13synthesis
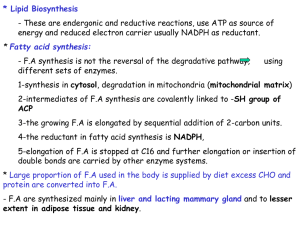
... - These are endergonic and reductive reactions, use ATP as source of energy and reduced electron carrier usually NADPH as reductant. * Fatty acid synthesis: - F.A synthesis is not the reversal of the degradative pathway, different sets of enzymes. ...
... - These are endergonic and reductive reactions, use ATP as source of energy and reduced electron carrier usually NADPH as reductant. * Fatty acid synthesis: - F.A synthesis is not the reversal of the degradative pathway, different sets of enzymes. ...
Complementation Analysis of Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders
... concentration of [3H]palmitate we employed routinely (22 MM) is not fully saturating, .2% ofthe substrate is converted to 3H20 by control cell lines (data available on request). The [3H]palmitate concentration is thus virtually constant throughout the incubation period, and MAD:S activities are cons ...
... concentration of [3H]palmitate we employed routinely (22 MM) is not fully saturating, .2% ofthe substrate is converted to 3H20 by control cell lines (data available on request). The [3H]palmitate concentration is thus virtually constant throughout the incubation period, and MAD:S activities are cons ...
Chapter 1 - Nutrition Gardener
... a. Muscles that repeatedly deplete glycogen through hard work will store greater amounts of glycogen. b. Conditioned muscles rely less on glycogen and more on fat for energy. c. Trained muscle cells have more mitochondria and can use oxygen better. d. Untrained muscle cells depend more heavily on a ...
... a. Muscles that repeatedly deplete glycogen through hard work will store greater amounts of glycogen. b. Conditioned muscles rely less on glycogen and more on fat for energy. c. Trained muscle cells have more mitochondria and can use oxygen better. d. Untrained muscle cells depend more heavily on a ...
Or see a presentation?
... What is Semantic Technology? The implication is Semantics: that enabling computers to thestudy meanings relationships 1.“understand” (Linguistics) The or scienceofof and meaning in language. ...
... What is Semantic Technology? The implication is Semantics: that enabling computers to thestudy meanings relationships 1.“understand” (Linguistics) The or scienceofof and meaning in language. ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Net Ionic Equation • To form the net ionic equation, cross out anything that does not change from the left side of the equation to the right. Ag+(aq) + NO3-(aq) + K+(aq) + Cl-(aq) AgCl (s) + K+(aq) + NO3-(aq) • The only things left in the equation are those things that change (i.e., react) durin ...
... Net Ionic Equation • To form the net ionic equation, cross out anything that does not change from the left side of the equation to the right. Ag+(aq) + NO3-(aq) + K+(aq) + Cl-(aq) AgCl (s) + K+(aq) + NO3-(aq) • The only things left in the equation are those things that change (i.e., react) durin ...
aq - Byron High School
... (g) – non-metal oxides & diatomics (l) – water, Mercury, some hydrocarbons (s) – Metal elements, insoluble substances (see rules) (aq) – soluble substances (see rules) Aqueous Reactions ...
... (g) – non-metal oxides & diatomics (l) – water, Mercury, some hydrocarbons (s) – Metal elements, insoluble substances (see rules) (aq) – soluble substances (see rules) Aqueous Reactions ...
Cell-Free Phospholipid Biosynthesis by Gene
... Both synthesized GPAT and LPAAT enzymes are active when coreconstituted in liposomes Having established that the full-length GPAT and LPAAT proteins can be synthesized in the PURE system and be incorporated in the membrane of liposomes we then explored the potential of mass spectrometry (MS) combine ...
... Both synthesized GPAT and LPAAT enzymes are active when coreconstituted in liposomes Having established that the full-length GPAT and LPAAT proteins can be synthesized in the PURE system and be incorporated in the membrane of liposomes we then explored the potential of mass spectrometry (MS) combine ...
Ventosimonas gracilis gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of the
... strain CV58T is likely an obligate aerobe. However, our in vitro tests for its ability to grow by ...
... strain CV58T is likely an obligate aerobe. However, our in vitro tests for its ability to grow by ...
The Age of the Common Ancestor of Eukaryotes and
... average over all possible combinations. It was shown that the asymptotic bias of the estimate cx can be significantly reduced if an appropriate weight function is chosen for combining the estimates of three-sequence sets (Gu 1996). The computer program, which was originally developed for nucleotide ...
... average over all possible combinations. It was shown that the asymptotic bias of the estimate cx can be significantly reduced if an appropriate weight function is chosen for combining the estimates of three-sequence sets (Gu 1996). The computer program, which was originally developed for nucleotide ...
Muscles
... Rigor mortis is a recognizable sign of death (L. mors, mortis, f.) that is caused by a chemical change in the muscles, causing the limbs of the corpse to become stiff (L. rigor, oris, m.) and difficult to move or manipulate. Assuming mild temperatures, rigor usually sets in about 3-4 hours after cli ...
... Rigor mortis is a recognizable sign of death (L. mors, mortis, f.) that is caused by a chemical change in the muscles, causing the limbs of the corpse to become stiff (L. rigor, oris, m.) and difficult to move or manipulate. Assuming mild temperatures, rigor usually sets in about 3-4 hours after cli ...
NITROGEN METABOLISM
... As pointed out in the previous section, nitrogen fixation is confined to selected microbes and plants. But all plants require nitrogen because it has a role to play in the general metabolism. Therefore, plants which do not fix nitrogen, use other combined nitrogen sources such as nitrate and ammonia ...
... As pointed out in the previous section, nitrogen fixation is confined to selected microbes and plants. But all plants require nitrogen because it has a role to play in the general metabolism. Therefore, plants which do not fix nitrogen, use other combined nitrogen sources such as nitrate and ammonia ...
P.abyssi PDF version
... 1764 genes, among which nearly 50% (864) had no attributed function (labelled as ‘hypothetical proteins’). Three hundred and one new functional assignments (among which 110 have ‘general function prediction’ only) could be made with good confidence in this particular set of genes, mostly based on se ...
... 1764 genes, among which nearly 50% (864) had no attributed function (labelled as ‘hypothetical proteins’). Three hundred and one new functional assignments (among which 110 have ‘general function prediction’ only) could be made with good confidence in this particular set of genes, mostly based on se ...
Beijerinckia derxii releases plant growth regulato
... ethylene itself, through different biochemical mechanisms (McKeon et al. 1995), including auto-inhibition. Exogenous ethylene is also effective in stimulating plant development (Taiz and Zeiger 1998). Ethylene and IAA may act together to stimulate the development of the cortical cell layer (Grichko ...
... ethylene itself, through different biochemical mechanisms (McKeon et al. 1995), including auto-inhibition. Exogenous ethylene is also effective in stimulating plant development (Taiz and Zeiger 1998). Ethylene and IAA may act together to stimulate the development of the cortical cell layer (Grichko ...
Lecture 53-
... • Function: Ascorbic acid is a water soluble antioxidant and it promotes the hydroxylation of proline residues of collagen. Ascorbic acid is also required in the synthesis of carnitine, dopamine and bile acids. • Effect of Deficiency: Scurvy (hemorrhage, impaired wound healing and bone formation). - ...
... • Function: Ascorbic acid is a water soluble antioxidant and it promotes the hydroxylation of proline residues of collagen. Ascorbic acid is also required in the synthesis of carnitine, dopamine and bile acids. • Effect of Deficiency: Scurvy (hemorrhage, impaired wound healing and bone formation). - ...
N-Terminal Intramolecularly Conserved Histidines of Three Domains
... N-terminal sequence of 111 amino acids, which is homologous to the N-terminal region of the substrate-binding protein, LBP. This is followed by three contiguous domains, designated D1, D2, and D3, which are homologous to one another. At the nucleotide level these are 75-80% identical in sequence ove ...
... N-terminal sequence of 111 amino acids, which is homologous to the N-terminal region of the substrate-binding protein, LBP. This is followed by three contiguous domains, designated D1, D2, and D3, which are homologous to one another. At the nucleotide level these are 75-80% identical in sequence ove ...
Document
... cannot be properly excreted , the amount of -------------- will rise a- Direct bilirubin b- Indirect bilirubin c- Total bilirubin d- Non of above 26- Bilirubin diglucouronide is hydrolyzed and reduced by bacteria in the gut to yield………………… a- Bilirubin b- Albumin c- Urobilinogens d- Vitamin B2 27- T ...
... cannot be properly excreted , the amount of -------------- will rise a- Direct bilirubin b- Indirect bilirubin c- Total bilirubin d- Non of above 26- Bilirubin diglucouronide is hydrolyzed and reduced by bacteria in the gut to yield………………… a- Bilirubin b- Albumin c- Urobilinogens d- Vitamin B2 27- T ...
The size, operation, and technical capabilities of protein and nucleic
... FOWLER, A. V.; KUTNY, R.; SMITH, A. J. The size, operation, and technical capabilities of protein and nucleic acid core facilities. ...
... FOWLER, A. V.; KUTNY, R.; SMITH, A. J. The size, operation, and technical capabilities of protein and nucleic acid core facilities. ...
Pluripotent stem cell metabolism and mitochondria: beyond ATP
... consumed to lactate. Unlike oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), which generates 36 ATP from the oxidation of glucose, glycolysis generates only 4 molecules of ATP. However, ATP can be generated more quickly through glycolysis [79], and provided there is a sufficient flux of glucose, equivalent level ...
... consumed to lactate. Unlike oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), which generates 36 ATP from the oxidation of glucose, glycolysis generates only 4 molecules of ATP. However, ATP can be generated more quickly through glycolysis [79], and provided there is a sufficient flux of glucose, equivalent level ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... • A strong electrolyte dissociates completely when dissolved in water & forms lots of ions. • A weak electrolyte only dissociates partially when dissolved in water & only forms a few ions. Aqueous Reactions © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... • A strong electrolyte dissociates completely when dissolved in water & forms lots of ions. • A weak electrolyte only dissociates partially when dissolved in water & only forms a few ions. Aqueous Reactions © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
Diversity and origins of anaerobic metabolism in mitochondria and
... Mitochondria and related organelles are ubiquitous among eukaryotes. The last half-century of cellular and molecular evolutionary research has conclusively shown that mitochondria are descended from an a-proteobacterial endosymbiont that took up residence within a host cell prior to the last eukaryo ...
... Mitochondria and related organelles are ubiquitous among eukaryotes. The last half-century of cellular and molecular evolutionary research has conclusively shown that mitochondria are descended from an a-proteobacterial endosymbiont that took up residence within a host cell prior to the last eukaryo ...
PDF
... However, the methodology to test many of these concepts experimentally has only become available rather recently (2, 16, 17). A considerable body of experimental and theoretical work suggests that the dimensions of unfolded proteins depend on parameters such as amino acid composition (4), temperatur ...
... However, the methodology to test many of these concepts experimentally has only become available rather recently (2, 16, 17). A considerable body of experimental and theoretical work suggests that the dimensions of unfolded proteins depend on parameters such as amino acid composition (4), temperatur ...
Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... bonds between their amino acids. Similarly, the special functions of polysaccharides, nucleic acids, and lipids can be understood as a direct manifestation of their chemical structure, with their characteristic monomeric subunits linked in precise functional polymers. Sugars linked together become e ...
... bonds between their amino acids. Similarly, the special functions of polysaccharides, nucleic acids, and lipids can be understood as a direct manifestation of their chemical structure, with their characteristic monomeric subunits linked in precise functional polymers. Sugars linked together become e ...
Polymer scaling laws of unfolded and intrinsically disordered
... However, the methodology to test many of these concepts experimentally has only become available rather recently (2, 16, 17). A considerable body of experimental and theoretical work suggests that the dimensions of unfolded proteins depend on parameters such as amino acid composition (4), temperatur ...
... However, the methodology to test many of these concepts experimentally has only become available rather recently (2, 16, 17). A considerable body of experimental and theoretical work suggests that the dimensions of unfolded proteins depend on parameters such as amino acid composition (4), temperatur ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.