Geometry 7
... diagram. What is the distance between the two campsites? The diagram is not to scale. ...
... diagram. What is the distance between the two campsites? The diagram is not to scale. ...
Essentials of Modern Physics
... Candidates should be able to: (a) change the subject of an equation. Most relevant equations involve only the simpler operations but may include positive and negative indices and square roots (b) solve simple algebraic equations. Most relevant equations are linear but some may involve inverse and in ...
... Candidates should be able to: (a) change the subject of an equation. Most relevant equations involve only the simpler operations but may include positive and negative indices and square roots (b) solve simple algebraic equations. Most relevant equations are linear but some may involve inverse and in ...
Collisional Shocks: in situ studies of astrophysical
... How does it change the role of the dispersion and nonlinearity? ...
... How does it change the role of the dispersion and nonlinearity? ...
QuestionSheet
... 4. In electron positron colliders, leptons scatter freely from each other and we do observe free leptons. In high energy proton colliders, quarks also freely scatter from each other but yet we do not observe free quarks. Explain this paradox. 5. Draw Feynman / quark flow diagrams for the following p ...
... 4. In electron positron colliders, leptons scatter freely from each other and we do observe free leptons. In high energy proton colliders, quarks also freely scatter from each other but yet we do not observe free quarks. Explain this paradox. 5. Draw Feynman / quark flow diagrams for the following p ...
Few-body insights into the fractional quantum Hall effect
... 3. Since these states are identifiable by a property of noninteracting electrons, it should be possible to probe these exceptional degeneracy states in other ways, e.g. without a magnetic field, or with neutral, ultracold polarized fermionic (or bosonic atoms) 4. One can use the approximate separabi ...
... 3. Since these states are identifiable by a property of noninteracting electrons, it should be possible to probe these exceptional degeneracy states in other ways, e.g. without a magnetic field, or with neutral, ultracold polarized fermionic (or bosonic atoms) 4. One can use the approximate separabi ...
- Sussex Research Online
... high energy scales has intrigued physicists for many years [1]. There are hints that the renormalization group evolution of the coupling constants of the standard model of particle physics, or possibly of its supersymmetric version, causes them to unify at a large energy scale of order 1016 GeV [2]. ...
... high energy scales has intrigued physicists for many years [1]. There are hints that the renormalization group evolution of the coupling constants of the standard model of particle physics, or possibly of its supersymmetric version, causes them to unify at a large energy scale of order 1016 GeV [2]. ...
Course Syllabus
... Note: I always recommend the Feynman Lectures on Physics, Vol. 3, as a most beautiful, illuminating source of Quantum Mechanics at an “elementary” level. Volume 3 of the Feynman Lectures represents a famous experiment at teaching Quantum Mechanics “correctly” at the sophomore level. In addition, the ...
... Note: I always recommend the Feynman Lectures on Physics, Vol. 3, as a most beautiful, illuminating source of Quantum Mechanics at an “elementary” level. Volume 3 of the Feynman Lectures represents a famous experiment at teaching Quantum Mechanics “correctly” at the sophomore level. In addition, the ...
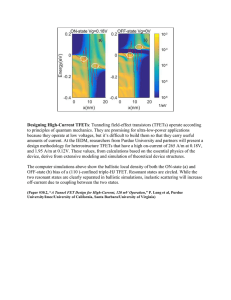
30-2 Designing High-Current TFETs
... Designing High-Current TFETs: Tunneling field-effect transistors (TFETs) operate according to principles of quantum mechanics. They are promising for ultra-low-power applications because they operate at low voltages, but it’s difficult to build them so that they carry useful amounts of current. At t ...
... Designing High-Current TFETs: Tunneling field-effect transistors (TFETs) operate according to principles of quantum mechanics. They are promising for ultra-low-power applications because they operate at low voltages, but it’s difficult to build them so that they carry useful amounts of current. At t ...
Document
... Coupling constants have an energy dependence due to (higher order) virtual interactions. These change the measured value of the coupling constant and make it depend on the energy scale at which it is measured (logarithmic dependence). The strong and weak couplings decrease with energy whilst the EM ...
... Coupling constants have an energy dependence due to (higher order) virtual interactions. These change the measured value of the coupling constant and make it depend on the energy scale at which it is measured (logarithmic dependence). The strong and weak couplings decrease with energy whilst the EM ...
A Brief Review of Thomas-Fermi Theory
... The same is true of molecules in this theory. If the scaling of the R j with Z are as described above then (3.4) still holds. This fact about the Thomas-Fermi density is mirrored in the true quantum ...
... The same is true of molecules in this theory. If the scaling of the R j with Z are as described above then (3.4) still holds. This fact about the Thomas-Fermi density is mirrored in the true quantum ...
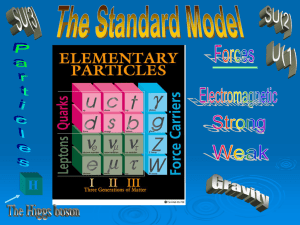
The Higgs Boson and Fermion Masses
... • Still unclear mechanism of EW symmetry breaking • CP-violation is not understood • The origin of the mass spectrum in unclear • Flavour mixing and the number of generations is arbitrary • Formal unification of strong and electroweak interactions The way beyond the SM: • The SAME fields with NEW ...
... • Still unclear mechanism of EW symmetry breaking • CP-violation is not understood • The origin of the mass spectrum in unclear • Flavour mixing and the number of generations is arbitrary • Formal unification of strong and electroweak interactions The way beyond the SM: • The SAME fields with NEW ...
Renormalization group

In theoretical physics, the renormalization group (RG) refers to a mathematical apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different distance scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in the underlying force laws (codified in a quantum field theory) as the energy scale at which physical processes occur varies, energy/momentum and resolution distance scales being effectively conjugate under the uncertainty principle (cf. Compton wavelength).A change in scale is called a ""scale transformation"". The renormalization group is intimately related to ""scale invariance"" and ""conformal invariance"", symmetries in which a system appears the same at all scales (so-called self-similarity). (However, note that scale transformations are included in conformal transformations, in general: the latter including additional symmetry generators associated with special conformal transformations.)As the scale varies, it is as if one is changing the magnifying power of a notional microscope viewing the system. In so-called renormalizable theories, the system at one scale will generally be seen to consist of self-similar copies of itself when viewed at a smaller scale, with different parameters describing the components of the system. The components, or fundamental variables, may relate to atoms, elementary particles, atomic spins, etc. The parameters of the theory typically describe the interactions of the components. These may be variable ""couplings"" which measure the strength of various forces, or mass parameters themselves. The components themselves may appear to be composed of more of the self-same components as one goes to shorter distances.For example, in quantum electrodynamics (QED), an electron appears to be composed of electrons, positrons (anti-electrons) and photons, as one views it at higher resolution, at very short distances. The electron at such short distances has a slightly different electric charge than does the ""dressed electron"" seen at large distances, and this change, or ""running,"" in the value of the electric charge is determined by the renormalization group equation.