Acids and Bases
... and the Lewis definitions (Section 2.5). In the Brønsted–Lowry definitions, an acid is a species that donates a proton, and a base is a species that accepts a proton. (Remember that positively charged hydrogen ions are called protons.) In the following reaction, hydrogen chloride (HCl) is an acid be ...
... and the Lewis definitions (Section 2.5). In the Brønsted–Lowry definitions, an acid is a species that donates a proton, and a base is a species that accepts a proton. (Remember that positively charged hydrogen ions are called protons.) In the following reaction, hydrogen chloride (HCl) is an acid be ...
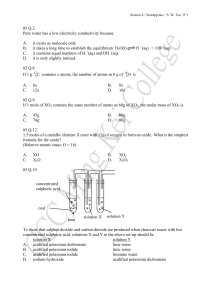
85 Q.2 Pure water has a low electricity conductivity because A. it
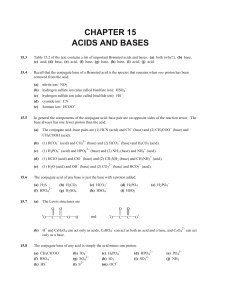
... An aqueous solution of ethanoic acid has a pH value of 4. Which of the following substances, when added to this solution, would increase its pH value? (1) solid calcium carbonate (2) solid sodium chloride ...
... An aqueous solution of ethanoic acid has a pH value of 4. Which of the following substances, when added to this solution, would increase its pH value? (1) solid calcium carbonate (2) solid sodium chloride ...
Topic 8 Acids and Bases File
... When a small amount of acid is added, the excess of H+ ions causes the equilibrium to shift to the left -> balances the difference. When a small amount of alkali is added, the OH- ions react with the H+ ions to form water. The decrease in [H+] is compensated for by an equilibrium shift to the right. ...
... When a small amount of acid is added, the excess of H+ ions causes the equilibrium to shift to the left -> balances the difference. When a small amount of alkali is added, the OH- ions react with the H+ ions to form water. The decrease in [H+] is compensated for by an equilibrium shift to the right. ...
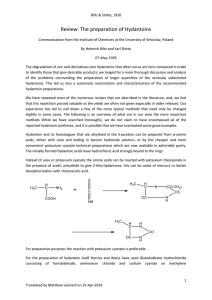
T-Shaped Molecular Building Units in the Porous Structure of Ag(4,4
... and transferred to a stainless steel bomb, which was sealed, heated at 140 °C for 5 h, and then cooled gradually to 110 °C for 3 h, followed by further cooling to 90 °C for 4 h prior to being cooled down to room temperature. Large, pale gray parallelepiped crystals of Ag(4,4′-bpy)‚NO3 were collected ...
... and transferred to a stainless steel bomb, which was sealed, heated at 140 °C for 5 h, and then cooled gradually to 110 °C for 3 h, followed by further cooling to 90 °C for 4 h prior to being cooled down to room temperature. Large, pale gray parallelepiped crystals of Ag(4,4′-bpy)‚NO3 were collected ...
2014_S4_CHM_NORMAL (ALL)
... 53. Element X (atomic number 11) reacts with element Y (atomic number 16) to form an ionic compound. Each atom of X loses one electron and each atom of Y accepts two electrons to form a compound with formula X2Y. 54. Consider the following information: ...
... 53. Element X (atomic number 11) reacts with element Y (atomic number 16) to form an ionic compound. Each atom of X loses one electron and each atom of Y accepts two electrons to form a compound with formula X2Y. 54. Consider the following information: ...
Nitrocellulose

Nitrocellulose (also: cellulose nitrate, flash paper, flash cotton, guncotton, flash string) is a highly flammable compound formed by nitrating cellulose through exposure to nitric acid or another powerful nitrating agent. When used as a propellant or low-order explosive, it was originally known as guncotton.Partially nitrated cellulose has found uses as a plastic film and in inks and wood coatings. In 1862 the first man-made plastic, nitrocellulose, (branded Parkesine) was created by Alexander Parkes from cellulose treated with nitric acid and a solvent. In 1868, American inventor John Wesley Hyatt developed a plastic material he named Celluloid, improving on Parkes' invention by plasticizing the nitrocellulose with camphor so that it could be processed into finished form and used as a photographic film. Celluloid was used by Kodak, and other suppliers, from the late 1880s as a film base in photography, X-ray films, and motion picture films, and was known as 'nitrate film'. After numerous fires caused by unstable nitrate films, safety film (cellulose acetate film) started to be used from the 1930s in the case of X-ray stock and from 1948 for motion picture film.