DHaganTalk1
... (heteropolymers) made up from 20 different L-a-amino acids, also referred to as residues • Two amino acids are combined in a condensation reaction. • The sequence of the different amino acids is considered the primary structure of the peptide or protein. ...
... (heteropolymers) made up from 20 different L-a-amino acids, also referred to as residues • Two amino acids are combined in a condensation reaction. • The sequence of the different amino acids is considered the primary structure of the peptide or protein. ...
H 3 O +
... – His has a side chain pKa of 6.0 and is only 10% protonated at pH 7 – Because His has a pKa near neutral, it plays important roles as a proton donor or acceptor in many enzymes. – His containing peptides are important biological buffers ...
... – His has a side chain pKa of 6.0 and is only 10% protonated at pH 7 – Because His has a pKa near neutral, it plays important roles as a proton donor or acceptor in many enzymes. – His containing peptides are important biological buffers ...
TCA cycle cross products (also known as “nothing is simple” My
... A pathway leading to the fixation of two molecules of CO2 and the production of one molecule of acetyl-CoA; essentially the oxidative TCA cycle running in reverse. Acetyl-CoA is reductively carboxylated to pyruvate, from which all other central metabolites can be formed. Most of the enzymes of reduc ...
... A pathway leading to the fixation of two molecules of CO2 and the production of one molecule of acetyl-CoA; essentially the oxidative TCA cycle running in reverse. Acetyl-CoA is reductively carboxylated to pyruvate, from which all other central metabolites can be formed. Most of the enzymes of reduc ...
AMINO ACIDS IN THE ASTEROIDAL WATER - USRA
... the presence of indigenous amino acids in the LL3 chondrites suggests that amino acids may be formed through Fischer-Tropsch type (FTT) gas-grain reactions after the meteorite parent body cooled to lower temperatures. β-alanine, which is a n-ω-amino acid [9], is also one of the most abundant amino a ...
... the presence of indigenous amino acids in the LL3 chondrites suggests that amino acids may be formed through Fischer-Tropsch type (FTT) gas-grain reactions after the meteorite parent body cooled to lower temperatures. β-alanine, which is a n-ω-amino acid [9], is also one of the most abundant amino a ...
UBC Dairy Education and Research Centre
... 80% of the atmosphere composed of N2 This N is unavailable for plant nutrition Ammonia (NH3 ) is the only form of nitrogen that can be utilized by the plant ...
... 80% of the atmosphere composed of N2 This N is unavailable for plant nutrition Ammonia (NH3 ) is the only form of nitrogen that can be utilized by the plant ...
Introduction to Carbohydrates
... • A portion of the free ammonia is excreted in the urine, but most is used in the synthesis of urea, which is quantitatively the most important route for disposing of nitrogen from the body. • In the second phase of amino acid catabolism, described in Chapter 20, the carbon skeletons of the α-keto ...
... • A portion of the free ammonia is excreted in the urine, but most is used in the synthesis of urea, which is quantitatively the most important route for disposing of nitrogen from the body. • In the second phase of amino acid catabolism, described in Chapter 20, the carbon skeletons of the α-keto ...
DB QS
... glycogenesis is the opposite, the formation of glycogen from glucose. Glycogenolysis takes place in the cells of muscle and liver tissues in response to hormonal and neural signals. In particular, glycogenolysis plays an important role in the adrenaline-induced fight-or-flight response and the regul ...
... glycogenesis is the opposite, the formation of glycogen from glucose. Glycogenolysis takes place in the cells of muscle and liver tissues in response to hormonal and neural signals. In particular, glycogenolysis plays an important role in the adrenaline-induced fight-or-flight response and the regul ...
Slide 1
... The NADH and FADH2 produced in the TCA cycle are sent to the Electron Transport System and used to create a proton gradient across the membrane of the mitochondria – this potential energy provides the energy to convert ADP to ATP. 90% of ATP synthesis happens during electron transport. The “mobile” ...
... The NADH and FADH2 produced in the TCA cycle are sent to the Electron Transport System and used to create a proton gradient across the membrane of the mitochondria – this potential energy provides the energy to convert ADP to ATP. 90% of ATP synthesis happens during electron transport. The “mobile” ...
167
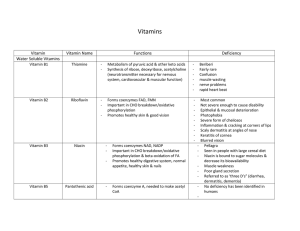
... Seen in people with large cereal diet Niacin is bound to sugar molecules & decrease its bioavailability Muscle weakness Poor gland secretion Referred to as ‘three D’s” (diarrhea, dermatitis, dementia) No deficiency has been identified in humans ...
... Seen in people with large cereal diet Niacin is bound to sugar molecules & decrease its bioavailability Muscle weakness Poor gland secretion Referred to as ‘three D’s” (diarrhea, dermatitis, dementia) No deficiency has been identified in humans ...
AS specification - word format File
... a demonstrate an understanding that there are series of organic compounds characterised by a general formula and one or more functional groups b apply the rules of IUPAC nomenclature to compounds relevant to this specification and draw these compounds, as they are encountered in the specification, u ...
... a demonstrate an understanding that there are series of organic compounds characterised by a general formula and one or more functional groups b apply the rules of IUPAC nomenclature to compounds relevant to this specification and draw these compounds, as they are encountered in the specification, u ...
Metabolism & Enzymes - Revere Local Schools
... most human enzymes = pH 6-8 depends on localized conditions pepsin (stomach) = pH 2-3 trypsin (small intestines) = pH 8 ...
... most human enzymes = pH 6-8 depends on localized conditions pepsin (stomach) = pH 2-3 trypsin (small intestines) = pH 8 ...
Cellular Respiration
... Wine making Grapes are crushed and the sugar they contain is fermented by yeasts to produce alcohol and carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide usually escapes but if the wine is bottled before fermentation is complete, the carbon dioxide dissolves and escapes as bubble when the bottle is opened This is ...
... Wine making Grapes are crushed and the sugar they contain is fermented by yeasts to produce alcohol and carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide usually escapes but if the wine is bottled before fermentation is complete, the carbon dioxide dissolves and escapes as bubble when the bottle is opened This is ...
Amino Acids - Angelo State University
... • Proteins are too large to pass through cell membranes, and are contained within the cells where they were formed unless the cell is damaged by disease or trauma. ...
... • Proteins are too large to pass through cell membranes, and are contained within the cells where they were formed unless the cell is damaged by disease or trauma. ...
Modeling Biomolecules
... their sequence determine the properties of that molecule. a. Structure and function of polymers are derived from the way their monomers are assembled. 2. In proteins, the specific order of amino acids in a polypeptide (Primary structure) interacts with the environment to determine the overall shape ...
... their sequence determine the properties of that molecule. a. Structure and function of polymers are derived from the way their monomers are assembled. 2. In proteins, the specific order of amino acids in a polypeptide (Primary structure) interacts with the environment to determine the overall shape ...
Translation - Crestwood Local Schools
... • Opposite end has three nucleotide bases called the anticodon – Anticodon: three tRNA nucleotides that will hydrogen bond with the mRNA codon ...
... • Opposite end has three nucleotide bases called the anticodon – Anticodon: three tRNA nucleotides that will hydrogen bond with the mRNA codon ...
Hand Outs B 1 - University of Wisconsin–Madison
... Definitions for Parents-complex concepts in simple language for you to use with your school-aged children ...
... Definitions for Parents-complex concepts in simple language for you to use with your school-aged children ...
What is topline and how do you get it?
... it is not necessarily the figure listed for protein percentage that matters as much as the quality of the protein. The science bit! Protein is made up of chains of amino acids. The amino acids build up the protein molecule like building blocks. There are two types of amino acids, essential and non- ...
... it is not necessarily the figure listed for protein percentage that matters as much as the quality of the protein. The science bit! Protein is made up of chains of amino acids. The amino acids build up the protein molecule like building blocks. There are two types of amino acids, essential and non- ...
Kaplan Medical Template Design
... Phosphatase is a group of enzymes that split phosphoric acid from organic phosphate esters (alkaline phosphatase). normally present in small amounts in serum, elevation indicates tissue/cell damage and death causing release ...
... Phosphatase is a group of enzymes that split phosphoric acid from organic phosphate esters (alkaline phosphatase). normally present in small amounts in serum, elevation indicates tissue/cell damage and death causing release ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.