AP® BIOLOGY 2010 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
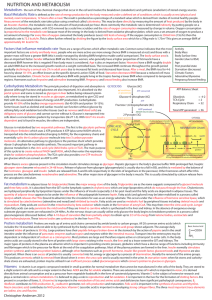
... • Describe type of mutation: duplication, frameshift, nonsense, deletion, substitution (point mutation). • Describe central dogma: DNA RNA protein. • Describe process of central dogma: transcription translation. • Translation of codons: 3 nucleotides 1 amino acid. • Redundancy in genetic cod ...
... • Describe type of mutation: duplication, frameshift, nonsense, deletion, substitution (point mutation). • Describe central dogma: DNA RNA protein. • Describe process of central dogma: transcription translation. • Translation of codons: 3 nucleotides 1 amino acid. • Redundancy in genetic cod ...
Biochem Fall 2011 Sample Exam I – Protein Structure
... PART B: If you have answered Yes in part A to the mutant having the capacity to bind oxygen reversibly, then predict how this mutation will perturb the oxygen binding curve below (sketch a new curve or curves on the drawing below and label with the name of the mutant). Normal Hb binding to oxygen is ...
... PART B: If you have answered Yes in part A to the mutant having the capacity to bind oxygen reversibly, then predict how this mutation will perturb the oxygen binding curve below (sketch a new curve or curves on the drawing below and label with the name of the mutant). Normal Hb binding to oxygen is ...
Document
... a. Acetyl CoA combines with bicarbonate to form malonyl CoA, which reacts with ACP to form malonyl ACP. Acetyl CoA + HCO3− + ATP → malonyl CoA + ADP + Pi + H+ Malonyl CoA + HS—ACP → malonyl ACP + HS—CoA b. The enzyme for the first reaction is acetyl CoA carboxylase. The enzyme for the second reactio ...
... a. Acetyl CoA combines with bicarbonate to form malonyl CoA, which reacts with ACP to form malonyl ACP. Acetyl CoA + HCO3− + ATP → malonyl CoA + ADP + Pi + H+ Malonyl CoA + HS—ACP → malonyl ACP + HS—CoA b. The enzyme for the first reaction is acetyl CoA carboxylase. The enzyme for the second reactio ...
Catabolism
... An overview of metabolism • Metabolism may be divided into two major parts: catabolism and anabolism. • Catabolism: larger and more complex molecules are broken down into smaller, simpler molecules with the release of energy. • Anabolism: the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones with th ...
... An overview of metabolism • Metabolism may be divided into two major parts: catabolism and anabolism. • Catabolism: larger and more complex molecules are broken down into smaller, simpler molecules with the release of energy. • Anabolism: the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones with th ...
Enzymology - Angelfire
... active site may not necessarily be exactly of the same shape as the substrate. But the enzyme can have an active site that attracts the substrate. When a substrate combines with an enzyme, it induces a change in the enzyme structure. The amino acids which constitute the active site are then moulded ...
... active site may not necessarily be exactly of the same shape as the substrate. But the enzyme can have an active site that attracts the substrate. When a substrate combines with an enzyme, it induces a change in the enzyme structure. The amino acids which constitute the active site are then moulded ...
Microbiology bio 123
... 2. Some are competitive inhibitors, they compete for the enzyme. (i.e. a→b→c→PABA+E→folic acid, Sulfonamide (synthetic antibiotics) competes with PABA for enzyme E.) Metabolism includes two major types of reactions: 1. Endergonic reactions require energy to be placed into the reaction to complete th ...
... 2. Some are competitive inhibitors, they compete for the enzyme. (i.e. a→b→c→PABA+E→folic acid, Sulfonamide (synthetic antibiotics) competes with PABA for enzyme E.) Metabolism includes two major types of reactions: 1. Endergonic reactions require energy to be placed into the reaction to complete th ...
I. virAL CHROMOSOMES
... (1) The number of times the two strands cross each other (2) T = L in non-supercoiled molecules d) L = W + T (1) If T decreases, either L will decrease or W will increase (2) The strain of underwiding can be accommodated by negative supercoiling (a) Single stranded region increases with temperature ...
... (1) The number of times the two strands cross each other (2) T = L in non-supercoiled molecules d) L = W + T (1) If T decreases, either L will decrease or W will increase (2) The strain of underwiding can be accommodated by negative supercoiling (a) Single stranded region increases with temperature ...
capitolo 1 - Structural Biology
... We recall briefly some features of the amino acids. Amino acids can be distinguished into different classes in view of their polarità. By varying the criterion for classification it changes the class to which the amino acids belong. Tryptophan and arginine for example, belong to different classes if ...
... We recall briefly some features of the amino acids. Amino acids can be distinguished into different classes in view of their polarità. By varying the criterion for classification it changes the class to which the amino acids belong. Tryptophan and arginine for example, belong to different classes if ...
Biology I What is pH?
... Can taste bitter, sweetish, or salty Strong bases can burn skin & eyes Bases react more easily with protein than with metal; they are often used for cleaning Examples: ...
... Can taste bitter, sweetish, or salty Strong bases can burn skin & eyes Bases react more easily with protein than with metal; they are often used for cleaning Examples: ...
capitolo 1 - Structural Biology
... We recall briefly some features of the amino acids. Amino acids can be distinguished into different classes in view of their polarity. By varying the criterion for classification it changes the class to which the amino acids belong. Tryptophan and arginine for example, belong to different classes i ...
... We recall briefly some features of the amino acids. Amino acids can be distinguished into different classes in view of their polarity. By varying the criterion for classification it changes the class to which the amino acids belong. Tryptophan and arginine for example, belong to different classes i ...
DNA and Gene Expression
... • Having SNPs in one or more of the proteins involved may alter the time the body is exposed to the active form of the drug – E.g., individuals with behaviourally similar forms of schizophrenia can react very differently to the same ...
... • Having SNPs in one or more of the proteins involved may alter the time the body is exposed to the active form of the drug – E.g., individuals with behaviourally similar forms of schizophrenia can react very differently to the same ...
antisense orfs, codon bias and the evo lu tion of the ge netic code
... Since we only know the genetic codes of a small percentage of all species it is highly probable that additional variations exist. The patterns thus far observed predict that further codon variation will involve primarily AT-only and AT-rich codons. Thus far none of the GC-only codons have been found ...
... Since we only know the genetic codes of a small percentage of all species it is highly probable that additional variations exist. The patterns thus far observed predict that further codon variation will involve primarily AT-only and AT-rich codons. Thus far none of the GC-only codons have been found ...
Preview Sample 1
... Facultative anaerobes utilize a molecule other than oxygen as the final electron acceptor in ATP synthesis. ...
... Facultative anaerobes utilize a molecule other than oxygen as the final electron acceptor in ATP synthesis. ...
Research with L-glutamate, a prototypical L-amino acid that activates umami... two G-protein coupled receptors, T1R1+T1R3 and t-mGluR4, are important in...
... is transduced by PLC-β2 dependent rise of IP3 followed by release of intracellular calcium. Umami research also suggests a Gα-dependent pathway that down-regulates cAMP. 5’ inosine monophosphate (IMP) is another umami taste stimulus and a potent flavor enhancer that synergistically enhances umami ta ...
... is transduced by PLC-β2 dependent rise of IP3 followed by release of intracellular calcium. Umami research also suggests a Gα-dependent pathway that down-regulates cAMP. 5’ inosine monophosphate (IMP) is another umami taste stimulus and a potent flavor enhancer that synergistically enhances umami ta ...
Nutrition and Metabolism
... Vitamins A vitamin is an organic compound needed in small quantities for normal metabolism that cannot be manufactured in the cells of the body. They are stored to a slight extent in all cells and to a major extent in the liver. ADEK are the fat soluble vitamins. There are extensive stores of A whic ...
... Vitamins A vitamin is an organic compound needed in small quantities for normal metabolism that cannot be manufactured in the cells of the body. They are stored to a slight extent in all cells and to a major extent in the liver. ADEK are the fat soluble vitamins. There are extensive stores of A whic ...
Endospore production by Bacillus subtilis The Bacterial Endospore
... Microm 410 Fall 2009: Endospores & heterocysts Dr. Parsek ...
... Microm 410 Fall 2009: Endospores & heterocysts Dr. Parsek ...
chapter 20 lecture (ppt file)
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Lecture 2- protein structure
... can often be repeated and organized into larger motifs. A small portion of a protein (typically less than 20 amino acids) In general, motifs may provide us with information about the folding of proteins, but not the biological function of the protein. ...
... can often be repeated and organized into larger motifs. A small portion of a protein (typically less than 20 amino acids) In general, motifs may provide us with information about the folding of proteins, but not the biological function of the protein. ...
Biology: Life on Earth
... repressor protein bound to operator, overlaps promoter free repressor proteins When lactose is not present, repressor proteins bind to the operator of the lactose operon. When RNA polymerase binds to the promoter, the repressor protein blocks access to the structural genes, which therefore cannot be ...
... repressor protein bound to operator, overlaps promoter free repressor proteins When lactose is not present, repressor proteins bind to the operator of the lactose operon. When RNA polymerase binds to the promoter, the repressor protein blocks access to the structural genes, which therefore cannot be ...
CELLular biology
... muscle cells have more ribosomes and mitochondria than ‘typical cells’ because of their increased protein and energy production. Liver cells have more lysosomes for waste removal than most cells. The size and shape of a cell are directly related to its structure and function. For example, skin cel ...
... muscle cells have more ribosomes and mitochondria than ‘typical cells’ because of their increased protein and energy production. Liver cells have more lysosomes for waste removal than most cells. The size and shape of a cell are directly related to its structure and function. For example, skin cel ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.