boltzmann`s entropy and time`s arrow
... Boltzmann's analysis implies the existence of a relation between phase space volume and probability. In particular, his explanation of the second law depends upon identifying a small fraction of the phase space volume with small probability. This is in the spirit of (but does not require) the assump ...
... Boltzmann's analysis implies the existence of a relation between phase space volume and probability. In particular, his explanation of the second law depends upon identifying a small fraction of the phase space volume with small probability. This is in the spirit of (but does not require) the assump ...
The enthalpy change
... 2 In the Contact Process, sulfur dioxide is converted into sulfur trioxide and the following equilibrium is set up: If sulfur dioxide is added to the mixture, what happens to the position of the equilibrium? o The equilibrium shifts to the right o The position of the equilibrium remains unchanged o ...
... 2 In the Contact Process, sulfur dioxide is converted into sulfur trioxide and the following equilibrium is set up: If sulfur dioxide is added to the mixture, what happens to the position of the equilibrium? o The equilibrium shifts to the right o The position of the equilibrium remains unchanged o ...
chemical equilibrium
... Simply states “If the concentrations of all the substances present at equilibrium are raised to the power of the number of moles they appear in the equation, the product of the concentrations of the products divided by the product of the concentrations of the reactants is a constant, provided the te ...
... Simply states “If the concentrations of all the substances present at equilibrium are raised to the power of the number of moles they appear in the equation, the product of the concentrations of the products divided by the product of the concentrations of the reactants is a constant, provided the te ...
chemical equilibrium
... When a chemical equilibrium is established ... • both the reactants and the products are present at all times • the equilibrium can be approached from either side • the reaction is dynamic - it is moving forwards and backwards • concentrations of reactants and products remain constant ...
... When a chemical equilibrium is established ... • both the reactants and the products are present at all times • the equilibrium can be approached from either side • the reaction is dynamic - it is moving forwards and backwards • concentrations of reactants and products remain constant ...
Hein and Arena
... Step 4 Add electrons (e-) to each halfreaction to bring them into electrical balance. Step 5 Since the loss and gain of electrons must be equal, multiply each halfreaction by the appropriate number to make the number of electrons the same in each half-reaction. ...
... Step 4 Add electrons (e-) to each halfreaction to bring them into electrical balance. Step 5 Since the loss and gain of electrons must be equal, multiply each halfreaction by the appropriate number to make the number of electrons the same in each half-reaction. ...
What is equilibrium?
... soluble ionic compound and its ions in solution. • If the ion product, Qsp, exceeds the Ksp when two solutions are mixed, a precipitate will form. • The presence of a common ion in a solution lowers the solubility of a dissolved substance. ...
... soluble ionic compound and its ions in solution. • If the ion product, Qsp, exceeds the Ksp when two solutions are mixed, a precipitate will form. • The presence of a common ion in a solution lowers the solubility of a dissolved substance. ...
MS PowerPoint - Catalysis Eprints database
... Langmuir model (iterative and semi empirical) Highly empirical (statistical analysis driven) ...
... Langmuir model (iterative and semi empirical) Highly empirical (statistical analysis driven) ...
1 HOOKE`S LAW AND SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Objectives
... balance using the knurled wheel until the lowest edge of the spring is at the pointer tip. Read and record the scale of the Jolly balance to one-tenth of a millimeter, using the Vernier. 4. Repeat Step 3 for 0.15, 0.20, 0.25, 0.30, 0.35, 0.40 kg loads of the spring. 5. Turn off the pointer from the ...
... balance using the knurled wheel until the lowest edge of the spring is at the pointer tip. Read and record the scale of the Jolly balance to one-tenth of a millimeter, using the Vernier. 4. Repeat Step 3 for 0.15, 0.20, 0.25, 0.30, 0.35, 0.40 kg loads of the spring. 5. Turn off the pointer from the ...
Chemical reactions
... a direction in the process is implicit, i.e. initial reactants (left) converting into products (right), whereas the last form is more simple for equilibrium studies where no direction is privileged. Notice that microscopically the reaction is always on both directions, to the right and to the left i ...
... a direction in the process is implicit, i.e. initial reactants (left) converting into products (right), whereas the last form is more simple for equilibrium studies where no direction is privileged. Notice that microscopically the reaction is always on both directions, to the right and to the left i ...
Name - Chemistry 302
... 2. Break reaction into to half-reactions: oxidation half-reaction and reduction half-reaction 3. Balance all species EXCEPT HYDROGEN AND OXYGEN. 4. Balance OXYGEN by adding water to the necessary sides of the half-reactions. 5. Balance HYDROGEN by adding protons (H+) to the necessary sides 5a. If in ...
... 2. Break reaction into to half-reactions: oxidation half-reaction and reduction half-reaction 3. Balance all species EXCEPT HYDROGEN AND OXYGEN. 4. Balance OXYGEN by adding water to the necessary sides of the half-reactions. 5. Balance HYDROGEN by adding protons (H+) to the necessary sides 5a. If in ...
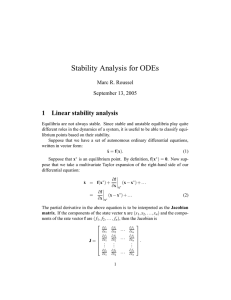
Lecture 2: Stability analysis for ODEs
... where J∗ is the Jacobian evaluated at the equilibrium point. The matrix J∗ is a constant, so this is just a linear differential equation. According to the theory of linear differential equations, the solution can be written as a superposition of terms of the form eλ j t where {λ j } is the set of ei ...
... where J∗ is the Jacobian evaluated at the equilibrium point. The matrix J∗ is a constant, so this is just a linear differential equation. According to the theory of linear differential equations, the solution can be written as a superposition of terms of the form eλ j t where {λ j } is the set of ei ...
small - UNSW
... (x,u) and up-down (z,w) components. In the vertical direction the acceleration is related to the difference between the water weight and the bouyancy (or pressure) force. When there is a vertical density gradient this leads to oscillations (Brunt Väisälä frequency N). The density gradient tries to i ...
... (x,u) and up-down (z,w) components. In the vertical direction the acceleration is related to the difference between the water weight and the bouyancy (or pressure) force. When there is a vertical density gradient this leads to oscillations (Brunt Väisälä frequency N). The density gradient tries to i ...