Note Set 11 1 GLYCOLYSIS (also known as: EMBDEN
... depends on the reoxidation of NADH formed at the G3PD step (G3-P to 1,3-BPG) 1. anaerobic metabolism in muscle tissue: •during periods of vigorous excerise, muscle tissue is functioning essentially under anaerobic conditions, and the ATP is derived almost exclusively from glycolysis under these cond ...
... depends on the reoxidation of NADH formed at the G3PD step (G3-P to 1,3-BPG) 1. anaerobic metabolism in muscle tissue: •during periods of vigorous excerise, muscle tissue is functioning essentially under anaerobic conditions, and the ATP is derived almost exclusively from glycolysis under these cond ...
List of molecular weight for each amino acid:
... What peptides and proteins are returned when you search by y” type ions? What peptides and proteins are returned when you search by b type ions? What peptides and proteins are returned when you search by both b type and y” type ions and without telling the program what amino acids are contained in t ...
... What peptides and proteins are returned when you search by y” type ions? What peptides and proteins are returned when you search by b type ions? What peptides and proteins are returned when you search by both b type and y” type ions and without telling the program what amino acids are contained in t ...
C) the gain of electrons.
... interfere with the cell's abilities to catalyze various reactions. C) Elevated body temperatures will increase the energy of activation needed to start various chemical reactions in the body. This will interfere with the ability of enzymes to catalyze vital chemical reactions. D) Elevated body tempe ...
... interfere with the cell's abilities to catalyze various reactions. C) Elevated body temperatures will increase the energy of activation needed to start various chemical reactions in the body. This will interfere with the ability of enzymes to catalyze vital chemical reactions. D) Elevated body tempe ...
Investigation of Orientational Isomers of Cyclodextrin Inclusion
... To mask undesired tastes in the food and cosmetic industries ...
... To mask undesired tastes in the food and cosmetic industries ...
Document
... • Fermentative result: Acid production on both (open and covered) tubes. The acid produced changes the pH indicator, bromthymol blue, from green to yellow. e.g. Escherichia coli • Oxidative result: Acid production in the open tube (aerobic) and not the oil-covered tube (anaerobic) indicates an oxid ...
... • Fermentative result: Acid production on both (open and covered) tubes. The acid produced changes the pH indicator, bromthymol blue, from green to yellow. e.g. Escherichia coli • Oxidative result: Acid production in the open tube (aerobic) and not the oil-covered tube (anaerobic) indicates an oxid ...
Reactive Oxygen Species
... (red), so that they would now contain a new mixture of molecules, such as crosslinkers and enzymes. Clustering could occur either extracellularly, within the membrane, or in the cytosol (a–c, respectively). Raft clustering could also occur through GPI-anchored proteins (yellow), either as a primary ...
... (red), so that they would now contain a new mixture of molecules, such as crosslinkers and enzymes. Clustering could occur either extracellularly, within the membrane, or in the cytosol (a–c, respectively). Raft clustering could also occur through GPI-anchored proteins (yellow), either as a primary ...
Lipids (lec 1, 2, 3)..
... Steps of transport: 1) acyl group is transferred from acylCoA into carnitine by CAT-1 to give acyl carnitine and free CoA which remains in cytoplasm. 2) Acyl carnitine is transported into mitochondria by the help of Carnitine acylcarnitine translocase. 3) CAT-2 catalyses the transfer of acyl group f ...
... Steps of transport: 1) acyl group is transferred from acylCoA into carnitine by CAT-1 to give acyl carnitine and free CoA which remains in cytoplasm. 2) Acyl carnitine is transported into mitochondria by the help of Carnitine acylcarnitine translocase. 3) CAT-2 catalyses the transfer of acyl group f ...
Self-assembly of Proteins
... structures can be achieved using self-assembly which is not possible by other techniques. Generally, self-assembly results in formation of structures that are thermodynamically stable and are defect-free. Biological system is one of the most investigated systems for understanding the selfassembly pr ...
... structures can be achieved using self-assembly which is not possible by other techniques. Generally, self-assembly results in formation of structures that are thermodynamically stable and are defect-free. Biological system is one of the most investigated systems for understanding the selfassembly pr ...
1. INTRODUCTION 1.1 THE ARACHIDONIC ACID - diss.fu
... and the specificity is rather substrate related. For instance, the 15-LOX oxidises linoleic acid to 13-HpODE, but it also exhibits 5-LOX activity with the 15-HETE methyl ester as substrate. Similarly, among the arachidonate 12-LOXs, a leukocyte-type 12-LOX has been identified which is similar to the ...
... and the specificity is rather substrate related. For instance, the 15-LOX oxidises linoleic acid to 13-HpODE, but it also exhibits 5-LOX activity with the 15-HETE methyl ester as substrate. Similarly, among the arachidonate 12-LOXs, a leukocyte-type 12-LOX has been identified which is similar to the ...
e is nline ion any er.`
... chemical interest, because of the novelty of the compounds present, and human health interest because the arsenicals occur in many common foods. The highest arsenic concentrations are found in seafoods, and many studies have reported on the type of arsenic compounds present in such foods.1 The vast ...
... chemical interest, because of the novelty of the compounds present, and human health interest because the arsenicals occur in many common foods. The highest arsenic concentrations are found in seafoods, and many studies have reported on the type of arsenic compounds present in such foods.1 The vast ...
Molecular Modeling Activity for Carbohydrates
... Just as double sugars were formed from two single sugar molecules using a dehydration synthesis reaction, polysaccharides and water are formed when many single sugars are chemically joined together. The prefix “poly-” means many. Starch, glycogen, and cellulose are the three most common polysacchari ...
... Just as double sugars were formed from two single sugar molecules using a dehydration synthesis reaction, polysaccharides and water are formed when many single sugars are chemically joined together. The prefix “poly-” means many. Starch, glycogen, and cellulose are the three most common polysacchari ...
Metabolism & Enzymes
... “conformational change” bring chemical groups in position to catalyze ...
... “conformational change” bring chemical groups in position to catalyze ...
2_Digestion of CHO_Students
... concentration gradient) and at the same time causes the carrier to transport glucose against its concentration gradient (from lower to higher concentrations) allowing for greater accumulation of glucose on one side of the membrane than on the other. ...
... concentration gradient) and at the same time causes the carrier to transport glucose against its concentration gradient (from lower to higher concentrations) allowing for greater accumulation of glucose on one side of the membrane than on the other. ...
Cellular Respiration
... Photosynthesis builds these large organic molecules using CO2 as building blocks and solar radiation as the energy source. ...
... Photosynthesis builds these large organic molecules using CO2 as building blocks and solar radiation as the energy source. ...
mcb101 praxexam 2 F`10
... 19) You are attempting to identify an unknown enteric bacterium that is one of the 12 species shown in the biochemical test key that is given above. Your unknown bacterium is positive for dulcitol fermentation, negative for raffinose fermentation and positive for Simmon’s citrate. Which one of the f ...
... 19) You are attempting to identify an unknown enteric bacterium that is one of the 12 species shown in the biochemical test key that is given above. Your unknown bacterium is positive for dulcitol fermentation, negative for raffinose fermentation and positive for Simmon’s citrate. Which one of the f ...
Document
... structures (ex. Cell membrane) and perform many cell functions (regulating reactions, transport, motion, protection, support, communication) It is the presence of specific proteins that determines how an organism develops & what characteristics an organism will have ...
... structures (ex. Cell membrane) and perform many cell functions (regulating reactions, transport, motion, protection, support, communication) It is the presence of specific proteins that determines how an organism develops & what characteristics an organism will have ...
Fuelling the future: microbial engineering for the production
... tion to ethanol, many other longer-chain alcohols, alkanes and fatty acid esters are desirable fuels because of their favourable properties for specific applications. However, although some of these compounds or their precursors can be produced from various metabolic pathways that naturally exist in ...
... tion to ethanol, many other longer-chain alcohols, alkanes and fatty acid esters are desirable fuels because of their favourable properties for specific applications. However, although some of these compounds or their precursors can be produced from various metabolic pathways that naturally exist in ...
Full text
... Selenium is a very potent antioxidant protecting the body from damage due to oxidation by free radicals. Dietary supplementation with selenium in animals increased selenium content in several tissues. The antioxidant effect of selenium on lipid peroxidation, enzyme activities and biochemical paramet ...
... Selenium is a very potent antioxidant protecting the body from damage due to oxidation by free radicals. Dietary supplementation with selenium in animals increased selenium content in several tissues. The antioxidant effect of selenium on lipid peroxidation, enzyme activities and biochemical paramet ...
Slide 1
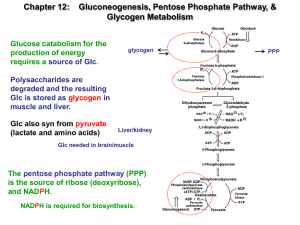
... Polysaccharides are degraded and the resulting Glc is stored as glycogen in muscle and liver. Glc also syn from pyruvate (lactate and amino acids) ...
... Polysaccharides are degraded and the resulting Glc is stored as glycogen in muscle and liver. Glc also syn from pyruvate (lactate and amino acids) ...
Module 1: Review of General and Organic Chemistry
... b. Draw the titration curve of Lysine identifying the pH zones at which the buffer capacity is maximum ...
... b. Draw the titration curve of Lysine identifying the pH zones at which the buffer capacity is maximum ...
Biochemical fossils of the ancient transition from geoenergetics to
... The deep dichotomy of archaea and bacteria is evident in many basic traits including ribosomal protein composition, membrane lipid synthesis, cell wall constituents, and flagellar composition. Here we explore that deep dichotomy further by examining the distribution of genes for the synthesis of the ...
... The deep dichotomy of archaea and bacteria is evident in many basic traits including ribosomal protein composition, membrane lipid synthesis, cell wall constituents, and flagellar composition. Here we explore that deep dichotomy further by examining the distribution of genes for the synthesis of the ...
Bioorthogonal chemical imaging of metabolic activities in live
... or electrical signals and relatively slow metabolic turnover of small metabolites into DNA, RNA, proteins and lipids. While the former signaling process has been extensively probed by electrophysiology and fluorescent techniques1–3, visualizing the overall downstream genetic replication, transcripti ...
... or electrical signals and relatively slow metabolic turnover of small metabolites into DNA, RNA, proteins and lipids. While the former signaling process has been extensively probed by electrophysiology and fluorescent techniques1–3, visualizing the overall downstream genetic replication, transcripti ...
Lysinuric protein intolerance: one gene, many
... experience intrauterine growth restriction, resulting in small pups, which were mostly cannabalized by their mothers. As a result, only two pups could be rescued and studied further. These two animals showed symptoms that closely resembled ...
... experience intrauterine growth restriction, resulting in small pups, which were mostly cannabalized by their mothers. As a result, only two pups could be rescued and studied further. These two animals showed symptoms that closely resembled ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.