Chem 11 Spring 2012 Practice Final
... B) shorter carbon chains. C) higher melting points. D) lower melting points. E) greater intermolecular attraction. 11) Glycerophospholipids can interact both with other lipids and water because they contain A) double bonds. B) polar regions and nonpolar regions. C) glycerol. D) saturated fatty acids ...
... B) shorter carbon chains. C) higher melting points. D) lower melting points. E) greater intermolecular attraction. 11) Glycerophospholipids can interact both with other lipids and water because they contain A) double bonds. B) polar regions and nonpolar regions. C) glycerol. D) saturated fatty acids ...
E. coli
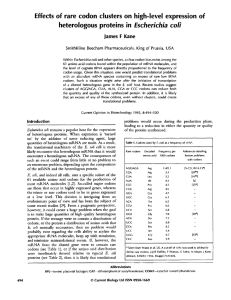
... type gene. The gene must then be transformed into a host cell where it can be expressed, and then the gene product purified. The most popular expression systems are E. coli, yeast and cultured mammalian cells. Each host has its own pros and cons which must be considered when choosing a system for th ...
... type gene. The gene must then be transformed into a host cell where it can be expressed, and then the gene product purified. The most popular expression systems are E. coli, yeast and cultured mammalian cells. Each host has its own pros and cons which must be considered when choosing a system for th ...
review nitrogen excretion: three end products
... of urea in response to environmental conditions that limit ammonia excretion (O. a. grahami, Randall et al. 1989; Opsanus beta, Walsh et al. 1990; Heteropneustes fossilis, Saha and Ratha, 1989). These species are unique in expressing the full complement of OUC enzymes, but in other adult teleosts, s ...
... of urea in response to environmental conditions that limit ammonia excretion (O. a. grahami, Randall et al. 1989; Opsanus beta, Walsh et al. 1990; Heteropneustes fossilis, Saha and Ratha, 1989). These species are unique in expressing the full complement of OUC enzymes, but in other adult teleosts, s ...
Chapter 2: Fuel Utilization and Muscle Metabolism During Exercise,
... Muscles are the ultimate engine’s driving performance, and they are nourished by oxygen captured from the air by the lungs, and they are fed by nutrients and oxygen carried through the bloodstream. It is essential to remember that a full understanding of muscle metabolism begins at the cellular leve ...
... Muscles are the ultimate engine’s driving performance, and they are nourished by oxygen captured from the air by the lungs, and they are fed by nutrients and oxygen carried through the bloodstream. It is essential to remember that a full understanding of muscle metabolism begins at the cellular leve ...
March 1972 EFFECTS OF VOLATILE FA`M`Y ACIDS, KETONE
... Large differences in basal and in noradrenalinstimulated lipolytic activity were observed between indi~dual biopsies. Therefore, in the figures and the table the results are given of several experiments. From these results it is clear, however, that the effects of the various additions can be observ ...
... Large differences in basal and in noradrenalinstimulated lipolytic activity were observed between indi~dual biopsies. Therefore, in the figures and the table the results are given of several experiments. From these results it is clear, however, that the effects of the various additions can be observ ...
BHS 150.2 Biochemistry Date: 01/25/13, 1st hour Notetaker: Laurel
... Our bodies can store enough glycogen for 12 hours, after that, our bodies undergo gluconeogenesis: using other sources such as amino acids and carbs to produce new glucose if glucose levels fall too low Glycogen Metabolism Glycogen: storage form of glucose Made in muscle for muscle use only for quic ...
... Our bodies can store enough glycogen for 12 hours, after that, our bodies undergo gluconeogenesis: using other sources such as amino acids and carbs to produce new glucose if glucose levels fall too low Glycogen Metabolism Glycogen: storage form of glucose Made in muscle for muscle use only for quic ...
1.1 Functional Groups of Biomolecules and their Reactions
... The following happens in one concerted step: a nucleophile (N) attacks the carbon atom as a more electronegative group (X) leaves, with inversion of stereochemistry through an unstable transition state. Note that N can be a neutral protic nucleophile that deprotonates after the substitution. This ty ...
... The following happens in one concerted step: a nucleophile (N) attacks the carbon atom as a more electronegative group (X) leaves, with inversion of stereochemistry through an unstable transition state. Note that N can be a neutral protic nucleophile that deprotonates after the substitution. This ty ...
... 1A. (4 pts) True & false (circle the correct answer). T or F: All 20 amino acids contain at least one chiral center. T or F: The peptide bond is planar and usually cis. T or F: Non-polar residues are found in the core of globular proteins due to van der Waals forces. T or F: Disulfide bonds are usua ...
UDP-sugar pyrophosphorylase controls the activity of proceeding
... composition. Except for UDP-glucose most other nucleotide sugars are present in low concentrations in plant cells, often below 10 µM in cellular extracts.5 Thus a coordinated and balanced formation of nucleotide sugars is a prerequisite for normal cell wall polymer biosynthesis During development of ...
... composition. Except for UDP-glucose most other nucleotide sugars are present in low concentrations in plant cells, often below 10 µM in cellular extracts.5 Thus a coordinated and balanced formation of nucleotide sugars is a prerequisite for normal cell wall polymer biosynthesis During development of ...
Chapter 14 cycles
... microbes as a source of carbon and energy. The first enzyme in the biodegradation pathway of methane is methane monooxygenase (MMO). This enzyme is of interest because it can aid in the degradation of highly chlorinated materials such as TCE (trichloroethylene). The oxidation of TCE does not provide ...
... microbes as a source of carbon and energy. The first enzyme in the biodegradation pathway of methane is methane monooxygenase (MMO). This enzyme is of interest because it can aid in the degradation of highly chlorinated materials such as TCE (trichloroethylene). The oxidation of TCE does not provide ...
... Choice A: Describe the basic reaction mechanism for a typical DNA polymerase. Discuss why the Gibbs energy for the overall reaction is negative and also comment on the fidelity of the reaction, or why the polymerase is more likely to incorporate the correct base (Note: do not discuss removal of an i ...
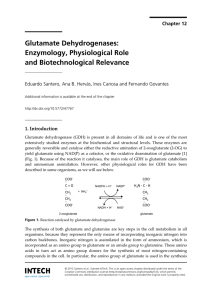
Glutamate Dehydrogenases: Enzymology, Physiological
... the aminating direction, but ammonium assimilation is also possible by the participation of two enzymes: glutamine synthetase (GS), and glutamate synthase, also named glutamine oxoglutarate aminotransferase or GOGAT (Figure 2). The disadvantage of this pathway is its extra energy requirement. Althou ...
... the aminating direction, but ammonium assimilation is also possible by the participation of two enzymes: glutamine synthetase (GS), and glutamate synthase, also named glutamine oxoglutarate aminotransferase or GOGAT (Figure 2). The disadvantage of this pathway is its extra energy requirement. Althou ...
Synthesis and isolation of a single-strand
... We then set up primer extension reactions with KOD DNA polymerase supplemented with dGTP, dCTP, dTTP, and either LNA ATP or dATP, as well as a fluorophore-labeled forward primer. The PCRamplified LNA library was used as template. Amplification with fluorophore-labeled primers enabled us to discern b ...
... We then set up primer extension reactions with KOD DNA polymerase supplemented with dGTP, dCTP, dTTP, and either LNA ATP or dATP, as well as a fluorophore-labeled forward primer. The PCRamplified LNA library was used as template. Amplification with fluorophore-labeled primers enabled us to discern b ...
Unit 1 Life Processes and Biochemistry
... How to identify: long chains of carbon and hydrogen (can ...
... How to identify: long chains of carbon and hydrogen (can ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... 3.3 Cells make large molecules from a limited set of small molecules • The four classes of biological molecules contain very large molecules. • They are often called macromolecules because of their large size. • They are also called polymers because they are made from identical or similar building ...
... 3.3 Cells make large molecules from a limited set of small molecules • The four classes of biological molecules contain very large molecules. • They are often called macromolecules because of their large size. • They are also called polymers because they are made from identical or similar building ...
Full-Text PDF
... ribosomal frameshifting, exact N- and C-terminal ends of the proteins are difficult to assign, but the deduced lengths are similar to other beta-retroviruses. The 5’ end of the protease ORF contains a dUTPase domain, which is common in many retrovirus families, including the beta-retroviruses [23]. ...
... ribosomal frameshifting, exact N- and C-terminal ends of the proteins are difficult to assign, but the deduced lengths are similar to other beta-retroviruses. The 5’ end of the protease ORF contains a dUTPase domain, which is common in many retrovirus families, including the beta-retroviruses [23]. ...
Part a
... • Fat catabolism yields 9 kcal per gram (vs 4 kcal per gram of carbohydrate or protein) ...
... • Fat catabolism yields 9 kcal per gram (vs 4 kcal per gram of carbohydrate or protein) ...
Lecture 9-lea
... phosphofructokinase and pyruvate kinase. • The most important rate-limiting step is that catalyzed by phosphofructokinase. • Phosphofructokinase is inhibited by high concentrations of ATP. • Note that the activity of glucose transporters (GLUTs) can affect the intracellular glucose concentration. In ...
... phosphofructokinase and pyruvate kinase. • The most important rate-limiting step is that catalyzed by phosphofructokinase. • Phosphofructokinase is inhibited by high concentrations of ATP. • Note that the activity of glucose transporters (GLUTs) can affect the intracellular glucose concentration. In ...
Unit 3
... Recommended exercises: From the above sections, all in-chapter “Your Turn” exercises, and chapterend (chapter 9) problems selected from #23 – 45. Presentation Detailed Outline (with references) due; Learning Outcomes and two questions due. 3/10, 3/12 Presentations (see last page) Participation in as ...
... Recommended exercises: From the above sections, all in-chapter “Your Turn” exercises, and chapterend (chapter 9) problems selected from #23 – 45. Presentation Detailed Outline (with references) due; Learning Outcomes and two questions due. 3/10, 3/12 Presentations (see last page) Participation in as ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.