Double-Stranded RNA: The Enigmatic Helix
... Viruses have long been known to produce dsRNA, and when dsRNA binding proteins (dsRBPs) in our bodies bind viral dsRNA they send an SOS that initiates an immune response to fight the infection. For many years it was thought that animals, including humans, did not make their own dsRNA. However, over ...
... Viruses have long been known to produce dsRNA, and when dsRNA binding proteins (dsRBPs) in our bodies bind viral dsRNA they send an SOS that initiates an immune response to fight the infection. For many years it was thought that animals, including humans, did not make their own dsRNA. However, over ...
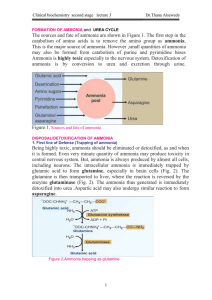
FORMATION OF AMMONIA
... 1. Coarse Regulation The enzyme levels change with the protein content of diet. During starvation, the activity of urea cycle enzymes is elevated to meet the increased rate of protein catabolism. 2. Fine Regulation The major regulatory step is catalyzed by CPS-I where the positive effector is N-acet ...
... 1. Coarse Regulation The enzyme levels change with the protein content of diet. During starvation, the activity of urea cycle enzymes is elevated to meet the increased rate of protein catabolism. 2. Fine Regulation The major regulatory step is catalyzed by CPS-I where the positive effector is N-acet ...
Activities for the -Helix and -Sheet Construction Kit
... The primary sequence of a protein, composed of amino acids, determines the organization of the sequence into the secondary structure. There are two periodic secondary structure motifs, α-helix and β-sheet. Proteins can be composed of primarily α-helices (for example, β-globin) or β-sheets (for examp ...
... The primary sequence of a protein, composed of amino acids, determines the organization of the sequence into the secondary structure. There are two periodic secondary structure motifs, α-helix and β-sheet. Proteins can be composed of primarily α-helices (for example, β-globin) or β-sheets (for examp ...
MAR - OSU Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
... You are expected to have a working knowledge of algebra, general chemistry, and organic chemistry. You will need to be able to use logarithms, exponents, and scientific notation; to rearrange algebraic equations; to balance chemical equations; to understand the relationships between atomic number, v ...
... You are expected to have a working knowledge of algebra, general chemistry, and organic chemistry. You will need to be able to use logarithms, exponents, and scientific notation; to rearrange algebraic equations; to balance chemical equations; to understand the relationships between atomic number, v ...
File
... 25. The graph below shows the effect of changing the substrate concentration on an enzyme controlled reaction. ...
... 25. The graph below shows the effect of changing the substrate concentration on an enzyme controlled reaction. ...
Detecting Constituent Sequences by Means of HP Pattern–Based
... signaling. Human Akt, has an N-terminal pleckstrin homology (PH) domain that binds to the lipid products of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), phosphatidylinositol-3,4bisphosphate [PI(3,4)P2] and phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5trisphosphate [PI(3,4,5)P3]. This binding happens at plasma membrane level, whe ...
... signaling. Human Akt, has an N-terminal pleckstrin homology (PH) domain that binds to the lipid products of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), phosphatidylinositol-3,4bisphosphate [PI(3,4)P2] and phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5trisphosphate [PI(3,4,5)P3]. This binding happens at plasma membrane level, whe ...
Exam 2 question possibility for 2008
... 3A. If the steady state concentrations of each reactant and product in this reaction in an E. coli cell growing in glucose minimal medium is 10-4M, then the reaction: (is proceeding to the right) (is proceeding to the left) (is at equilibrium) and the change in free energy for the reaction is approx ...
... 3A. If the steady state concentrations of each reactant and product in this reaction in an E. coli cell growing in glucose minimal medium is 10-4M, then the reaction: (is proceeding to the right) (is proceeding to the left) (is at equilibrium) and the change in free energy for the reaction is approx ...
ANN 303 PRINCIPLES OF ANIMAL NUTRITION (A)
... The study of plant nutrition is important because animals depends on them for survival. Plants are capable to synthesize complex food materials using simple substances such as CO2 from the air and water and inorganic elements from the soil by means of photosynthesis. The greatest part of the energy ...
... The study of plant nutrition is important because animals depends on them for survival. Plants are capable to synthesize complex food materials using simple substances such as CO2 from the air and water and inorganic elements from the soil by means of photosynthesis. The greatest part of the energy ...
File
... of energy levels for electrons. Eg. Elements with 3 energy levels (more than 10 electrons) are found in period (row) 3. Groups – elements have similar properties as those found above and below them. Sometimes called “families” eg. Group 1 is the Alkali Metals (look on page 25 for the name of the r ...
... of energy levels for electrons. Eg. Elements with 3 energy levels (more than 10 electrons) are found in period (row) 3. Groups – elements have similar properties as those found above and below them. Sometimes called “families” eg. Group 1 is the Alkali Metals (look on page 25 for the name of the r ...
Amino Acids and Their Properties
... Amino acid matching works better as evolutionary distance increases (why?) We’d like to be able to assess relatedness of organisms that diverged long ago ...
... Amino acid matching works better as evolutionary distance increases (why?) We’d like to be able to assess relatedness of organisms that diverged long ago ...
Document
... Enzymes are used in animal feed to breakdown cellulose (cellulase) New use of enzymes (phytases) which breakdown phytic acid This allows better utilization of plant phosphorus stores Allowing bone-meal to be removed from feeds ...
... Enzymes are used in animal feed to breakdown cellulose (cellulase) New use of enzymes (phytases) which breakdown phytic acid This allows better utilization of plant phosphorus stores Allowing bone-meal to be removed from feeds ...
Introduction into Metabolism and Energy Exchange in Human
... The most important substances in the cell are: proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, carbohydrates, water, some simple substances: O2, vitamins, ions and many others. So, first of all, we have to discuss the metabolic pathways for these substances. All metabolic pathways are divided in three groups: Anab ...
... The most important substances in the cell are: proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, carbohydrates, water, some simple substances: O2, vitamins, ions and many others. So, first of all, we have to discuss the metabolic pathways for these substances. All metabolic pathways are divided in three groups: Anab ...
+ E A.
... Genetic defects for both the synthase and the lyase. Missing or impaired cystathionine synthase leads to homocystinuria. High concentration of homocysteine and methionine in the urine. Homocysteine is highly reactive molecule. Disease is often associated with mental retardation, multisystemic disord ...
... Genetic defects for both the synthase and the lyase. Missing or impaired cystathionine synthase leads to homocystinuria. High concentration of homocysteine and methionine in the urine. Homocysteine is highly reactive molecule. Disease is often associated with mental retardation, multisystemic disord ...
Three functionally diverged major structural proteins of white spot
... by intramuscular injections in the lateral area of the fourth abdominal segment. Virions were purified from haemolymph of infected P. monodon as described by Van Hulten et al. (2000 b). As a negative control, haemolymph was taken from uninfected P. monodon. The preparations were analysed by electron ...
... by intramuscular injections in the lateral area of the fourth abdominal segment. Virions were purified from haemolymph of infected P. monodon as described by Van Hulten et al. (2000 b). As a negative control, haemolymph was taken from uninfected P. monodon. The preparations were analysed by electron ...
magnesium chloride TDS
... biological roles in enzymology, cell membrane and wall structural integrity, muscle cell physiology, and ...
... biological roles in enzymology, cell membrane and wall structural integrity, muscle cell physiology, and ...
Role of Liver In Triglyceride Homeostasis
... • De novo lipogenesis and the regulation of fatty acid synthesis • Sources of fatty acids for liver TG biosynthesis • Secretion of hepatic TG with VLDL and the fate of TG-rich particles • Insulin resistance and its impact on hepatic TG ...
... • De novo lipogenesis and the regulation of fatty acid synthesis • Sources of fatty acids for liver TG biosynthesis • Secretion of hepatic TG with VLDL and the fate of TG-rich particles • Insulin resistance and its impact on hepatic TG ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.