I/P voltage or load resistance changes, particularly when the load current is high. This has led to the development of transistor controlled regulators that have excellent regulating ...
... Although the Zener diode makes a reasonable voltage regulator, there are still minor variations in O/P voltage as the I/P voltage or load resistance changes, particularly when the load current is high. This has led to the development of transistor controlled regulators that have excellent regulating ...
2SB1705
... otherwise dispose of the same, no express or implied right or license to practice or commercially exploit any intellectual property rights or other proprietary rights owned or controlled by ROHM CO., LTD. is granted to any such buyer. Products listed in this document are no antiradiation design. ...
... otherwise dispose of the same, no express or implied right or license to practice or commercially exploit any intellectual property rights or other proprietary rights owned or controlled by ROHM CO., LTD. is granted to any such buyer. Products listed in this document are no antiradiation design. ...
M3 Semiconductor Analyzer Manual
... A bipolar transistor (BJT) is a semiconductor device commonly used for amplification. Physically, a bipolar transistor amplifies current, but it can be connected in circuits designed to amplify voltage or power. There are two major types of bipolar transistors, PNP and NPN. The ratio of the collecto ...
... A bipolar transistor (BJT) is a semiconductor device commonly used for amplification. Physically, a bipolar transistor amplifies current, but it can be connected in circuits designed to amplify voltage or power. There are two major types of bipolar transistors, PNP and NPN. The ratio of the collecto ...
US6T4
... otherwise dispose of the same, no express or implied right or license to practice or commercially exploit any intellectual property rights or other proprietary rights owned or controlled by ROHM CO., LTD. is granted to any such buyer. Products listed in this document are no antiradiation design. ...
... otherwise dispose of the same, no express or implied right or license to practice or commercially exploit any intellectual property rights or other proprietary rights owned or controlled by ROHM CO., LTD. is granted to any such buyer. Products listed in this document are no antiradiation design. ...
Transistors - University of Toronto Physics
... • This is a load-line curve, representing a line that intersects the IC axis at VCC/RC and the VCE axis at VCC, with slope -1/RC. • This line intersects all of the collector characteristic curves. • The point at which this line intersects the the curve for IB= IBB is the Q point. ...
... • This is a load-line curve, representing a line that intersects the IC axis at VCC/RC and the VCE axis at VCC, with slope -1/RC. • This line intersects all of the collector characteristic curves. • The point at which this line intersects the the curve for IB= IBB is the Q point. ...
Method for Determining the Effective Base Resistance of Bipolar
... where a diminution of a factor 4 is expected. This is due to 2-D effects and agrees very well with the study performed by 1~9].In this case measurements have been performed on devices issued from a 5GHz complementary technology. Using devices from this process this method was applied with success on ...
... where a diminution of a factor 4 is expected. This is due to 2-D effects and agrees very well with the study performed by 1~9].In this case measurements have been performed on devices issued from a 5GHz complementary technology. Using devices from this process this method was applied with success on ...
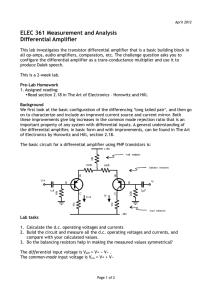
ELEC 361 Measurement and Analysis Differential Amplifier
... •Read section 2.18 in The Art of Electronics – Horowitz and Hill. Background We first look at the basic configuration of the differencing ‘long tailed pair’, and then go on to characterize and include an improved current source and current mirror. Both these improvements give big increases in the co ...
... •Read section 2.18 in The Art of Electronics – Horowitz and Hill. Background We first look at the basic configuration of the differencing ‘long tailed pair’, and then go on to characterize and include an improved current source and current mirror. Both these improvements give big increases in the co ...
IMT4
... otherwise dispose of the same, no express or implied right or license to practice or commercially exploit any intellectual property rights or other proprietary rights owned or controlled by ROHM CO., LTD. is granted to any such buyer. Products listed in this document are no antiradiation design. ...
... otherwise dispose of the same, no express or implied right or license to practice or commercially exploit any intellectual property rights or other proprietary rights owned or controlled by ROHM CO., LTD. is granted to any such buyer. Products listed in this document are no antiradiation design. ...
Amateur Extra Licensing Class
... Free electrons are the majority charge carriers in N-type semiconductor material. P-type semiconductor material contains fewer free electrons than pure germanium or silicon crystals. E6A18… The names of the three terminals of a field-effect transistor are gate, drain, and source. Field-effect transi ...
... Free electrons are the majority charge carriers in N-type semiconductor material. P-type semiconductor material contains fewer free electrons than pure germanium or silicon crystals. E6A18… The names of the three terminals of a field-effect transistor are gate, drain, and source. Field-effect transi ...
your New Radio
... Free electrons are the majority charge carriers in N-type semiconductor material. P-type semiconductor material contains fewer free electrons than pure germanium or silicon crystals. E6A18… The names of the three terminals of a field-effect transistor are gate, drain, and source. Field-effect transi ...
... Free electrons are the majority charge carriers in N-type semiconductor material. P-type semiconductor material contains fewer free electrons than pure germanium or silicon crystals. E6A18… The names of the three terminals of a field-effect transistor are gate, drain, and source. Field-effect transi ...
ELG4139: Power Diodes and Power Transistors
... Silicon Controlled Rectifier Industrially SCRs are applied to produce DC voltages for motors from AC line voltage. As rectifier, they can be half-wave rectifiers and fullwave rectifier. ...
... Silicon Controlled Rectifier Industrially SCRs are applied to produce DC voltages for motors from AC line voltage. As rectifier, they can be half-wave rectifiers and fullwave rectifier. ...
Slide 1 - UniMAP Portal
... • 3 hours per week for 14 weeks (Total = 42 hours) • Laboratory • 2 hours per week for 11 weeks (Total = 22 hours) • Tutorial/ Assignment – 2 hours per week for 3 weeks (Total = 6 hours) ...
... • 3 hours per week for 14 weeks (Total = 42 hours) • Laboratory • 2 hours per week for 11 weeks (Total = 22 hours) • Tutorial/ Assignment – 2 hours per week for 3 weeks (Total = 6 hours) ...
Transistor
.jpg?width=300)
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Today, some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits.The transistor is the fundamental building block of modern electronic devices, and is ubiquitous in modern electronic systems. Following its development in 1947 by American physicists John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley, the transistor revolutionized the field of electronics, and paved the way for smaller and cheaper radios, calculators, and computers, among other things. The transistor is on the list of IEEE milestones in electronics, and the inventors were jointly awarded the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics for their achievement.