Problem 14. MAGNESIUM DETERMINATION
... The superposition principle is applicable to quantum systems only and is not valid when applied to macrosystems. To illustrate this idea, E. Schrödinger proposed the following mental experiment. Consider the Geiger counter which detects the entering electrons. The counter is connected to a device wh ...
... The superposition principle is applicable to quantum systems only and is not valid when applied to macrosystems. To illustrate this idea, E. Schrödinger proposed the following mental experiment. Consider the Geiger counter which detects the entering electrons. The counter is connected to a device wh ...
Lecture 8. Biogeochemical Cycles
... emerged because nitrogen was a limiting element for microbial growth. Although molecular nitrogen was abundant in the atmosphere, microbial cells could not directly utilize nitrogen as N2 gas. Cells require organic nitrogen compounds or reduced inorganic forms of nitrogen for growth. Therefore, unde ...
... emerged because nitrogen was a limiting element for microbial growth. Although molecular nitrogen was abundant in the atmosphere, microbial cells could not directly utilize nitrogen as N2 gas. Cells require organic nitrogen compounds or reduced inorganic forms of nitrogen for growth. Therefore, unde ...
An acidic region of the 89K murine cytomegalovirus immediate early
... are characterized by deletions in the N-terminal region (for sequence details see Fig. 4c), all bound D N A strongly (Fig. 4b, lanes 2 to 5). It is apparent that several fusion proteins were not stable and that some, but not all, degradation products were still capable of binding DNA. Deletion mutan ...
... are characterized by deletions in the N-terminal region (for sequence details see Fig. 4c), all bound D N A strongly (Fig. 4b, lanes 2 to 5). It is apparent that several fusion proteins were not stable and that some, but not all, degradation products were still capable of binding DNA. Deletion mutan ...
CHAPTER 16: ANSWERS TO SELECTED PROBLEMS
... the cell, but most of the RNA is located in the cytoplasm. Section 16.3 16.18 DNA replication is the process in which a cell makes an exact copy of its DNA. 16.19 Most cells in the human body contain 46 chromosomes, of which 44 are autosomal chromosomes and two are sex chromosomes. 16.20 Building DN ...
... the cell, but most of the RNA is located in the cytoplasm. Section 16.3 16.18 DNA replication is the process in which a cell makes an exact copy of its DNA. 16.19 Most cells in the human body contain 46 chromosomes, of which 44 are autosomal chromosomes and two are sex chromosomes. 16.20 Building DN ...
The Monocarboxylate Transporter Family—Role and Regulation
... the proton-linked transport of monocarboxylates such as L-lactate across the plasma membrane, whereas MCT8 and MCT10 are thyroid hormone and aromatic amino acid transporters, respectively. The importance of MCTs is becoming increasingly evident as their extensive physiological and pathological roles ...
... the proton-linked transport of monocarboxylates such as L-lactate across the plasma membrane, whereas MCT8 and MCT10 are thyroid hormone and aromatic amino acid transporters, respectively. The importance of MCTs is becoming increasingly evident as their extensive physiological and pathological roles ...
The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidants in Oxidative
... knowledge as presented in this review will be important in the management of oxidative stress and its associated diseases. Keywords: Role, Oxidative stress, Antioxidant, ROS ...
... knowledge as presented in this review will be important in the management of oxidative stress and its associated diseases. Keywords: Role, Oxidative stress, Antioxidant, ROS ...
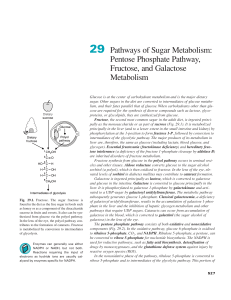
29 Pathways of Sugar Metabolism: Pentose
... phosphorylation at the 1-position to form fructose 1-P, followed by conversion to intermediates of the glycolytic pathway. The major products of its metabolism in liver are, therefore, the same as glucose (including lactate, blood glucose, and glycogen). Essential fructosuria (fructokinase deficienc ...
... phosphorylation at the 1-position to form fructose 1-P, followed by conversion to intermediates of the glycolytic pathway. The major products of its metabolism in liver are, therefore, the same as glucose (including lactate, blood glucose, and glycogen). Essential fructosuria (fructokinase deficienc ...
The Effect of Temperature on the Metabolism of
... 25' had a smaller mean cell volume, greater yield value and nitrogen utilization. Ethanol, pyruvate and a-ketoglutarate were secreted to a greater degree in cultures grown at 38". Yeast grown at 25' had a smaller capacity to produce carbon dioxide but greater ability to take up oxygen. Enzymes assoc ...
... 25' had a smaller mean cell volume, greater yield value and nitrogen utilization. Ethanol, pyruvate and a-ketoglutarate were secreted to a greater degree in cultures grown at 38". Yeast grown at 25' had a smaller capacity to produce carbon dioxide but greater ability to take up oxygen. Enzymes assoc ...
Chapter 1. introduction
... and cells Selective filter to allow the entry of nutrients necessary for the cell’s growth and development and the exit of metabolic waste products Communication ith its surroundings through protein receptors Energy transduction-Mitochondria and photosynthetic organisams ...
... and cells Selective filter to allow the entry of nutrients necessary for the cell’s growth and development and the exit of metabolic waste products Communication ith its surroundings through protein receptors Energy transduction-Mitochondria and photosynthetic organisams ...
Consequences of Stop Codon Reassignment on
... et al. 1987; Osawa 1995) suggests that codons can be reassigned by a neutral mechanism if we assume a stage in which the codon entirely disappears from the genome— drift or GC pressure can account for this elimination; the codon could then reemerge by genetic drift and be decoded (captured) by a tRN ...
... et al. 1987; Osawa 1995) suggests that codons can be reassigned by a neutral mechanism if we assume a stage in which the codon entirely disappears from the genome— drift or GC pressure can account for this elimination; the codon could then reemerge by genetic drift and be decoded (captured) by a tRN ...
DNA Lesson Plan - Penn Arts and Sciences
... issues such as cloning and genetically modified foods. They should also be aware that the sequence of bases within the DNA encodes all of the genetic information for a given organism. The issue for this lesson is how that information is used to synthesize the many proteins within our body. The lesso ...
... issues such as cloning and genetically modified foods. They should also be aware that the sequence of bases within the DNA encodes all of the genetic information for a given organism. The issue for this lesson is how that information is used to synthesize the many proteins within our body. The lesso ...
Lactic acid bacteria as a cell factory: rerouting of carbon metabolism
... generated by PEP conversion to pyruvate by pyruvate kinase (pyk) (Fig. 2). Recently, the ptsHI operon of L. lactis, encoding the general PTS components HPr and enzyme I, respectively, has been cloned and characterized. HPr plays an important role regulation of sugar utilization, both at the level of ...
... generated by PEP conversion to pyruvate by pyruvate kinase (pyk) (Fig. 2). Recently, the ptsHI operon of L. lactis, encoding the general PTS components HPr and enzyme I, respectively, has been cloned and characterized. HPr plays an important role regulation of sugar utilization, both at the level of ...
Discovering the Interaction Propensities of Amino Acids and
... Dataset generation Protein-RNA complex structures were obtained from the PDB database (Berman et al., 2000). Complexes solved by X-ray crystallography at a resolution better than 3.0 Å were selected. As of September 2002, there were 188 protein-RNA complexes in the PDB database, 139 of them at a res ...
... Dataset generation Protein-RNA complex structures were obtained from the PDB database (Berman et al., 2000). Complexes solved by X-ray crystallography at a resolution better than 3.0 Å were selected. As of September 2002, there were 188 protein-RNA complexes in the PDB database, 139 of them at a res ...
The biological meaning of pairwise alignments
... • What is the biological question? Examples: • Which proteins of the database are similar to my protein sequence? • Which proteins of the database are similar to the conceptual translation of my DNA sequence? • Which nucleotide sequences in the database are similar to my nucleotide sequence? • Which ...
... • What is the biological question? Examples: • Which proteins of the database are similar to my protein sequence? • Which proteins of the database are similar to the conceptual translation of my DNA sequence? • Which nucleotide sequences in the database are similar to my nucleotide sequence? • Which ...
Classification and substrate head-group specificity of membrane
... at the next step utilize acyl-CoA substrates [20]. Thus, for acyl-PC-specific Δ6 desaturases, the product of the Δ6 desaturation has to be converted into an acyl-CoA molecule by an acyltransferase, which limits the metabolic flux in the recombinant ω3-LCPUFA biosynthesis pathway in plants [20]. Secon ...
... at the next step utilize acyl-CoA substrates [20]. Thus, for acyl-PC-specific Δ6 desaturases, the product of the Δ6 desaturation has to be converted into an acyl-CoA molecule by an acyltransferase, which limits the metabolic flux in the recombinant ω3-LCPUFA biosynthesis pathway in plants [20]. Secon ...
Pseudo-Replication of [GADV]-Proteins and Origin of Life
... Furthermore, there are major weak points in the RNA world hypothesis [5,6]: (i) The numbers of atoms (in parentheses) of four nucleotides, AMP (37), UMP (34), GMP (37) or CMP (35), are much larger than those (in parentheses) of four amino acids, Gly (10), Ala (13), Asp (16) or Val (19). This means t ...
... Furthermore, there are major weak points in the RNA world hypothesis [5,6]: (i) The numbers of atoms (in parentheses) of four nucleotides, AMP (37), UMP (34), GMP (37) or CMP (35), are much larger than those (in parentheses) of four amino acids, Gly (10), Ala (13), Asp (16) or Val (19). This means t ...
Agoraphobia - Orthomolecular.org
... consumption are consistent with a defect in aerobic metabolism and a high anaerobic metabolism. (Cohen and White, p. 847). A characteristic of both disorders is breathlessness or air hunger which is particularly evident in crowded or stuffy atmospheres. Cohen and White noted that sufferers report av ...
... consumption are consistent with a defect in aerobic metabolism and a high anaerobic metabolism. (Cohen and White, p. 847). A characteristic of both disorders is breathlessness or air hunger which is particularly evident in crowded or stuffy atmospheres. Cohen and White noted that sufferers report av ...
Proteogest - User`s Guide - A-Z Directory
... acid(s) to be modified and the modification (weight differential) to be used. Proteogest will modify the specified amino acid(s) according to the weight specified. These modifications can be carried out in two ways, one is ‘complete’ and the other is ‘incomplete’. If you choose ‘complete’, then al ...
... acid(s) to be modified and the modification (weight differential) to be used. Proteogest will modify the specified amino acid(s) according to the weight specified. These modifications can be carried out in two ways, one is ‘complete’ and the other is ‘incomplete’. If you choose ‘complete’, then al ...
Chemistry English
... The atomic theory was presented by the British chemist John Dalton (1766-1844) in the early 1800s. It is one of the greatest advances in the history of chemistry. “Whether matter be atomic or not, this much is certain, that granting it to be atomic, it would appear as it now does.”(by Micheal Farada ...
... The atomic theory was presented by the British chemist John Dalton (1766-1844) in the early 1800s. It is one of the greatest advances in the history of chemistry. “Whether matter be atomic or not, this much is certain, that granting it to be atomic, it would appear as it now does.”(by Micheal Farada ...
A metabolic link to skeletal muscle wasting and regeneration
... Cleavage of F1,6BP generates two molecules of glyceraldehyde3-phosphate (G3P), which are then converted to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP). The final step of glycolysis involves the conversion of PEP to pyruvate to release ATP; a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme pyruvate kinase (PK) (Lunt and Vander Heide ...
... Cleavage of F1,6BP generates two molecules of glyceraldehyde3-phosphate (G3P), which are then converted to phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP). The final step of glycolysis involves the conversion of PEP to pyruvate to release ATP; a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme pyruvate kinase (PK) (Lunt and Vander Heide ...
INSULIN
... • Insulin increases Glycogenesis but when 5-6% of liver mass is Glycogen, then additional Glucose entering the liver is converted to Fat. • FA synthesized by liver cells are used by them for TG synthesis. • Insulin inhibits lipolysis by inhibiting action of hormone-sensitive lipase. Thus, TG present ...
... • Insulin increases Glycogenesis but when 5-6% of liver mass is Glycogen, then additional Glucose entering the liver is converted to Fat. • FA synthesized by liver cells are used by them for TG synthesis. • Insulin inhibits lipolysis by inhibiting action of hormone-sensitive lipase. Thus, TG present ...
Dulbecco`s Modified Eagle Medium/Nutrient Mixture F
... in certain instances. This can be indicated by change in colour, change in appearance and presence of particulate matter and haziness after dissolution. 2. Preparation of concentrated medium is not recommended since free base amino acids and salt complexes having low solubility may precipitate in co ...
... in certain instances. This can be indicated by change in colour, change in appearance and presence of particulate matter and haziness after dissolution. 2. Preparation of concentrated medium is not recommended since free base amino acids and salt complexes having low solubility may precipitate in co ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.














![Pseudo-Replication of [GADV]-Proteins and Origin of Life](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015397345_1-c189eb37b7232bb5a87b48dfe8b0c10b-300x300.png)