Biocatalytic degradation of pollutants
... chemotaxis (che) genes as well as 27 genes that appear to encode methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins, the majority of which have no known function. These findings highlight the enormous amount of information about P. putida metabolism that remains unexplored. Rhodopseudomonas palustris is able to a ...
... chemotaxis (che) genes as well as 27 genes that appear to encode methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins, the majority of which have no known function. These findings highlight the enormous amount of information about P. putida metabolism that remains unexplored. Rhodopseudomonas palustris is able to a ...
Gas-forming Reactions
... Oxidation-Reduction Reactions (Synthesis, Decomposition and Single Replacement Reactions) In addition to precipitation and neutralization reactions, aqueous ions can participate in oxidation-reduction reactions. Oxidation-reduction reactions involve the transfer of electrons from one chemical speci ...
... Oxidation-Reduction Reactions (Synthesis, Decomposition and Single Replacement Reactions) In addition to precipitation and neutralization reactions, aqueous ions can participate in oxidation-reduction reactions. Oxidation-reduction reactions involve the transfer of electrons from one chemical speci ...
Application Note
... been worked out to determine the amino acid concentrations and composition of baby food. Short columns with small particles are the most suitable way to prevent long equilibration and analysis times. This application uses a 100 mm column with a high speed gradient UHPLC method for the separation of ...
... been worked out to determine the amino acid concentrations and composition of baby food. Short columns with small particles are the most suitable way to prevent long equilibration and analysis times. This application uses a 100 mm column with a high speed gradient UHPLC method for the separation of ...
part the second - Астраханский Государственный Медицинский
... A. phosphorylation of pyruvate kinase B. allosteric effects of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate on pyruvate kinase C. activation of phosphofructokinase 1 by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate D. allosteric effects of AMP on fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase 4. Pyruvate dehydrogenase activity is regulated by: A. acceptor ...
... A. phosphorylation of pyruvate kinase B. allosteric effects of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate on pyruvate kinase C. activation of phosphofructokinase 1 by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate D. allosteric effects of AMP on fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase 4. Pyruvate dehydrogenase activity is regulated by: A. acceptor ...
6 Aerobic Degradation by Microorganisms
... the organic pollutants. The chemicals must be accessible to the organisms having biodegrading activities. For example, hydrocarbons are water-insoluble and their degradation requires the production of biosurfactants. (2) The initial intracellular attack of organic pollutants is an oxidative process, ...
... the organic pollutants. The chemicals must be accessible to the organisms having biodegrading activities. For example, hydrocarbons are water-insoluble and their degradation requires the production of biosurfactants. (2) The initial intracellular attack of organic pollutants is an oxidative process, ...
Bingo - GRADE 12 BIOLOGY RESOURCE
... • Replace the title entry with your topic title. • Replace each cell with the words or phrases you want the students to become familiar with. – Do the same for all the other slides. ...
... • Replace the title entry with your topic title. • Replace each cell with the words or phrases you want the students to become familiar with. – Do the same for all the other slides. ...
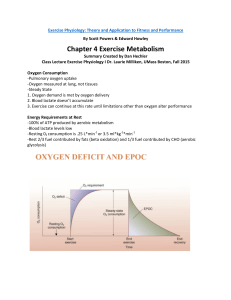
Chapter 4 Exercise Metabolism
... -Rest 2/3 fuel contributed by fats (beta oxidation) and 1/3 fuel contributed by CHO (aerobic glycolysis) ...
... -Rest 2/3 fuel contributed by fats (beta oxidation) and 1/3 fuel contributed by CHO (aerobic glycolysis) ...
Exam 3 Quarter 2 Review Sheet
... why they cause a problem. For example, why would DNP be an excellent weight loss drug? 27. It turns out that you need only very small amounts of vitamin B3 (niacin), which is used to make NAD+. The same goes for riboflavin, the vitamin used in the synthesis of FAD. However, you have incredible numbe ...
... why they cause a problem. For example, why would DNP be an excellent weight loss drug? 27. It turns out that you need only very small amounts of vitamin B3 (niacin), which is used to make NAD+. The same goes for riboflavin, the vitamin used in the synthesis of FAD. However, you have incredible numbe ...
Physiology 8 Endocrine and Gastroenterology
... Regarding the flavoprotein – cytochrome system: a) cytochrome oxidase is the first step in the chain b) occurs within the endoplasmic reticulum c) substrates are pyruvate, water and oxygen and ATP ...
... Regarding the flavoprotein – cytochrome system: a) cytochrome oxidase is the first step in the chain b) occurs within the endoplasmic reticulum c) substrates are pyruvate, water and oxygen and ATP ...
Mitochondrial Biogenesis - Liberation Chiropractic and Wellness
... known as ‘mitochondria’ that often referred to as “cellular power plants” because they generate most of the cell’s adenosine triphosphate (ATP) which is the source of the body’s chemical energy. Mitochondria are also involved in cellular communication (signaling) where the cell’s innate intelligence ...
... known as ‘mitochondria’ that often referred to as “cellular power plants” because they generate most of the cell’s adenosine triphosphate (ATP) which is the source of the body’s chemical energy. Mitochondria are also involved in cellular communication (signaling) where the cell’s innate intelligence ...
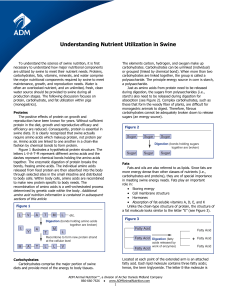
Nutrient Utilization in Swine
... Ten of the 20 amino acids can be synthesized within the pig’s body in sufficient quantities and are referred to as non-essential amino acids. The other ten amino acids that cannot be synthesized or cannot be synthesized at a sufficient rate to enable optimal growth or reproduction must be provided i ...
... Ten of the 20 amino acids can be synthesized within the pig’s body in sufficient quantities and are referred to as non-essential amino acids. The other ten amino acids that cannot be synthesized or cannot be synthesized at a sufficient rate to enable optimal growth or reproduction must be provided i ...
Syllabus
... What is Chemistry ? Chemistry is the study of how matter and energy behave. It is also a scientific method for observing the world and all of life. Knowledge of chemistry is used to make new discoveries about the world (research) and to change some aspects of the world by the invention of new materi ...
... What is Chemistry ? Chemistry is the study of how matter and energy behave. It is also a scientific method for observing the world and all of life. Knowledge of chemistry is used to make new discoveries about the world (research) and to change some aspects of the world by the invention of new materi ...
Chapter One
... Van der Waals interactions are not affected by structural complementarity, while hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds and hydrophobic interaction are affected by structural complementarity. e. Hydrogen, van der Waals, and hydrophobic interactions do not form linear bonds. ...
... Van der Waals interactions are not affected by structural complementarity, while hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds and hydrophobic interaction are affected by structural complementarity. e. Hydrogen, van der Waals, and hydrophobic interactions do not form linear bonds. ...
Introduction to Structure Biology
... Each domain is made of two beta sheets with a topology similar to two Greek key motifs ...
... Each domain is made of two beta sheets with a topology similar to two Greek key motifs ...
Cellular Respiration
... broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of reactions. How much ATP is released during the Krebs cycle? ...
... broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of reactions. How much ATP is released during the Krebs cycle? ...
Chemotropism of Achlya ambisexualis to Methionine
... other reports (Fischer & Werner, 1955; Musgrave et al., 1977) could stem from the use of different species of Achlya. It is also possible that Musgrave et al. (1977) may not have included methionine in their experiments using single amino acids. Their tests on agar substrate containing casein hydrol ...
... other reports (Fischer & Werner, 1955; Musgrave et al., 1977) could stem from the use of different species of Achlya. It is also possible that Musgrave et al. (1977) may not have included methionine in their experiments using single amino acids. Their tests on agar substrate containing casein hydrol ...
Observations during muscle contraction
... phosphokinase) moves phosphate from phosphocreatine to ATP ...
... phosphokinase) moves phosphate from phosphocreatine to ATP ...
Lesson
... ELONGATION: THE STEPS 1. The start codon (methionine, AUG) is the first codon recognized by the ribosome. 2. Aminoacyl-tRNA carrying AUG enters the P site. 3. The next aminoacyl-tRNA enters the A site. 4. A peptide bond forms between the two amino acids. 5. The ribosome translocates over one codon ...
... ELONGATION: THE STEPS 1. The start codon (methionine, AUG) is the first codon recognized by the ribosome. 2. Aminoacyl-tRNA carrying AUG enters the P site. 3. The next aminoacyl-tRNA enters the A site. 4. A peptide bond forms between the two amino acids. 5. The ribosome translocates over one codon ...
Autism
... The structure of glutathione (GSH) is composed of the amino acids (AA) glutamic acid, glycine and once again, that sulfur containing essential amino acid, cysteine. Studies show autistic children to be deficient in glutathione.(12) When toxic metals such as mercury and cadmium enter the system, MT w ...
... The structure of glutathione (GSH) is composed of the amino acids (AA) glutamic acid, glycine and once again, that sulfur containing essential amino acid, cysteine. Studies show autistic children to be deficient in glutathione.(12) When toxic metals such as mercury and cadmium enter the system, MT w ...
A1980JC93500001
... There was a growing conviction that the three-dimensional structure and biological activity of proteins are uniquely determined by the amino acid sequence of their constituent polypeptide chains. The conviction was based on the spontaneous recovery of structure and function after denaturation by gua ...
... There was a growing conviction that the three-dimensional structure and biological activity of proteins are uniquely determined by the amino acid sequence of their constituent polypeptide chains. The conviction was based on the spontaneous recovery of structure and function after denaturation by gua ...
Students will - Perry County Schools
... apply information to real-world situations. Energy is released when the bonds of food molecules are broken and new compounds with lower energy bonds are formed. Cells usually store this energy temporarily in the phosphate bonds of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). During the process of cellular respir ...
... apply information to real-world situations. Energy is released when the bonds of food molecules are broken and new compounds with lower energy bonds are formed. Cells usually store this energy temporarily in the phosphate bonds of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). During the process of cellular respir ...
Unit 2: Nervous System
... • Inside of your nose is lined with olfactory receptors… – Air flows in carrying organic molecules – Organic molecules dissolve in mucus lining – Organic molecules bind to receptors – Impulse sent through Olfactory Nerve ...
... • Inside of your nose is lined with olfactory receptors… – Air flows in carrying organic molecules – Organic molecules dissolve in mucus lining – Organic molecules bind to receptors – Impulse sent through Olfactory Nerve ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.