Analysis of Simple Charged Particle Systems that Exhibit Chaos
... future. This has long been known to be a feature of weather systems. Forecasters have difficulty making accurate weather predictions more than a week in advance because of the large number of small effects that are difficult to take into account. There are countless other experiences in daily life t ...
... future. This has long been known to be a feature of weather systems. Forecasters have difficulty making accurate weather predictions more than a week in advance because of the large number of small effects that are difficult to take into account. There are countless other experiences in daily life t ...
A mean-field approach to attractive few
... solid state systems, cold atomic gases and so forth. Setting up the mathematical description for these problems can be quite straightforward, but actually solving them is difficult and a source of many open research questions. Broadly speaking, we could say that there are two edge cases that are mos ...
... solid state systems, cold atomic gases and so forth. Setting up the mathematical description for these problems can be quite straightforward, but actually solving them is difficult and a source of many open research questions. Broadly speaking, we could say that there are two edge cases that are mos ...
Quantum Decoherence and the - Philsci
... thermodynamical evolutions are not impossible; there are infinitely many of them. (The existence of anti-thermodynamical trajectories in phase space was the basis for Loschmidt’s reversibility objection to Boltzmann’s first H theorem; see Ehrenfest and Ehrenfest 1912.) One question we shall address ...
... thermodynamical evolutions are not impossible; there are infinitely many of them. (The existence of anti-thermodynamical trajectories in phase space was the basis for Loschmidt’s reversibility objection to Boltzmann’s first H theorem; see Ehrenfest and Ehrenfest 1912.) One question we shall address ...
Momentum - USU Physics
... are conserved on impact. • As the masses of both balls are the same the only solution to conserve both KE and momentum is for all the energy and momentum to be transferred to the other (red) ball. • It’s a fact…try it for yourself!!! ...
... are conserved on impact. • As the masses of both balls are the same the only solution to conserve both KE and momentum is for all the energy and momentum to be transferred to the other (red) ball. • It’s a fact…try it for yourself!!! ...
AP Physics 2: Algebra- Based Practice Exam Sample Responses from the Sample Questions
... that energy flows from the system of higher temperature to systems of lower temperature. The response exhibited an understanding that higher temperature corresponds to higher kinetic energy and that the energy will continue until thermal equilibrium is reached. The fifth point listed in the scoring ...
... that energy flows from the system of higher temperature to systems of lower temperature. The response exhibited an understanding that higher temperature corresponds to higher kinetic energy and that the energy will continue until thermal equilibrium is reached. The fifth point listed in the scoring ...
Spin-valley lifetimes in a silicon quantum dot with tunable valley
... nowadays billions of nanometre-scale transistors per chip. Remarkably, silicon is also an ideal material to manipulate quantum information encoded in individual electron spins1–3. This is a consequence of the weak spin–orbit coupling and the existence of an abundant spin-zero isotope, which can be f ...
... nowadays billions of nanometre-scale transistors per chip. Remarkably, silicon is also an ideal material to manipulate quantum information encoded in individual electron spins1–3. This is a consequence of the weak spin–orbit coupling and the existence of an abundant spin-zero isotope, which can be f ...
Quantum electrical transport in samples of limited
... The ability to make electrically conducting structures of ever smaller size by nanofabrication techniques ~the playground of mesoscopic physics! has brought with it entry into a wonderful new range of unexpected quantum phenomena. Interpretation of these phenomena requires full recognition of the wa ...
... The ability to make electrically conducting structures of ever smaller size by nanofabrication techniques ~the playground of mesoscopic physics! has brought with it entry into a wonderful new range of unexpected quantum phenomena. Interpretation of these phenomena requires full recognition of the wa ...
Consciousness as a State of Matter
... made, are there Everettian parallel universes, or does it make no sense to talk about an an observer-independent reality, as argued by QBism advocates [3]? Is our persistent failure to unify general relativity with quantum mechanics linked to the different roles of observers in the two theories? Aft ...
... made, are there Everettian parallel universes, or does it make no sense to talk about an an observer-independent reality, as argued by QBism advocates [3]? Is our persistent failure to unify general relativity with quantum mechanics linked to the different roles of observers in the two theories? Aft ...
1_CrivellinFPCP2017
... Avoid vector-like quarks by assigning charges to baryons as well Same mechanism in the quark and lepton sector Lμ-Lτ in lepton sector Good symmetry for the PMNS matrix ...
... Avoid vector-like quarks by assigning charges to baryons as well Same mechanism in the quark and lepton sector Lμ-Lτ in lepton sector Good symmetry for the PMNS matrix ...
2 Quantum Theory of Spin Waves
... So far so good, but what about spin? None of these calculations has explicitly taken spin into account, so how can the spin affect the energy? We have seen that the energy difference between the symmetric and antisymmetric states can be thought of as arising from the overlap of electronic wave functio ...
... So far so good, but what about spin? None of these calculations has explicitly taken spin into account, so how can the spin affect the energy? We have seen that the energy difference between the symmetric and antisymmetric states can be thought of as arising from the overlap of electronic wave functio ...
Document
... forward to explain a set of observations. It may be expressed in terms of a mathematical model. The model makes a number of predictions that can be tested in experiments. After many tests have been made, if the model can be refined to correctly describe the outcome of all experiments, it begins to h ...
... forward to explain a set of observations. It may be expressed in terms of a mathematical model. The model makes a number of predictions that can be tested in experiments. After many tests have been made, if the model can be refined to correctly describe the outcome of all experiments, it begins to h ...
Introduction to Quantum Computation
... environment at temperature T , given by ∆Q ≥ kT ln 2 This is exactly like the heat given off when one molecule of an ideal gas is isothermally compressed to half the original volume. Thus classical computation using irreversible gates inevitably generates heat. For present day computers this heat is ...
... environment at temperature T , given by ∆Q ≥ kT ln 2 This is exactly like the heat given off when one molecule of an ideal gas is isothermally compressed to half the original volume. Thus classical computation using irreversible gates inevitably generates heat. For present day computers this heat is ...
here.
... • Classically, suppose we are in a stationary state of angular momentum, i.e., one where ~L points in a fixed direction with fixed magnitude over time. For example, we can be in a classical state where Lz = 105 ~, Ly = 0, L x = 0. We can visualize this in terms of a rigid body that is rotating with ...
... • Classically, suppose we are in a stationary state of angular momentum, i.e., one where ~L points in a fixed direction with fixed magnitude over time. For example, we can be in a classical state where Lz = 105 ~, Ly = 0, L x = 0. We can visualize this in terms of a rigid body that is rotating with ...
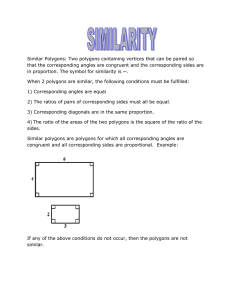
Similar Polygons: Two polygons containing vertices that can
... that the corresponding angles are congruent and the corresponding sides are in proportion. The symbol for similarity is ~. When 2 polygons are similar, the following conditions must be fulfilled: 1) Corresponding angles are equal 2) The ratios of pairs of corresponding sides must all be equal. 3) Co ...
... that the corresponding angles are congruent and the corresponding sides are in proportion. The symbol for similarity is ~. When 2 polygons are similar, the following conditions must be fulfilled: 1) Corresponding angles are equal 2) The ratios of pairs of corresponding sides must all be equal. 3) Co ...
Renormalization group

In theoretical physics, the renormalization group (RG) refers to a mathematical apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different distance scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in the underlying force laws (codified in a quantum field theory) as the energy scale at which physical processes occur varies, energy/momentum and resolution distance scales being effectively conjugate under the uncertainty principle (cf. Compton wavelength).A change in scale is called a ""scale transformation"". The renormalization group is intimately related to ""scale invariance"" and ""conformal invariance"", symmetries in which a system appears the same at all scales (so-called self-similarity). (However, note that scale transformations are included in conformal transformations, in general: the latter including additional symmetry generators associated with special conformal transformations.)As the scale varies, it is as if one is changing the magnifying power of a notional microscope viewing the system. In so-called renormalizable theories, the system at one scale will generally be seen to consist of self-similar copies of itself when viewed at a smaller scale, with different parameters describing the components of the system. The components, or fundamental variables, may relate to atoms, elementary particles, atomic spins, etc. The parameters of the theory typically describe the interactions of the components. These may be variable ""couplings"" which measure the strength of various forces, or mass parameters themselves. The components themselves may appear to be composed of more of the self-same components as one goes to shorter distances.For example, in quantum electrodynamics (QED), an electron appears to be composed of electrons, positrons (anti-electrons) and photons, as one views it at higher resolution, at very short distances. The electron at such short distances has a slightly different electric charge than does the ""dressed electron"" seen at large distances, and this change, or ""running,"" in the value of the electric charge is determined by the renormalization group equation.