Implementable Set Theory and Consistency of ZFC
... Another philosophical note is in place, when we are saying that we ”make with an axiom” and denote this as an implication A =⇒ B. In common mathematics, the implication =⇒ just means what is defined by a truth table in propositional logic. But there is another form of mathematics, called constructiv ...
... Another philosophical note is in place, when we are saying that we ”make with an axiom” and denote this as an implication A =⇒ B. In common mathematics, the implication =⇒ just means what is defined by a truth table in propositional logic. But there is another form of mathematics, called constructiv ...
Lesson 12
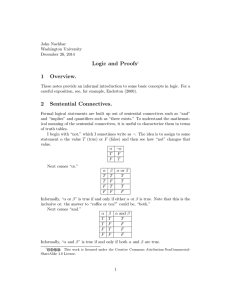
... 1. A, B are not formulas, but meta-symbols denoting any formula. Each axiom schema denotes an infinite class of formulas of a given form. If axioms were specified by concrete formulas, like 1. p (q p) 2. (p (q r)) ((p q) (p r)) 3. (q p) (p q) we would have to extend the set o ...
... 1. A, B are not formulas, but meta-symbols denoting any formula. Each axiom schema denotes an infinite class of formulas of a given form. If axioms were specified by concrete formulas, like 1. p (q p) 2. (p (q r)) ((p q) (p r)) 3. (q p) (p q) we would have to extend the set o ...
Introduction to Theoretical Computer Science, lesson 3
... First, determine the elements of the universe denoted by terms, then determine the truth-values of atomic formulas, and finally, determine the truth-value of the (composed) formula Evaluation of terms: Let v be a valuation that associates each variable x with an element of the universe: v(x) U. By ...
... First, determine the elements of the universe denoted by terms, then determine the truth-values of atomic formulas, and finally, determine the truth-value of the (composed) formula Evaluation of terms: Let v be a valuation that associates each variable x with an element of the universe: v(x) U. By ...
Programming and Problem Solving with Java: Chapter 14
... If a statement A is contingent then we say that A is possibly true, which is written: ◊A If A is non-contingent, then it is necessarily true, which is written: A ...
... If a statement A is contingent then we say that A is possibly true, which is written: ◊A If A is non-contingent, then it is necessarily true, which is written: A ...
The Discovery of the Computer
... expressed in a logical system is true or false, without producing all the possible theorems of the system. This so-called “decision problem” was answered by Alan Turing, who showed that it is not possible to decide if any theorem is true or false. In doing this, he discovered the computer. The story ...
... expressed in a logical system is true or false, without producing all the possible theorems of the system. This so-called “decision problem” was answered by Alan Turing, who showed that it is not possible to decide if any theorem is true or false. In doing this, he discovered the computer. The story ...
Methods of Proof - Department of Mathematics
... • N, Z, Q and R are all closed under multiplication. • Z, Q and R are closed under subtraction. N is not closed under subtraction. • Q and R are closed under division. N and Z are not closed under division. There are two basic theorems which will be stated without proof. You may assume these theorem ...
... • N, Z, Q and R are all closed under multiplication. • Z, Q and R are closed under subtraction. N is not closed under subtraction. • Q and R are closed under division. N and Z are not closed under division. There are two basic theorems which will be stated without proof. You may assume these theorem ...
Real Analysis Lecture 2
... forego detailed discussion of everything else. For Q we will again suppress most of the steps, but shall go into more details about 1 and 4. The axioms are: A1. Associativity of addition: a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c. M1. Associativity of multiplicatin: a(bc) = (ab)c. A2. Commutativity of addition: a + ...
... forego detailed discussion of everything else. For Q we will again suppress most of the steps, but shall go into more details about 1 and 4. The axioms are: A1. Associativity of addition: a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c. M1. Associativity of multiplicatin: a(bc) = (ab)c. A2. Commutativity of addition: a + ...
Distance, Ruler Postulate and Plane Separation Postulate
... The Ruler Postulate implicitly defines two functions 1. The metric function that measures the distance 2. A coordinate function that tells us how to place the ruler ● When we place a ruler to measure a distance we can use any section of the ruler to measure ● The easiest way to place the ruler is to ...
... The Ruler Postulate implicitly defines two functions 1. The metric function that measures the distance 2. A coordinate function that tells us how to place the ruler ● When we place a ruler to measure a distance we can use any section of the ruler to measure ● The easiest way to place the ruler is to ...