Atomic Precision Tests and Light Scalar Couplings
... photon couplings. This seems unnatural although such hierarchies are not uncommon in nature. From an effective field theory point of view, one must simply try to confront this possibility with more data. From a theoretical point of view, only an embedding of the scalar field model coupled to the sta ...
... photon couplings. This seems unnatural although such hierarchies are not uncommon in nature. From an effective field theory point of view, one must simply try to confront this possibility with more data. From a theoretical point of view, only an embedding of the scalar field model coupled to the sta ...
photon may be totally absorbed by electron, but not have enough
... Bohr had proposed. In addition, it makes more reasonable the fact that the electrons do not radiate, as one would otherwise expect from an accelerating charge. quantization: de Broglie wavelength: ...
... Bohr had proposed. In addition, it makes more reasonable the fact that the electrons do not radiate, as one would otherwise expect from an accelerating charge. quantization: de Broglie wavelength: ...
bacal - Crossword Labs
... 40. a line that connects any two points on a curve 41. is the velocity of an object in motion at a specific point in time. 42. the lowest point in a graph 43. the trigonometric ratio for an angle made up of the ratio of the opposite side and the hypotenuse 45. is a point on the graph that is undefin ...
... 40. a line that connects any two points on a curve 41. is the velocity of an object in motion at a specific point in time. 42. the lowest point in a graph 43. the trigonometric ratio for an angle made up of the ratio of the opposite side and the hypotenuse 45. is a point on the graph that is undefin ...
Physics 601 Syllabus
... collected on Wednesday of each week. The homework will be graded and returned the next week. Homework counts 50% towards the final grade. A midterm exam at a date suitable for the class will be given. It will also count 50% towards the final grade. There is no final exam. April 27’th is the last day ...
... collected on Wednesday of each week. The homework will be graded and returned the next week. Homework counts 50% towards the final grade. A midterm exam at a date suitable for the class will be given. It will also count 50% towards the final grade. There is no final exam. April 27’th is the last day ...
Variant 1. 1) There are four different ways in which the various
... one another. Each of these is a particular variety of interaction or to use a more old-fashioned but more common term a force. These four forces are the nuclear, the electromagnetic, the weak and the gravitational. Each particle in the Universe is the source of one or more of these forces. Each part ...
... one another. Each of these is a particular variety of interaction or to use a more old-fashioned but more common term a force. These four forces are the nuclear, the electromagnetic, the weak and the gravitational. Each particle in the Universe is the source of one or more of these forces. Each part ...
GAUGE FIELD THEORY Examples
... construct the conserved current associated with the phase symmetry ψ → eiθ ψ, ψ̄ → e−iθ ψ̄, where θ is a constant, and explain its physical significance. Discuss the consequences of taking θ to be a function of the space-time coordinates. ...
... construct the conserved current associated with the phase symmetry ψ → eiθ ψ, ψ̄ → e−iθ ψ̄, where θ is a constant, and explain its physical significance. Discuss the consequences of taking θ to be a function of the space-time coordinates. ...
Slides - Agenda INFN
... process is hiding one of the deepest mysteries of QT: the “measurement problem”. A system evolves, according to the QT, as being in a linear superposition of all the allowed states, but, when a measurement takes place, only one state emerges as the unambiguous “event”. How (even whether) the wave fu ...
... process is hiding one of the deepest mysteries of QT: the “measurement problem”. A system evolves, according to the QT, as being in a linear superposition of all the allowed states, but, when a measurement takes place, only one state emerges as the unambiguous “event”. How (even whether) the wave fu ...
What is Entanglement? Entangled Fields Looking at Entangled
... cannot really be considered as separate objects, but are intrinsically connected or “entangled” with each other. For example, performing a measurement on one, such as measuring the particles spin as in the diagram above, instantaneously affects the result of measuring the other. This phenomena occur ...
... cannot really be considered as separate objects, but are intrinsically connected or “entangled” with each other. For example, performing a measurement on one, such as measuring the particles spin as in the diagram above, instantaneously affects the result of measuring the other. This phenomena occur ...
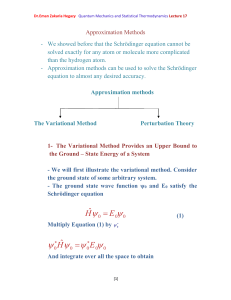
Dr.Eman Zakaria Hegazy Quantum Mechanics and Statistical
... varitional parameters and there by determine the best possible ground-state energy that can be obtained from our trial wave function. As a specific example, consider the ground state of the hydrogen atom. Although we know that we can solve this problem exactly , let’s assume that we cannot and use t ...
... varitional parameters and there by determine the best possible ground-state energy that can be obtained from our trial wave function. As a specific example, consider the ground state of the hydrogen atom. Although we know that we can solve this problem exactly , let’s assume that we cannot and use t ...
Syllabus
... The main objective of this course is to examine the theoretical basis for our present understanding of the structure of matter at the atomic and molecular level. To that end we will review those aspects of quantum mechanics that play the most important role in this understanding. This includes the s ...
... The main objective of this course is to examine the theoretical basis for our present understanding of the structure of matter at the atomic and molecular level. To that end we will review those aspects of quantum mechanics that play the most important role in this understanding. This includes the s ...
PhD dissertation - Pierre
... of nature that relates empirical observations of phenomena to each other in a way which is consistent with a fundamental theory, but without being ...
... of nature that relates empirical observations of phenomena to each other in a way which is consistent with a fundamental theory, but without being ...
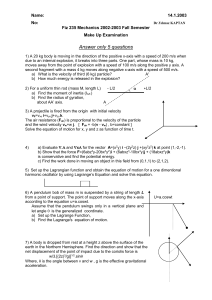
Fiz 235 Mechanics 2002
... due to an internal explosion, it breaks into three parts. One part, whose mass is 10 kg, moves away from the point of explosion with a speed of 100 m/s along the positive y axis. A second fragment with a mass 4 kg moves along negative x-axis with a speed of 500 m/s. a) What is the velocity of third ...
... due to an internal explosion, it breaks into three parts. One part, whose mass is 10 kg, moves away from the point of explosion with a speed of 100 m/s along the positive y axis. A second fragment with a mass 4 kg moves along negative x-axis with a speed of 500 m/s. a) What is the velocity of third ...
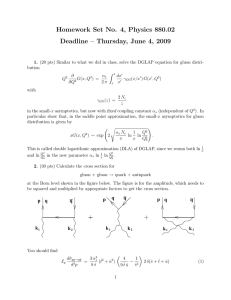
Homework Set No. 4, Physics 880.02
... with the Mandelstam variables ŝ = (k1 + k2 )2 , t̂ = (k1 − p)2 , û = (k2 − p)2 . The factor of 2 in front of the δ-function in Eq. (1) comes from the fact that either the quark or the antiquark can carry momentum p. (q and q̄ in the figure denote the quark and the antiquark. Time flows upward.) A ...
... with the Mandelstam variables ŝ = (k1 + k2 )2 , t̂ = (k1 − p)2 , û = (k2 − p)2 . The factor of 2 in front of the δ-function in Eq. (1) comes from the fact that either the quark or the antiquark can carry momentum p. (q and q̄ in the figure denote the quark and the antiquark. Time flows upward.) A ...
Renormalization group

In theoretical physics, the renormalization group (RG) refers to a mathematical apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different distance scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in the underlying force laws (codified in a quantum field theory) as the energy scale at which physical processes occur varies, energy/momentum and resolution distance scales being effectively conjugate under the uncertainty principle (cf. Compton wavelength).A change in scale is called a ""scale transformation"". The renormalization group is intimately related to ""scale invariance"" and ""conformal invariance"", symmetries in which a system appears the same at all scales (so-called self-similarity). (However, note that scale transformations are included in conformal transformations, in general: the latter including additional symmetry generators associated with special conformal transformations.)As the scale varies, it is as if one is changing the magnifying power of a notional microscope viewing the system. In so-called renormalizable theories, the system at one scale will generally be seen to consist of self-similar copies of itself when viewed at a smaller scale, with different parameters describing the components of the system. The components, or fundamental variables, may relate to atoms, elementary particles, atomic spins, etc. The parameters of the theory typically describe the interactions of the components. These may be variable ""couplings"" which measure the strength of various forces, or mass parameters themselves. The components themselves may appear to be composed of more of the self-same components as one goes to shorter distances.For example, in quantum electrodynamics (QED), an electron appears to be composed of electrons, positrons (anti-electrons) and photons, as one views it at higher resolution, at very short distances. The electron at such short distances has a slightly different electric charge than does the ""dressed electron"" seen at large distances, and this change, or ""running,"" in the value of the electric charge is determined by the renormalization group equation.