Life as We Don`t Know It
... intermediary metabolism. It occurs in numerous metabolic pathways, notably the reductive citric acid cycle and the pathways that produce amino acids and sugars. It has been suggested that pyruvic acid or its anion pyruvate formed primordially by double carbonylation (4). Cody et al. provide experime ...
... intermediary metabolism. It occurs in numerous metabolic pathways, notably the reductive citric acid cycle and the pathways that produce amino acids and sugars. It has been suggested that pyruvic acid or its anion pyruvate formed primordially by double carbonylation (4). Cody et al. provide experime ...
bile acid testing - Blue Cross Animal Hospital
... mass". The bile acid test is based on the principle that a healthy liver, with adequate functional mass and a good blood supply, can “recycle” bile acids, while a damaged or defective liver cannot. Bile acid testing may be recommended for pets that have elevated liver enzymes or low albumin levels, ...
... mass". The bile acid test is based on the principle that a healthy liver, with adequate functional mass and a good blood supply, can “recycle” bile acids, while a damaged or defective liver cannot. Bile acid testing may be recommended for pets that have elevated liver enzymes or low albumin levels, ...
4.2 Respiration – Page 1 S. Preston 1 From the
... 5. The link reaction involves the conversion of pyruvate to acetate as a result of the loss of carbon dioxide followed by the removal of hydrogen by the reduction of NAD (oxidative decarboxylation); the acetyl then combines with co-enzyme A. The link reaction takes place in the matrix of the mitocho ...
... 5. The link reaction involves the conversion of pyruvate to acetate as a result of the loss of carbon dioxide followed by the removal of hydrogen by the reduction of NAD (oxidative decarboxylation); the acetyl then combines with co-enzyme A. The link reaction takes place in the matrix of the mitocho ...
“The function and synthesis of ribosomes.” Nature Reviews Mol Cell
... of translation, and a key function of the small subunit is to discriminate against aminoacyl-tRNAs that do not match the codon on the message48. This crucial step in the decoding process was poorly understood until the demonstration that the conformation of several residues on the 16S rRNA is sensit ...
... of translation, and a key function of the small subunit is to discriminate against aminoacyl-tRNAs that do not match the codon on the message48. This crucial step in the decoding process was poorly understood until the demonstration that the conformation of several residues on the 16S rRNA is sensit ...
Metabolic Pathway Flux Enhancement by Synthetic
... synthetic scaffolds; however, all strategies discussed here must eventually be performed in concert with existing proven methodologies to achieve optimal yields. Since our mechanistic understanding of scaffold function is still at an early stage, we describe here the parameters empirically derived t ...
... synthetic scaffolds; however, all strategies discussed here must eventually be performed in concert with existing proven methodologies to achieve optimal yields. Since our mechanistic understanding of scaffold function is still at an early stage, we describe here the parameters empirically derived t ...
the function and synthesis of ribosomes
... of translation, and a key function of the small subunit is to discriminate against aminoacyl-tRNAs that do not match the codon on the message48. This crucial step in the decoding process was poorly understood until the demonstration that the conformation of several residues on the 16S rRNA is sensit ...
... of translation, and a key function of the small subunit is to discriminate against aminoacyl-tRNAs that do not match the codon on the message48. This crucial step in the decoding process was poorly understood until the demonstration that the conformation of several residues on the 16S rRNA is sensit ...
Kinetic analysis of cooperativity of phosphorylated L
... reactions. First, L-PK catalyses the formation of pyruvate and ATP (Eq. 1). Secondly, the pyruvate formed in this reaction is used by LDH to form L-lactate converting simultaneously NADH into NAD+. The latter change can be followed spectrophotometrically, as absorbance of the solution strongly decre ...
... reactions. First, L-PK catalyses the formation of pyruvate and ATP (Eq. 1). Secondly, the pyruvate formed in this reaction is used by LDH to form L-lactate converting simultaneously NADH into NAD+. The latter change can be followed spectrophotometrically, as absorbance of the solution strongly decre ...
Acid CleavageLDeprotection in Fmoc/tBu Solid
... In general, a solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) consists of the assembly of a protected peptide chain on a polymeric support (=synthetic step) and the subsequentcleavage/deprotectionto releasethe crude, deprotected peptide from the solid support (=cleavage step). Usually, these two steps are foll ...
... In general, a solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) consists of the assembly of a protected peptide chain on a polymeric support (=synthetic step) and the subsequentcleavage/deprotectionto releasethe crude, deprotected peptide from the solid support (=cleavage step). Usually, these two steps are foll ...
Invariant amino acids essential for decoding function of polypeptide
... controversies may be derived by a methodological distinction between in vivo and in vitro strategies or between genetic versus biochemical approaches. Here, we introduced various amino acid substitutions into four positions in the N domain of human eRF1. Two of them, 55 and 125, are invariant in all ...
... controversies may be derived by a methodological distinction between in vivo and in vitro strategies or between genetic versus biochemical approaches. Here, we introduced various amino acid substitutions into four positions in the N domain of human eRF1. Two of them, 55 and 125, are invariant in all ...
Purification and Partial Characterization of an Acid
... slow moving component with a molecular weight of about 155000 and a second protein band of molecular weight 87 100. The molecular weight of the acid phosphatase was estimated to be 93000 by gel filtration on Sephadex G-100. This suggested that the faster moving component on SDS-polyacrylamide gel el ...
... slow moving component with a molecular weight of about 155000 and a second protein band of molecular weight 87 100. The molecular weight of the acid phosphatase was estimated to be 93000 by gel filtration on Sephadex G-100. This suggested that the faster moving component on SDS-polyacrylamide gel el ...
Purification and Partial Characterization of an Acid
... slow moving component with a molecular weight of about 155000 and a second protein band of molecular weight 87 100. The molecular weight of the acid phosphatase was estimated to be 93000 by gel filtration on Sephadex G-100. This suggested that the faster moving component on SDS-polyacrylamide gel el ...
... slow moving component with a molecular weight of about 155000 and a second protein band of molecular weight 87 100. The molecular weight of the acid phosphatase was estimated to be 93000 by gel filtration on Sephadex G-100. This suggested that the faster moving component on SDS-polyacrylamide gel el ...
Developing a Novel Means of Observing the
... Axonogenesis- the growth of axons- is an essential component of development for all organisms with a functioning nervous system. Once the process is complete, the axons, or nerve fibers, allow signals to be transmitted from one part of the body to the next in response to a series of chemical changes ...
... Axonogenesis- the growth of axons- is an essential component of development for all organisms with a functioning nervous system. Once the process is complete, the axons, or nerve fibers, allow signals to be transmitted from one part of the body to the next in response to a series of chemical changes ...
Protein Folding Cell and Mol Biology Lab
... into HOW AN ENZYME WORKS. When a substrate binds, the enzyme is distorted; what does this mean? Look at this Flash animation showing the first steps of the enzyme mechanism of carbarboxypeptidase A: CLICK HERE. (to download free Flash player, click here). The animation shows that amino acids move as ...
... into HOW AN ENZYME WORKS. When a substrate binds, the enzyme is distorted; what does this mean? Look at this Flash animation showing the first steps of the enzyme mechanism of carbarboxypeptidase A: CLICK HERE. (to download free Flash player, click here). The animation shows that amino acids move as ...
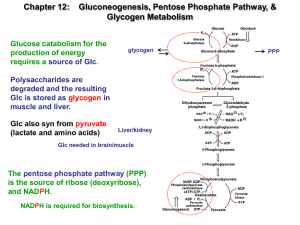
Carbohydrate metabolism
... •In absence of O2 re-oxidation of NADH at glyceraldehyde-3-Pdehydrogenase stage cannot take place in electron-transport chain. But the cells have limited coenzyme. Hence to continue the glycolytic pathway NADH must be oxidized to NAD+. This is achieved by reoxidation of NADH by conversion of pyruvat ...
... •In absence of O2 re-oxidation of NADH at glyceraldehyde-3-Pdehydrogenase stage cannot take place in electron-transport chain. But the cells have limited coenzyme. Hence to continue the glycolytic pathway NADH must be oxidized to NAD+. This is achieved by reoxidation of NADH by conversion of pyruvat ...
Plant Physiology
... attributed in part to the indeterminate nature of these nodules, in which an active meristem is maintained, and a developmental gradient of infection is present over a period of months following initial infection by Frankia. Since Dg93 transcripts also accumulated in tissues of mature nodules, the t ...
... attributed in part to the indeterminate nature of these nodules, in which an active meristem is maintained, and a developmental gradient of infection is present over a period of months following initial infection by Frankia. Since Dg93 transcripts also accumulated in tissues of mature nodules, the t ...
View Full Text-PDF
... The effect of various amino acids on the enzyme activity was studied. These amino acids were glycine, tyrosine, phenylalanine, arginine, asparagine and cysteine. Each amino acid was tested at 10 mM in the reaction mixture. The results in Fig. 8 indicate that all tested amino acids inhibited the enzy ...
... The effect of various amino acids on the enzyme activity was studied. These amino acids were glycine, tyrosine, phenylalanine, arginine, asparagine and cysteine. Each amino acid was tested at 10 mM in the reaction mixture. The results in Fig. 8 indicate that all tested amino acids inhibited the enzy ...
Table S6: Domains present in the primary network generated from
... This family of ion channels contains 10 or 12 transmembrane helices. Each protein forms a single pore. It has been shown that some members of this family form homodimers. In terms of primary structure, they are unrelated to known cation channels or other types of anion channels. Three ClC subfamilie ...
... This family of ion channels contains 10 or 12 transmembrane helices. Each protein forms a single pore. It has been shown that some members of this family form homodimers. In terms of primary structure, they are unrelated to known cation channels or other types of anion channels. Three ClC subfamilie ...
A Toc75-like protein import channel is abundant in chloroplasts
... 1990; Flack et al., 1995). We conclude that atToc75-V represents the most ancestral or earliest form of a Toc75-like channel, which was further modified during endosymbiosis. The Toc75 channels and their bacterial homologues are most highly conserved in the C-terminal region. Here, four domains that ...
... 1990; Flack et al., 1995). We conclude that atToc75-V represents the most ancestral or earliest form of a Toc75-like channel, which was further modified during endosymbiosis. The Toc75 channels and their bacterial homologues are most highly conserved in the C-terminal region. Here, four domains that ...
A Toc75like protein import channel is abundant in
... 1990; Flack et al., 1995). We conclude that atToc75-V represents the most ancestral or earliest form of a Toc75-like channel, which was further modified during endosymbiosis. The Toc75 channels and their bacterial homologues are most highly conserved in the C-terminal region. Here, four domains that ...
... 1990; Flack et al., 1995). We conclude that atToc75-V represents the most ancestral or earliest form of a Toc75-like channel, which was further modified during endosymbiosis. The Toc75 channels and their bacterial homologues are most highly conserved in the C-terminal region. Here, four domains that ...
Biosynthesis

Biosynthesis (also called biogenesis or anabolism) is a multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined together to form macromolecules. This process often consists of metabolic pathways. Some of these biosynthetic pathways are located within a single cellular organelle, while others involve enzymes that are located within multiple cellular organelles. Examples of these biosynthetic pathways include the production of lipid membrane components and nucleotides.The prerequisite elements for biosynthesis include: precursor compounds, chemical energy (e.g. ATP), and catalytic enzymes which may require coenzymes (e.g.NADH, NADPH). These elements create monomers, the building blocks for macromolecules. Some important biological macromolecules include: proteins, which are composed of amino acid monomers joined via peptide bonds, and DNA molecules, which are composed of nucleotides joined via phosphodiester bonds.