Optimal codon randomization via mathematical programming
... Two techniques provide additional flexibility in shaping codon bias beyond conventional codon degeneracy. The first is the use of so-called “spiked” or “doped” oligonucleotides, whereby during DNA synthesis, non-equimolar proportions of the four bases are used at some – or all – of the codon's three n ...
... Two techniques provide additional flexibility in shaping codon bias beyond conventional codon degeneracy. The first is the use of so-called “spiked” or “doped” oligonucleotides, whereby during DNA synthesis, non-equimolar proportions of the four bases are used at some – or all – of the codon's three n ...
biol 161 aerobic cellular respiration
... B. The two pyruvate molecules formed from glycolysis will lose one carbon each in the form of a gas. What is the name of this gas? C. How many molecules of CO2 are made in prep reaction per one glucose molecule? D. Therefore, after losing a carbon atom, the acetyl group that is left has how many car ...
... B. The two pyruvate molecules formed from glycolysis will lose one carbon each in the form of a gas. What is the name of this gas? C. How many molecules of CO2 are made in prep reaction per one glucose molecule? D. Therefore, after losing a carbon atom, the acetyl group that is left has how many car ...
Nutreval Interpretation Guide
... Essential Amino Acids) are high, the problem seems to be that they are not being fed into the Krebs cycle. The explanation would be a functional deficiency in B12, if methylmalonic acid is also hi ...
... Essential Amino Acids) are high, the problem seems to be that they are not being fed into the Krebs cycle. The explanation would be a functional deficiency in B12, if methylmalonic acid is also hi ...
Revving up glycolysis
... is mainly expressed in cancer cells. Both enzymes catalyze the final step in the energy-producing process of glycolysis. The major difference between PKM1 and PKM2 is that PKM1 is constitutively active, whereas PKM2 has low basal activity that can be fine-tuned up or down by other metabolic and sign ...
... is mainly expressed in cancer cells. Both enzymes catalyze the final step in the energy-producing process of glycolysis. The major difference between PKM1 and PKM2 is that PKM1 is constitutively active, whereas PKM2 has low basal activity that can be fine-tuned up or down by other metabolic and sign ...
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
... mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space resulting in a higher concentration on ...
... mitochondrial matrix into the intermembrane space resulting in a higher concentration on ...
Mutational properties of amino acid residues
... residue in that it is the only amino acid whose six codons are distributed in two different groups, AGY and TCN, that are so far apart from each other (at least two nucleotide mutations away). As a consequence, serine will be more easily reached from another amino acid after mutation, i.e. it is ver ...
... residue in that it is the only amino acid whose six codons are distributed in two different groups, AGY and TCN, that are so far apart from each other (at least two nucleotide mutations away). As a consequence, serine will be more easily reached from another amino acid after mutation, i.e. it is ver ...
Chapter 27 - Extras Springer
... Increased dietary protein may lower urinary pH and increase calcium excretion (Barzel & Massey, 1998). Increased calcium intake can offset the elevated calcium losses (Dawson-hughes, 2003) 20:1 is the typical recommended ratio for a middle-aged woman (Heaney, 1998). An athlete’s need may be differen ...
... Increased dietary protein may lower urinary pH and increase calcium excretion (Barzel & Massey, 1998). Increased calcium intake can offset the elevated calcium losses (Dawson-hughes, 2003) 20:1 is the typical recommended ratio for a middle-aged woman (Heaney, 1998). An athlete’s need may be differen ...
BioInformatics at FSU - whose job is it and why it needs
... DDBJ began in 1984, GenBank in 1982, and EMBL in 1980. They are all attempts at establishing an organized, reliable, comprehensive and openly available library of genetic sequences. Each program needs to recognize particular aspects of the sequence files; flexibility of the program is a headache. NC ...
... DDBJ began in 1984, GenBank in 1982, and EMBL in 1980. They are all attempts at establishing an organized, reliable, comprehensive and openly available library of genetic sequences. Each program needs to recognize particular aspects of the sequence files; flexibility of the program is a headache. NC ...
DNA and RNA:
... shape and to speed up important chemical reactions such as photosynthesis and respiration. A cell will not live long if it cannot reliably create the proteins that it needs for survival. This chapter looks at how cells reliably make proteins. To place these ideas in the proper context, remember that ...
... shape and to speed up important chemical reactions such as photosynthesis and respiration. A cell will not live long if it cannot reliably create the proteins that it needs for survival. This chapter looks at how cells reliably make proteins. To place these ideas in the proper context, remember that ...
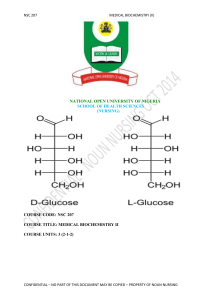
NSC 207 - National Open University of Nigeria
... provides building blocks for synthetic reactions. The rate of conversion of glucose into pyruvate is regulated to meet these 2 major cellular needs. Enzymes catalyzing essentially irreversible reactions are potential sites of control. In glycolysis, the reactions catalyzed by Hexokinase ( HK), phosp ...
... provides building blocks for synthetic reactions. The rate of conversion of glucose into pyruvate is regulated to meet these 2 major cellular needs. Enzymes catalyzing essentially irreversible reactions are potential sites of control. In glycolysis, the reactions catalyzed by Hexokinase ( HK), phosp ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... The transition from closed to open complex involves structural changes in the enzyme and the opening of the DNA double helix to reveal the template and nontemplate strands. In bacterial enzyme with σ70, this transition called isomerization, does not require energy from ATP hydrolysis. The active si ...
... The transition from closed to open complex involves structural changes in the enzyme and the opening of the DNA double helix to reveal the template and nontemplate strands. In bacterial enzyme with σ70, this transition called isomerization, does not require energy from ATP hydrolysis. The active si ...
167
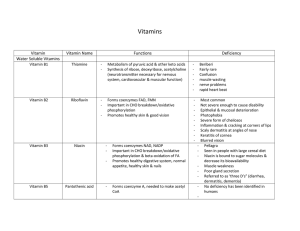
... Integrity of skin & mucosa Found in animal foods Plant based foods have beta carotene & are converted to vitamin A in body Produced by skin from UVB light Aids in absorption of calcium from GI & controls its deposit in bones Muscle & nerve function Bone formation Powerful antioxidant Prevents oxidat ...
... Integrity of skin & mucosa Found in animal foods Plant based foods have beta carotene & are converted to vitamin A in body Produced by skin from UVB light Aids in absorption of calcium from GI & controls its deposit in bones Muscle & nerve function Bone formation Powerful antioxidant Prevents oxidat ...
Solution Worksheet Respiration
... How many ATP are made in the glycolysis part of cellular respiration? 2 ATP are needed to energize glycolysis but 4 ATP’s are produced. So, the net effect is 2 ATP produced ( via substrate phosphorylation = direct enzymatic transfer of a phosphate from a substrate to ADP to form ATP) How many ATP ar ...
... How many ATP are made in the glycolysis part of cellular respiration? 2 ATP are needed to energize glycolysis but 4 ATP’s are produced. So, the net effect is 2 ATP produced ( via substrate phosphorylation = direct enzymatic transfer of a phosphate from a substrate to ADP to form ATP) How many ATP ar ...
Chapter 26 Nutrition and Metabolism *Lecture PowerPoint
... – No effect on cholesterol and LDL levels – Absorbs water in intestines, softens stool, increases bulk 40% to 100%, stretches colon, and stimulates peristalsis thereby quickening passage of feces – No clear effect on incidence of colorectal cancer – Excessive intake can interfere with absorption of ...
... – No effect on cholesterol and LDL levels – Absorbs water in intestines, softens stool, increases bulk 40% to 100%, stretches colon, and stimulates peristalsis thereby quickening passage of feces – No clear effect on incidence of colorectal cancer – Excessive intake can interfere with absorption of ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.