Nonribosomal peptide synthesis in Aspergillus
... In fungi, nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRP synthetases) are large multi-functional enzymes containing adenylation, thiolation (or peptidyl carrier protein, PCP) and condensation domains. These enzymes are often encoded within gene clusters. Multiple NRP synthetase ORFs have also been identified ...
... In fungi, nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRP synthetases) are large multi-functional enzymes containing adenylation, thiolation (or peptidyl carrier protein, PCP) and condensation domains. These enzymes are often encoded within gene clusters. Multiple NRP synthetase ORFs have also been identified ...
Aerobic respiration - Wesleyan
... Glycolysis is the first stage of carbohydrate breakdown in both aerobic respiration and fermentation The reactions of glycolysis occur in the cytoplasm Glycolysis converts one molecule of glucose to two molecules of pyruvate, with a net energy yield of two ATP; two NADH also form ...
... Glycolysis is the first stage of carbohydrate breakdown in both aerobic respiration and fermentation The reactions of glycolysis occur in the cytoplasm Glycolysis converts one molecule of glucose to two molecules of pyruvate, with a net energy yield of two ATP; two NADH also form ...
Slide 1
... 6.9 The citric acid cycle completes the oxidation of organic molecules, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules The citric acid cycle – is also called the Krebs cycle (after the German-British researcher Hans Krebs, who worked out much of this pathway in the 1930s), – completes the oxidation of ...
... 6.9 The citric acid cycle completes the oxidation of organic molecules, generating many NADH and FADH2 molecules The citric acid cycle – is also called the Krebs cycle (after the German-British researcher Hans Krebs, who worked out much of this pathway in the 1930s), – completes the oxidation of ...
Lecture_5_Control_of_glycolysis
... muscle. However, liver pyruvate kinase is also regulated by covalent modification. Low blood glucose leads to the phosphorylation and inhibition of liver pyruvate kinase. ...
... muscle. However, liver pyruvate kinase is also regulated by covalent modification. Low blood glucose leads to the phosphorylation and inhibition of liver pyruvate kinase. ...
Link - Semantic Scholar
... host cell degradation of polymeric biomass components, in particular proteins (Fig 1). Coxiella resides in phagolysosomes, where it resists the highly adverse conditions and captures amino acids released from proteins as part of the normal host cell protein turnover [22]. Anaplasma phagocytophilum u ...
... host cell degradation of polymeric biomass components, in particular proteins (Fig 1). Coxiella resides in phagolysosomes, where it resists the highly adverse conditions and captures amino acids released from proteins as part of the normal host cell protein turnover [22]. Anaplasma phagocytophilum u ...
PAGE PROOFS
... Hydrochloric acid is found in our stomachs, where it is used to help break down food. It is also used in industry, where it is sometimes called ‘spirit of salts’, to clean bricks and to clean off the coating of oxide on corroded iron or steel before plating the metal with a protective layer of zinc ...
... Hydrochloric acid is found in our stomachs, where it is used to help break down food. It is also used in industry, where it is sometimes called ‘spirit of salts’, to clean bricks and to clean off the coating of oxide on corroded iron or steel before plating the metal with a protective layer of zinc ...
Preview Sample 2
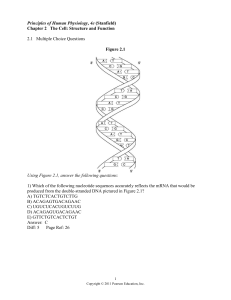
... 33) Which of the following chemical groups are necessary components of a nucleotide? A) phosphate, peptide, and base B) carbohydrate, phosphate, and peptide C) phosphate, carbohydrate, and base D) peptide, phosphate, and carbohydrate E) carbohydrate, base, and peptide Answer: C Diff: 4 Page Ref: 27 ...
... 33) Which of the following chemical groups are necessary components of a nucleotide? A) phosphate, peptide, and base B) carbohydrate, phosphate, and peptide C) phosphate, carbohydrate, and base D) peptide, phosphate, and carbohydrate E) carbohydrate, base, and peptide Answer: C Diff: 4 Page Ref: 27 ...
Full-Text PDF
... Fatigue always occurs upon reaching a certain peak of mental or physical status [1], which not only marks a temporary decrease in work ability, but may also be a precursor to several diseases [2]. With the rapid development of modern society, fatigue and stress are becoming increasingly common healt ...
... Fatigue always occurs upon reaching a certain peak of mental or physical status [1], which not only marks a temporary decrease in work ability, but may also be a precursor to several diseases [2]. With the rapid development of modern society, fatigue and stress are becoming increasingly common healt ...
Sequence and phylogenetic analysis of the gp200 protein of
... Ehrlichia (E.) canis is a Gram-negative obligate intracellular bacterium responsible for canine monocytic ehrlichiosis. Currently, the genetic diversity of E. canis strains worldwide is poorly defined. In the present study, sequence analysis of the nearly full-length 16S rDNA (1,620 bp) and the comp ...
... Ehrlichia (E.) canis is a Gram-negative obligate intracellular bacterium responsible for canine monocytic ehrlichiosis. Currently, the genetic diversity of E. canis strains worldwide is poorly defined. In the present study, sequence analysis of the nearly full-length 16S rDNA (1,620 bp) and the comp ...
KATABOLISME KARBOHIDRAT
... gradient, namely an H+ gradient. • Once formed, ATP molecules are transported out of the mitochondrial matrix. ...
... gradient, namely an H+ gradient. • Once formed, ATP molecules are transported out of the mitochondrial matrix. ...
Aromatic Chemistry - heckgrammar.co.uk
... only applies to systems at equilibrium so don’t use initial concentrations Kc is calculated from concentrations at equilibrium (note that the concentration of a solid is constant and so solids do not appear in the equilibrium expression) equilibrium constant (Kc) is related to reaction stoichiometry ...
... only applies to systems at equilibrium so don’t use initial concentrations Kc is calculated from concentrations at equilibrium (note that the concentration of a solid is constant and so solids do not appear in the equilibrium expression) equilibrium constant (Kc) is related to reaction stoichiometry ...
c Syun-Ru Yeh‡ and Denis L. Rousseau
... 2.0 M (Fig. 2A). It is plausible that the positive charges distributed over the polypeptide chain resulting from the protonation of certain amino acid residues introduce electrostatic repulsion between polypeptide segments. They destabilize the molecule and loosen the structure. In contrast to the c ...
... 2.0 M (Fig. 2A). It is plausible that the positive charges distributed over the polypeptide chain resulting from the protonation of certain amino acid residues introduce electrostatic repulsion between polypeptide segments. They destabilize the molecule and loosen the structure. In contrast to the c ...
Improving penicillin biosynthesis in Penicillium chrysogenum
... antibiotic penicillin (PEN) is industrially produced by the filamentous fungus Penicillium chrysogenum. The PEN biosynthetic machinery is compartmentalized in P. chrysogenum in the cytosol and microbodies (peroxisomes) (Evers et al., 2004; Müller et al., 1991; Turner, 1992). The process starts with t ...
... antibiotic penicillin (PEN) is industrially produced by the filamentous fungus Penicillium chrysogenum. The PEN biosynthetic machinery is compartmentalized in P. chrysogenum in the cytosol and microbodies (peroxisomes) (Evers et al., 2004; Müller et al., 1991; Turner, 1992). The process starts with t ...
File
... 52) Brown fat cells produce a protein called thermogenin in their mitochondrial inner membrane. Thermogenin is a channel for facilitated transport of protons across the membrane. What will occur in the brown fat cells when they produce thermogenin? A) ATP synthesis and heat generation will both dec ...
... 52) Brown fat cells produce a protein called thermogenin in their mitochondrial inner membrane. Thermogenin is a channel for facilitated transport of protons across the membrane. What will occur in the brown fat cells when they produce thermogenin? A) ATP synthesis and heat generation will both dec ...
Gluconeogenesis
... A metal ion such as Mn++ is required for the PEP Carboxykinase reaction, in addition to a Mg++ ion that binds with the nucleotide substrate at the active site. Mn++ is thought to promote Pi transfer by interacting simultaneously with the enolate oxygen atom and an oxygen atom of the terminal phospha ...
... A metal ion such as Mn++ is required for the PEP Carboxykinase reaction, in addition to a Mg++ ion that binds with the nucleotide substrate at the active site. Mn++ is thought to promote Pi transfer by interacting simultaneously with the enolate oxygen atom and an oxygen atom of the terminal phospha ...
The Metabolic Network of Synechocystis sp. PCC
... Pro + 0.054 L-Ser + 0.033 L-Tyr / 2 GDP + 1 AMP + pyrophosphate + 2 orthophosphate + 1 protein 0.222 dCTP + 0.279 dTTP + 0.222 dGTP + 0.279 dATP / 1 diphosphate + 1 DNA 0.322 GTP + 0.262 ATP + 0.2 CTP + 0.216 UTP / 1 diphosphate + 1 RNA 0.1379 UDP-Glc + 0.8143 dTDP-Rha + 0.0478 glycogen / 0.8143 dTD ...
... Pro + 0.054 L-Ser + 0.033 L-Tyr / 2 GDP + 1 AMP + pyrophosphate + 2 orthophosphate + 1 protein 0.222 dCTP + 0.279 dTTP + 0.222 dGTP + 0.279 dATP / 1 diphosphate + 1 DNA 0.322 GTP + 0.262 ATP + 0.2 CTP + 0.216 UTP / 1 diphosphate + 1 RNA 0.1379 UDP-Glc + 0.8143 dTDP-Rha + 0.0478 glycogen / 0.8143 dTD ...
Effects of low crude-protein diets fortified with crystalline amino acids
... excreted in the urine as urea (in pigs I or uric acid (in poultry). The carbon skeletons of excess amino acids are converted into glucose, fatty acids, ketone bodies, and other compounds or are excreted as CO. after complete oxidation in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle (Riis, 1983; Voet and Voet, ...
... excreted in the urine as urea (in pigs I or uric acid (in poultry). The carbon skeletons of excess amino acids are converted into glucose, fatty acids, ketone bodies, and other compounds or are excreted as CO. after complete oxidation in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle (Riis, 1983; Voet and Voet, ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.