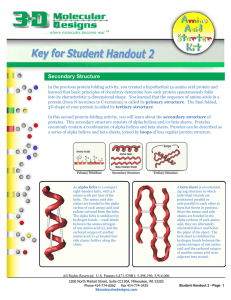
Secondary Structure - 3D Molecular Designs
... 1050 North Market Street, Suite CC130A, Milwaukee, WI 53202 Phone 414-774-6562 Fax 414-774-3435 3dmoleculardesigns.com ...
... 1050 North Market Street, Suite CC130A, Milwaukee, WI 53202 Phone 414-774-6562 Fax 414-774-3435 3dmoleculardesigns.com ...
Assay the Activity of Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) in Serum
... of disodium phenyl phosphate forming phosphate and ...
... of disodium phenyl phosphate forming phosphate and ...
A general trend for invertebrate mitochondrial genome evolution
... base and amino acids substitutions are equal. However, we also know that each organism will be affected by nature selection and a general trend for amino acids and nucleotides change should be existed. In 2005, Jordan et al reported the trends of amino acid changes were similar in 15 taxa representi ...
... base and amino acids substitutions are equal. However, we also know that each organism will be affected by nature selection and a general trend for amino acids and nucleotides change should be existed. In 2005, Jordan et al reported the trends of amino acid changes were similar in 15 taxa representi ...
chemical reaction
... • Often, energy is released or absorbed during a chemical reaction. • For example, energy of a welding torch is released when hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water. ...
... • Often, energy is released or absorbed during a chemical reaction. • For example, energy of a welding torch is released when hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water. ...
ijbbjune2k2
... Received 5 April 2002 Purines have long been known for their roles in extracellular signaling. One of the most interesting functions to come to light recently has been the involvement, particularly of adenosine 5’-triphosphate (ATP), as a neurotransmitter in the central and the sympathetic nervous s ...
... Received 5 April 2002 Purines have long been known for their roles in extracellular signaling. One of the most interesting functions to come to light recently has been the involvement, particularly of adenosine 5’-triphosphate (ATP), as a neurotransmitter in the central and the sympathetic nervous s ...
Enzymes and pH Review Game with Answers 2013 2014
... interfere with the cell's abilities to catalyze various reactions. C) Elevated body temperatures will increase the energy of activation needed to start various chemical reactions in the body. This will interfere with the ability of enzymes to catalyze vital chemical reactions. D) Elevated body tempe ...
... interfere with the cell's abilities to catalyze various reactions. C) Elevated body temperatures will increase the energy of activation needed to start various chemical reactions in the body. This will interfere with the ability of enzymes to catalyze vital chemical reactions. D) Elevated body tempe ...
Study Guide for Chapter 1 Test
... Explain why they are needed for life in terms of their functions Sec 38-2 o Describe the overall function of the digestive system and of its parts o Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion o Identify the parts of the digestive system in a diagram *Refer to Fig. 38-10 on p ...
... Explain why they are needed for life in terms of their functions Sec 38-2 o Describe the overall function of the digestive system and of its parts o Distinguish between chemical digestion and mechanical digestion o Identify the parts of the digestive system in a diagram *Refer to Fig. 38-10 on p ...
Elucidating the complete reaction cycle for membrane
... This potential can be used to drive other cellular reactions such as ATP synthesis and the primary active transport of solutes. MPPases are found in bacteria, archaea, protozoans and plants, but not in mammals. Crucially, MPPases are found in numerous bacterial and protozoan parasites such as Plasmo ...
... This potential can be used to drive other cellular reactions such as ATP synthesis and the primary active transport of solutes. MPPases are found in bacteria, archaea, protozoans and plants, but not in mammals. Crucially, MPPases are found in numerous bacterial and protozoan parasites such as Plasmo ...
lecture9
... Our approach is to discover the enzymes for the synthesis and utilization of poly P in bacteria, yeast and animal cells. These enzymes will reveal novel mechanisms and insights and when purified will open the route of reverse genetics: the peptide sequence leads to the gene and thereby the means to ...
... Our approach is to discover the enzymes for the synthesis and utilization of poly P in bacteria, yeast and animal cells. These enzymes will reveal novel mechanisms and insights and when purified will open the route of reverse genetics: the peptide sequence leads to the gene and thereby the means to ...
Amino Acids as Acids, Bases and Buffers
... Many organisms can make all 20 of the amino acids o Bacteria, yeast, and plants Some amino acids are made from common metabolic intermediates directly o For example, alanine is made from pyruvate (transamination of pyruvate with glutamate as the amino donor) Some amino acids are made as products fro ...
... Many organisms can make all 20 of the amino acids o Bacteria, yeast, and plants Some amino acids are made from common metabolic intermediates directly o For example, alanine is made from pyruvate (transamination of pyruvate with glutamate as the amino donor) Some amino acids are made as products fro ...
General and Organic Chemistry: Theory content HT 2016
... Key concepts amines: Nomenclature . Hybridization . Preparation 1) from halides, 2) by reducing a) nitro-compounds, b) nitriles, c) imines (reductive amination). Reactions: 1) acid base relationship, factors affecting base strength, 2 ) alkylation with RX, 3) acylation with acid chloride, 4) reactio ...
... Key concepts amines: Nomenclature . Hybridization . Preparation 1) from halides, 2) by reducing a) nitro-compounds, b) nitriles, c) imines (reductive amination). Reactions: 1) acid base relationship, factors affecting base strength, 2 ) alkylation with RX, 3) acylation with acid chloride, 4) reactio ...
Taxonomy, biology and physiology of fungi
... The vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane at the tip, and release their contents. ...
... The vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane at the tip, and release their contents. ...
ENERGY CURRENCY
... order for it to be utilized, it first must be converted into ATP. In order for this conversion to occur, oxidative pathways must be available. NAD+ is nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and is found in all cells. It is actually classified as a coenzyme . In its reduced high energy form it is official ...
... order for it to be utilized, it first must be converted into ATP. In order for this conversion to occur, oxidative pathways must be available. NAD+ is nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and is found in all cells. It is actually classified as a coenzyme . In its reduced high energy form it is official ...
... 9. The pKa of an ionizable side chain, such as imidazole in histidine, can be determined with NMR because a) the pKa is near neutrality. b) protonated imidazole has twice the number of protons. c) unprotonated imidazole is invisible in the spectrum. d) the chemical shift of His differs from His+. 10 ...
CARBON SKELETONS COVALENT BONDS - U
... Carbon and hydrogen combine together to make stable compounds (or chemical groups) called hydrocarbons. These are nonpolar, do not form hydrogen bonds, and are generally insoluble in water. Atoms joined by two or more covalent bonds cannot rotate freely around the bond axis. This restriction is a ma ...
... Carbon and hydrogen combine together to make stable compounds (or chemical groups) called hydrocarbons. These are nonpolar, do not form hydrogen bonds, and are generally insoluble in water. Atoms joined by two or more covalent bonds cannot rotate freely around the bond axis. This restriction is a ma ...
General Biochemistry 115:403
... 1. Thermodynamics and the influence of water on biochemical reactions 2. The role of pH, pKa and buffers in biochemical systems 3. The relationship between structure and function of biological molecules 4. Enzyme kinetics 5. The biochemical mechanisms of nucleotide (DNA/RNA) structure and metabolism ...
... 1. Thermodynamics and the influence of water on biochemical reactions 2. The role of pH, pKa and buffers in biochemical systems 3. The relationship between structure and function of biological molecules 4. Enzyme kinetics 5. The biochemical mechanisms of nucleotide (DNA/RNA) structure and metabolism ...
Powerpoint
... Proteins are major components of most biological systems: Organ level (liver, per kg wet weight): 146 g protein, 2.6 g DNA, 49 g total lipid, 3.9 g cholesterol. Cellular level (per 1012 leukocytes): 100 g protein, 6.9 g DNA, 8.2 g RNA, 15.6 g total lipid, 2 g cholesterol. Plasma (per dm3): 73 g prot ...
... Proteins are major components of most biological systems: Organ level (liver, per kg wet weight): 146 g protein, 2.6 g DNA, 49 g total lipid, 3.9 g cholesterol. Cellular level (per 1012 leukocytes): 100 g protein, 6.9 g DNA, 8.2 g RNA, 15.6 g total lipid, 2 g cholesterol. Plasma (per dm3): 73 g prot ...
11.1 Types of Lipids 11.2 Fatty Acids
... known. Quaternary structures are typically composed of two or more protein subunits (tertiary structures). Nonprotein components may also be present. Hemoglobin is a tetramer (four subunits) containing two copies of one polypeptide and two copies of another: two identical chains of 141 amino acid re ...
... known. Quaternary structures are typically composed of two or more protein subunits (tertiary structures). Nonprotein components may also be present. Hemoglobin is a tetramer (four subunits) containing two copies of one polypeptide and two copies of another: two identical chains of 141 amino acid re ...
it_health_summary - Center for Biological Sequence Analysis
... are needed to s ee this pic ture. ...
... are needed to s ee this pic ture. ...
4-Catabolism of Purine Nucleotides
... Due to this deficiency adenosine & deoxy-adenosine cannot be degraded concentration increases converted into ...
... Due to this deficiency adenosine & deoxy-adenosine cannot be degraded concentration increases converted into ...
Bio07_TR__U04_CH12.QXD
... a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it relea ...
... a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it relea ...
Thin-Layer Chromatography of Amino Acids
... Chromatography is a process used to separate a mixture of different substances back into their individual forms. For example, if you mixed red, yellow, green, and blue food coloring together chromatography could be used to separate them back into their individual colors. There are many different typ ...
... Chromatography is a process used to separate a mixture of different substances back into their individual forms. For example, if you mixed red, yellow, green, and blue food coloring together chromatography could be used to separate them back into their individual colors. There are many different typ ...
Bio07_TR__U04_CH12.QXD
... a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it relea ...
... a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it relea ...
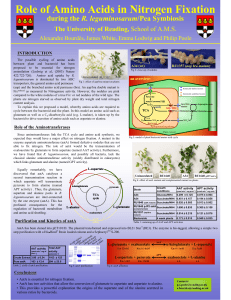
Role of Amino Acids in Nitrogen Fixation
... Since aminotransferases link the TCA cycle and amino acid synthesis, we expected they would have a major effect on nitrogen fixation. A mutant in the enzyme aspartate aminotransferase (aatA) formed defective nodules that are not able to fix nitrogen. The role of aatA would be the transamination of o ...
... Since aminotransferases link the TCA cycle and amino acid synthesis, we expected they would have a major effect on nitrogen fixation. A mutant in the enzyme aspartate aminotransferase (aatA) formed defective nodules that are not able to fix nitrogen. The role of aatA would be the transamination of o ...
Section 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it relea ...
... a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it relea ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.