Protein Synthesis
... DNA Begins the Process • DNA is found inside the nucleus • Proteins, however, are made in the cytoplasm of cells by organelles called ribosomes • Ribosomes may be free in the cytosol or attached to the surface of rough ER ...
... DNA Begins the Process • DNA is found inside the nucleus • Proteins, however, are made in the cytoplasm of cells by organelles called ribosomes • Ribosomes may be free in the cytosol or attached to the surface of rough ER ...
Ecology Pre
... SC.912.L.16.3 Describe the basic process of DNA replication and how it relates to the transmission and conservation of the genetic information. SC.912.L.16.10 Evaluate the impact of biotechnology on the individual, society and the environment, including medical and ethical issues. SC.912.L.16.4 Expl ...
... SC.912.L.16.3 Describe the basic process of DNA replication and how it relates to the transmission and conservation of the genetic information. SC.912.L.16.10 Evaluate the impact of biotechnology on the individual, society and the environment, including medical and ethical issues. SC.912.L.16.4 Expl ...
1 - Wsfcs
... 29. To link amino acids together, a _______ must be removed from the amino group and an _______ must be removed from the COOH to form water. The covalent bond is called a _________________ 30. The ______________________ and ______________________ of amino acids are important in determining its shape ...
... 29. To link amino acids together, a _______ must be removed from the amino group and an _______ must be removed from the COOH to form water. The covalent bond is called a _________________ 30. The ______________________ and ______________________ of amino acids are important in determining its shape ...
PHYS 498 Quiz 1 Solution Starting with double
... the GTP on EF-tu hydrolyzes, and EF-tu dissociates from tRNA iv. ribosome catalyzes new peptide bond between the growing peptide chain at P-site and new amino acid on A-site. It does this through a dramatic ...
... the GTP on EF-tu hydrolyzes, and EF-tu dissociates from tRNA iv. ribosome catalyzes new peptide bond between the growing peptide chain at P-site and new amino acid on A-site. It does this through a dramatic ...
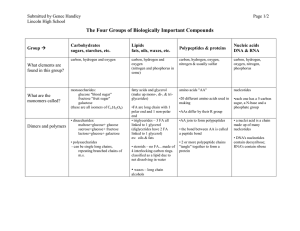
The Four Groups of Biologically Important Compounds
... lactose=glucose+ galactose • polysaccharides - can be single long chains, repeating branched chains of m.s. ...
... lactose=glucose+ galactose • polysaccharides - can be single long chains, repeating branched chains of m.s. ...
macromolecule packet
... acid chains may be saturated (only single bonds between carbons) or unsaturated (contain at least one double bond). A carboxyl functional group (-COOH) is found on the end of the fatty acid that does NOT attach to glycerol. Circle and label the carboxyl groups in the 2 fatty acids on this worksheet. ...
... acid chains may be saturated (only single bonds between carbons) or unsaturated (contain at least one double bond). A carboxyl functional group (-COOH) is found on the end of the fatty acid that does NOT attach to glycerol. Circle and label the carboxyl groups in the 2 fatty acids on this worksheet. ...
Chapter 29 Biosynthetic Pathways 308 29.1 Your text states in
... 29.12 (a) The letter n refers to the number of glucose residues in a glycogen polymer. (b) The number of glucose residues may be as high as 1,000,000. 29.13 Uridine triphosphate (UTP) is a nucleoside triphosphate similar to ATP. The constituents are: a nitrogen base, uracil; a sugar, ribose; and thr ...
... 29.12 (a) The letter n refers to the number of glucose residues in a glycogen polymer. (b) The number of glucose residues may be as high as 1,000,000. 29.13 Uridine triphosphate (UTP) is a nucleoside triphosphate similar to ATP. The constituents are: a nitrogen base, uracil; a sugar, ribose; and thr ...
Learning Targets - Unit 9 DNA, RNA, Proteins, Mutation
... diagram and label the 3 parts of a nucleotide explain the role of complementary base pairing in the replication of DNA summarize the main features of DNA replication explain the primary functions of each type of RNA compare the structure of DNA with RNA summarize the process of transcription summari ...
... diagram and label the 3 parts of a nucleotide explain the role of complementary base pairing in the replication of DNA summarize the main features of DNA replication explain the primary functions of each type of RNA compare the structure of DNA with RNA summarize the process of transcription summari ...
Chapter 17 - Amino Acid Metabolism
... •The others are classed as "essential" amino acids and must be obtained in the diet ...
... •The others are classed as "essential" amino acids and must be obtained in the diet ...
Unit 7 - Cobb Learning
... Now What?...Translation! Translation: Process in which mRNA attaches to the __________________ and a protein is assembled/made. Codon: 3 base code in DNA or RNA ...
... Now What?...Translation! Translation: Process in which mRNA attaches to the __________________ and a protein is assembled/made. Codon: 3 base code in DNA or RNA ...
2013 ProSyn PREAP
... 3. The ribosome forms a peptide bond between the first and second amino acids. 4. The polypeptide chain continues to grow until the ribosome reaches a stop codon on the mRNA molecule and a protein has been ...
... 3. The ribosome forms a peptide bond between the first and second amino acids. 4. The polypeptide chain continues to grow until the ribosome reaches a stop codon on the mRNA molecule and a protein has been ...
Protein Synthesis - Katy Independent School District
... 3. The ribosome forms a peptide bond between the first and second amino acids. 4. The polypeptide chain continues to grow until the ribosome reaches a stop codon on the mRNA molecule and a protein has been ...
... 3. The ribosome forms a peptide bond between the first and second amino acids. 4. The polypeptide chain continues to grow until the ribosome reaches a stop codon on the mRNA molecule and a protein has been ...
biol-1406_ch3.ppt
... • Each carbon can form up to four bonds (single(2 electrons), double, or triple) and rings • Carbon makes bonds mostly with H, N, and O in living systems • Biomolecules are large and contain “functional groups” attached to the carbon backbone. • Functional groups in organic molecules confer chemical ...
... • Each carbon can form up to four bonds (single(2 electrons), double, or triple) and rings • Carbon makes bonds mostly with H, N, and O in living systems • Biomolecules are large and contain “functional groups” attached to the carbon backbone. • Functional groups in organic molecules confer chemical ...
Translation - The Citadel
... Translation Termination: When the "stop codon" of the mRNA gets to the ribosome, translation stops. mRNA is released from the ribosome; tRNA is released; newly synthesized protein is released. How does the mRNA sequence of nucleotides direct a ribosome to connect the proper protein sequence of amino ...
... Translation Termination: When the "stop codon" of the mRNA gets to the ribosome, translation stops. mRNA is released from the ribosome; tRNA is released; newly synthesized protein is released. How does the mRNA sequence of nucleotides direct a ribosome to connect the proper protein sequence of amino ...
ALE 10.
... 6. a.) What is the name of the process that produces RNA? _________________________________ b.) Where does the process occur in the cell? __________________________________________ 7. Looking at the synthesis of messenger RNA..... a.) What enzyme is needed for its creation? _________________________ ...
... 6. a.) What is the name of the process that produces RNA? _________________________________ b.) Where does the process occur in the cell? __________________________________________ 7. Looking at the synthesis of messenger RNA..... a.) What enzyme is needed for its creation? _________________________ ...
Slide 1
... Question: Is there a design substitute, or is the design from an intelligent source? ...
... Question: Is there a design substitute, or is the design from an intelligent source? ...
Document
... entails the synthesis of a single-stranded polynucleotide of RNA at an unwound section of DNA with one of the DNA strands serving as a template for the synthesis of the RNA. The product of this process is called an RNA transcript, or messenger RNA (mRNA). The result of transcription is that the gene ...
... entails the synthesis of a single-stranded polynucleotide of RNA at an unwound section of DNA with one of the DNA strands serving as a template for the synthesis of the RNA. The product of this process is called an RNA transcript, or messenger RNA (mRNA). The result of transcription is that the gene ...
No Slide Title - Suffolk County Community College
... - Catabolic reactions: break complex organic compounds into simper ones, usually via hydrolysis, usually exergonic - Anabolic reactions: build complex molecules from simpler ones, usually via dehydration synthesis, usually endergonic *Catabolic reactions provide the energy (ATP) and building blocks ...
... - Catabolic reactions: break complex organic compounds into simper ones, usually via hydrolysis, usually exergonic - Anabolic reactions: build complex molecules from simpler ones, usually via dehydration synthesis, usually endergonic *Catabolic reactions provide the energy (ATP) and building blocks ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.