Quantum phase transition - Condensed Matter Theory and Quantum
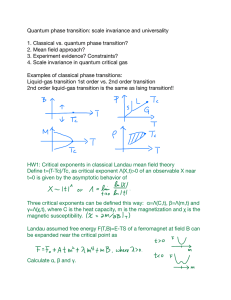
... Three critical exponents can be defined this way: α=Λ(C,t), β=Λ(m,t) and γ=Λ(χ,t), where C is the heat capacity, m is the magnetization and χ is the magnetic susceptibility. ...
... Three critical exponents can be defined this way: α=Λ(C,t), β=Λ(m,t) and γ=Λ(χ,t), where C is the heat capacity, m is the magnetization and χ is the magnetic susceptibility. ...
AGAINST THE COPENHAGEN ORTHODOXY The
... microscopic objects go from a state to a neighboring one without making sense what is in between. The second characteristic is that it describes a world of potentialities, that is, of possible events, that remain mere probabilities until the system is forced to make a decision, choosing one of them. ...
... microscopic objects go from a state to a neighboring one without making sense what is in between. The second characteristic is that it describes a world of potentialities, that is, of possible events, that remain mere probabilities until the system is forced to make a decision, choosing one of them. ...
Optics, Light and Lasers: The Practical Approach to RIAO/OPTILAS
... necessary, since he explains a field that is growing fast and in which some conceptual questions are still being discussed. What makes this remarkable as a textbook is that it treats topics as diverse as the quantum Hall effect and Shubnikov-de Haas oscillations, size quantification, phase coherence ...
... necessary, since he explains a field that is growing fast and in which some conceptual questions are still being discussed. What makes this remarkable as a textbook is that it treats topics as diverse as the quantum Hall effect and Shubnikov-de Haas oscillations, size quantification, phase coherence ...
The Current Model of the Atom Name This Element Building on Bohr
... wave properties of subatomic particles • It’s impossible to know the exact position, speed and direction of an electron (Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle) • So Bohr’s “orbits” were replaced by orbitals ...
... wave properties of subatomic particles • It’s impossible to know the exact position, speed and direction of an electron (Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle) • So Bohr’s “orbits” were replaced by orbitals ...
Quantum Mechanics Lecture Course for 4 Semester Students by W.B. von Schlippe
... (i) Newton’s 1st law of mechanics, the relativity principle, remains in force; (ii) Newton’s 3rd law of mechanics, “action equals reaction”, also remains in force. The first one of these was later extended to electromagnetism: it is one of the postulates of Einstein’s (special) theory of relativity. ...
... (i) Newton’s 1st law of mechanics, the relativity principle, remains in force; (ii) Newton’s 3rd law of mechanics, “action equals reaction”, also remains in force. The first one of these was later extended to electromagnetism: it is one of the postulates of Einstein’s (special) theory of relativity. ...
Document
... all occupied by one electron before any orbital is occupied by a second electron and all singly occupied orbitals have the same spin Fill in one at a time “Bus rule” ...
... all occupied by one electron before any orbital is occupied by a second electron and all singly occupied orbitals have the same spin Fill in one at a time “Bus rule” ...
Quantum spin
... applied to numerous other quantum integrable systems. It is the combinatorics and the algebraic aspects behind Bethe's ansatz which are of mathematical importance. Another milestone in the history of integrable systems is Onsager's 1944 solution of the planar Ising model. Quite a few modern mathemat ...
... applied to numerous other quantum integrable systems. It is the combinatorics and the algebraic aspects behind Bethe's ansatz which are of mathematical importance. Another milestone in the history of integrable systems is Onsager's 1944 solution of the planar Ising model. Quite a few modern mathemat ...