AlumniDay_IOP_2 - Princeton University
... short distance .. but perhaps with non-canonical dimension values. Elaborate analysis needed to connect all this with the deep inelastic story ...
... short distance .. but perhaps with non-canonical dimension values. Elaborate analysis needed to connect all this with the deep inelastic story ...
Gregory Moore - Rutgers Physics
... Later, Moore & Witten explained in greater detail how these new invariants are related to the invariants of Donaldson. And Marino, Moore, and Peradze used the existence of N=2 superconformal fixed points to predict new results in the topology of four-manifolds. ...
... Later, Moore & Witten explained in greater detail how these new invariants are related to the invariants of Donaldson. And Marino, Moore, and Peradze used the existence of N=2 superconformal fixed points to predict new results in the topology of four-manifolds. ...
part 3
... from below Large magnetic fields can cause O(1) change in hard particle trajectories on short time scales - ...
... from below Large magnetic fields can cause O(1) change in hard particle trajectories on short time scales - ...
4.1-4.3 - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... – or, in other words, we use waves to make predictions as to what we will find when we make our measurement. ...
... – or, in other words, we use waves to make predictions as to what we will find when we make our measurement. ...
235_lecture6_080219
... need to spend a little bit of time thinking about: the kinds of values variables can take on what those values mean how we can combine them ...
... need to spend a little bit of time thinking about: the kinds of values variables can take on what those values mean how we can combine them ...
Key Concepts for Exam #2
... If the frequency of incident light is above the threshold frequency, then as the intensity of light increases, the kinetic energy of ejected electrons remains constant and the number of electrons increases. In addition, as the frequency of light increases, the kinetic energy of ejected electrons inc ...
... If the frequency of incident light is above the threshold frequency, then as the intensity of light increases, the kinetic energy of ejected electrons remains constant and the number of electrons increases. In addition, as the frequency of light increases, the kinetic energy of ejected electrons inc ...
32 The Atom and the Quantum Answers and Solutions for Chapter
... 1. Most particles remain undeflected because of the empty space within atoms. 2. Rutherford discovered the atomic nucleus, that it was tiny, positive, and massive. 3. Franklin postulated that electricity is an electric fluid that flows from place to place. 4. A cathode ray is a beam of electrons. 5. ...
... 1. Most particles remain undeflected because of the empty space within atoms. 2. Rutherford discovered the atomic nucleus, that it was tiny, positive, and massive. 3. Franklin postulated that electricity is an electric fluid that flows from place to place. 4. A cathode ray is a beam of electrons. 5. ...
Physics 880.06: Problem Set 5
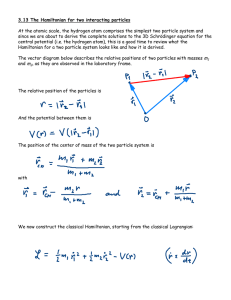
... Physics 880.06: Problem Set 5 Due Tuesday, May 17 by 11:59 P. M. 1. Consider the Ginzburg-Landau differential equation for ψ as applied to an order parameter ψ which varies in only one spatial direction, say z. If there is no vector potential, this differential equation can be written h̄2 ′′ ψ (z) = ...
... Physics 880.06: Problem Set 5 Due Tuesday, May 17 by 11:59 P. M. 1. Consider the Ginzburg-Landau differential equation for ψ as applied to an order parameter ψ which varies in only one spatial direction, say z. If there is no vector potential, this differential equation can be written h̄2 ′′ ψ (z) = ...
UNIT - STUDY GUIDES - SPH 409 QUANTUM MECHANICS II
... 9. Understand the meaning of second quantization for identical particles. SPH 103: Course outline 1. Recall of Basic Ideas of Quantum Theory: Matter waves, de Broglie relations, Heisenberg uncertainty principle, the Schrodinger equation; 2. Approximation Methods: Time – Independent Perturbation Theo ...
... 9. Understand the meaning of second quantization for identical particles. SPH 103: Course outline 1. Recall of Basic Ideas of Quantum Theory: Matter waves, de Broglie relations, Heisenberg uncertainty principle, the Schrodinger equation; 2. Approximation Methods: Time – Independent Perturbation Theo ...
Document
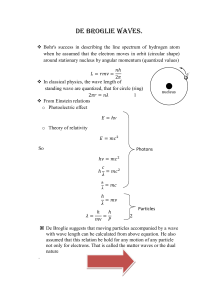
... Electromagnetic waves: Probability per unit volume of finding a photon in a given region of space at an instant of time is proportional to the number N of photons per unit volume V at that time which its proportional to the intensity of the radiation I or the Square of the electric field amplitude E ...
... Electromagnetic waves: Probability per unit volume of finding a photon in a given region of space at an instant of time is proportional to the number N of photons per unit volume V at that time which its proportional to the intensity of the radiation I or the Square of the electric field amplitude E ...
Renormalization group

In theoretical physics, the renormalization group (RG) refers to a mathematical apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different distance scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in the underlying force laws (codified in a quantum field theory) as the energy scale at which physical processes occur varies, energy/momentum and resolution distance scales being effectively conjugate under the uncertainty principle (cf. Compton wavelength).A change in scale is called a ""scale transformation"". The renormalization group is intimately related to ""scale invariance"" and ""conformal invariance"", symmetries in which a system appears the same at all scales (so-called self-similarity). (However, note that scale transformations are included in conformal transformations, in general: the latter including additional symmetry generators associated with special conformal transformations.)As the scale varies, it is as if one is changing the magnifying power of a notional microscope viewing the system. In so-called renormalizable theories, the system at one scale will generally be seen to consist of self-similar copies of itself when viewed at a smaller scale, with different parameters describing the components of the system. The components, or fundamental variables, may relate to atoms, elementary particles, atomic spins, etc. The parameters of the theory typically describe the interactions of the components. These may be variable ""couplings"" which measure the strength of various forces, or mass parameters themselves. The components themselves may appear to be composed of more of the self-same components as one goes to shorter distances.For example, in quantum electrodynamics (QED), an electron appears to be composed of electrons, positrons (anti-electrons) and photons, as one views it at higher resolution, at very short distances. The electron at such short distances has a slightly different electric charge than does the ""dressed electron"" seen at large distances, and this change, or ""running,"" in the value of the electric charge is determined by the renormalization group equation.