GonzalesMestres
... The approach by Anchordoqui et al. explicitly breaks Lorentz symmetry => requires a VRF The need of new physics for Pamir data is not obvious, and LSV can in principle yield other ways to solve problems related to renormalization. Furthermore, does one need, in LSV models, such a drastic dimensiona ...
... The approach by Anchordoqui et al. explicitly breaks Lorentz symmetry => requires a VRF The need of new physics for Pamir data is not obvious, and LSV can in principle yield other ways to solve problems related to renormalization. Furthermore, does one need, in LSV models, such a drastic dimensiona ...
vocab chap 6
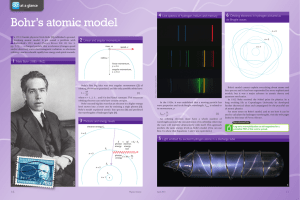
... packed nucleus and that atoms are mostly empty space; also discovered the proton ...
... packed nucleus and that atoms are mostly empty space; also discovered the proton ...
Modern Physics - No Brain Too Small
... Describe and explain Atomic line spectra (infrared, visible and ultraviolet): Rydberg formula for the hydrogen atom and the Lyman, Balmer and Paschen series. Calculate the energy associated with a particular emission or absorption line using E = hf. Define the electron volt. Describe the Bohr model ...
... Describe and explain Atomic line spectra (infrared, visible and ultraviolet): Rydberg formula for the hydrogen atom and the Lyman, Balmer and Paschen series. Calculate the energy associated with a particular emission or absorption line using E = hf. Define the electron volt. Describe the Bohr model ...
poster
... • Interactive lectures on the foundations of quantum mechanics engage students in questions of classical and quantum reality: • Clicker questions stimulate student discussion, where the answers can sometimes be a matter of interpretation. • Make realist expectations explicit and help students deve ...
... • Interactive lectures on the foundations of quantum mechanics engage students in questions of classical and quantum reality: • Clicker questions stimulate student discussion, where the answers can sometimes be a matter of interpretation. • Make realist expectations explicit and help students deve ...
Principles of Computer Architecture Dr. Mike Frank
... • No form of information (including quantum information) can propagate through space at a velocity (relative to its local surroundings) that is greater than the speed of light, c, ~3×108 m/s. • Some consequences: – No closed system can propagate faster than c. ...
... • No form of information (including quantum information) can propagate through space at a velocity (relative to its local surroundings) that is greater than the speed of light, c, ~3×108 m/s. • Some consequences: – No closed system can propagate faster than c. ...
QGP - CERN Indico
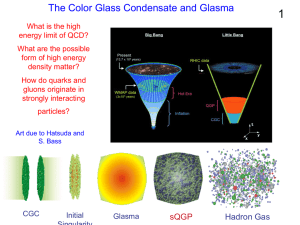
... • Higher temperature → higher energy density → create more new particles (by E = mc2) • When the energy density exceeds 1GeV/fm3, many new particles are made → packed close together • matter will exist not as hadrons (protons, neutrons…), but as independent quarks and gluons. • In this medium, the q ...
... • Higher temperature → higher energy density → create more new particles (by E = mc2) • When the energy density exceeds 1GeV/fm3, many new particles are made → packed close together • matter will exist not as hadrons (protons, neutrons…), but as independent quarks and gluons. • In this medium, the q ...
Symmetry and Its Violation -unifying concept of universe
... anti-quarks and (W, Z0) anti-leptons strong (gluon: g) The Standard Model ...
... anti-quarks and (W, Z0) anti-leptons strong (gluon: g) The Standard Model ...
Introduction - High Energy Physics Group
... (photon) and completely specifies the form of the interaction between the particle and field. Photons (all gauge bosons) are intrinsically massless (though gauge bosons of the Weak Force evade this requirement by “symmetry breaking”) ...
... (photon) and completely specifies the form of the interaction between the particle and field. Photons (all gauge bosons) are intrinsically massless (though gauge bosons of the Weak Force evade this requirement by “symmetry breaking”) ...
1 PHY4605–Introduction to Quantum Mechanics II Spring 2004 Test 1 Solutions
... atom, the first-order shift is zero, so the shift is quadratic in the field. If the line is degenerate, a linear term may result. ...
... atom, the first-order shift is zero, so the shift is quadratic in the field. If the line is degenerate, a linear term may result. ...
Document
... • Compton showed Dp = hkinitial - hkfinal, so an photon (wave) is particle-like • DeBroglie hypothesized a particle could be wave-like, l = h/p • Davisson and Germer demonstrated wave-like interference phenomena for electrons to complete the duality model L1 January 18 ...
... • Compton showed Dp = hkinitial - hkfinal, so an photon (wave) is particle-like • DeBroglie hypothesized a particle could be wave-like, l = h/p • Davisson and Germer demonstrated wave-like interference phenomena for electrons to complete the duality model L1 January 18 ...
Geometry Final Exam Review Sheet
... 4. What is the measure of the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle if one of its base angles measures 58º? 5. ∠1 and ∠2 are supplementary angles. m∠1 = x – 15, and m∠2 = x + 79. Find the measure of each angle. 6. Find the values of x and y. ...
... 4. What is the measure of the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle if one of its base angles measures 58º? 5. ∠1 and ∠2 are supplementary angles. m∠1 = x – 15, and m∠2 = x + 79. Find the measure of each angle. 6. Find the values of x and y. ...
Lecture 26 - Purdue Physics
... • Photons are quanta of electromagnetic radiation • Energy can be measured in electron-volts: ...
... • Photons are quanta of electromagnetic radiation • Energy can be measured in electron-volts: ...
Renormalization group

In theoretical physics, the renormalization group (RG) refers to a mathematical apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different distance scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in the underlying force laws (codified in a quantum field theory) as the energy scale at which physical processes occur varies, energy/momentum and resolution distance scales being effectively conjugate under the uncertainty principle (cf. Compton wavelength).A change in scale is called a ""scale transformation"". The renormalization group is intimately related to ""scale invariance"" and ""conformal invariance"", symmetries in which a system appears the same at all scales (so-called self-similarity). (However, note that scale transformations are included in conformal transformations, in general: the latter including additional symmetry generators associated with special conformal transformations.)As the scale varies, it is as if one is changing the magnifying power of a notional microscope viewing the system. In so-called renormalizable theories, the system at one scale will generally be seen to consist of self-similar copies of itself when viewed at a smaller scale, with different parameters describing the components of the system. The components, or fundamental variables, may relate to atoms, elementary particles, atomic spins, etc. The parameters of the theory typically describe the interactions of the components. These may be variable ""couplings"" which measure the strength of various forces, or mass parameters themselves. The components themselves may appear to be composed of more of the self-same components as one goes to shorter distances.For example, in quantum electrodynamics (QED), an electron appears to be composed of electrons, positrons (anti-electrons) and photons, as one views it at higher resolution, at very short distances. The electron at such short distances has a slightly different electric charge than does the ""dressed electron"" seen at large distances, and this change, or ""running,"" in the value of the electric charge is determined by the renormalization group equation.