Challenging Modern Physics
... This approach is trying to explain macroscopic properties in terms of microscopic components. Its main focus is on the discrete parts in isolation from the whole. Modern physics, for instance, is based on the so-called atomic theory. So far it has been ecumenical for more than one hundred years. How ...
... This approach is trying to explain macroscopic properties in terms of microscopic components. Its main focus is on the discrete parts in isolation from the whole. Modern physics, for instance, is based on the so-called atomic theory. So far it has been ecumenical for more than one hundred years. How ...
Quantum simulators of lattice gauge theories
... A ``working´´ definition of a quantum simulator could be: I. Quantum simulator is an experimental system that mimics ...
... A ``working´´ definition of a quantum simulator could be: I. Quantum simulator is an experimental system that mimics ...
Lecture 9
... Expectation values The reason for the repetition is that quantum mechanics does not make definite predictions for the position, momentum, etc. When we do the exact same measurement on identically prepared systems, we do not get always get the same result, as we do in classical mechanics. But probabi ...
... Expectation values The reason for the repetition is that quantum mechanics does not make definite predictions for the position, momentum, etc. When we do the exact same measurement on identically prepared systems, we do not get always get the same result, as we do in classical mechanics. But probabi ...
Physics PHYS 354 Electricity and Magnetism II Problem Set #3
... Could you have predicted this result from the result of Problem 1 on Problem Set #1? Why or why not? From this expression determine on the surface of the sphere. Also show that the total charge on the surface of the sphere is +Q. Finally, determine the dipole moment of the induced charge on t ...
... Could you have predicted this result from the result of Problem 1 on Problem Set #1? Why or why not? From this expression determine on the surface of the sphere. Also show that the total charge on the surface of the sphere is +Q. Finally, determine the dipole moment of the induced charge on t ...
Time in Quantum Theory
... principle, this dynamics has to be derived from the unitary (Schrödinger) evolution of an entangled global quantum state, that would include all 'external interventions'. Under realistic assumptions this leads to permanently growing →entanglement with the environment – locally observed as →decoheren ...
... principle, this dynamics has to be derived from the unitary (Schrödinger) evolution of an entangled global quantum state, that would include all 'external interventions'. Under realistic assumptions this leads to permanently growing →entanglement with the environment – locally observed as →decoheren ...
2013.9.23
... Si Conduction-Band Structure in wave vector k-space (Constant-Energy Surfaces in k-space)Effective mass approximation: Kinetic energy ...
... Si Conduction-Band Structure in wave vector k-space (Constant-Energy Surfaces in k-space)Effective mass approximation: Kinetic energy ...
Generalized Momentum Operators
... momentum operator p (and in which [ !i ∂x ]n does not serve to represent powers p n of the momentum operator) has been frequently noted, and came forcibly to my own attention while writing the final pages of “E. T. Whittaker’s quantum formalism” (). I make reference there to (among other papers) ...
... momentum operator p (and in which [ !i ∂x ]n does not serve to represent powers p n of the momentum operator) has been frequently noted, and came forcibly to my own attention while writing the final pages of “E. T. Whittaker’s quantum formalism” (). I make reference there to (among other papers) ...
(2 hours) This paper con - University of Southampton
... Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate answer books Answer all questions in Section A and only two questions in Section B. Section A carries 1/3 of the total marks for the exam paper and you should aim to spend about 40 mins on it. Section B carries 2/3 of the total marks for the exa ...
... Answers to Section A and Section B must be in separate answer books Answer all questions in Section A and only two questions in Section B. Section A carries 1/3 of the total marks for the exam paper and you should aim to spend about 40 mins on it. Section B carries 2/3 of the total marks for the exa ...
Review of Bernard d`Espagnat, On physics and philosophy
... apart in opposite spatial directions. When the two photons are separated by a space-like interval so that there no longer is any interaction between them, spin-parameters are fixed that are to be measured on each of the two photons, and two such measurements are carried out. The measurement outcomes ...
... apart in opposite spatial directions. When the two photons are separated by a space-like interval so that there no longer is any interaction between them, spin-parameters are fixed that are to be measured on each of the two photons, and two such measurements are carried out. The measurement outcomes ...
Diapositive 1
... We should definitively define what we are doing (Energy Density Functional)! New perspective for/from Time-Dependent DFT Non-locality in time / causality in mean-field like approximations ...
... We should definitively define what we are doing (Energy Density Functional)! New perspective for/from Time-Dependent DFT Non-locality in time / causality in mean-field like approximations ...
Quantum gravitational contributions to quantum electrodynamics
... the electric charge at high energies, a result known as asymptotic freedom. The standard model of particle physics is based in part on quantised Yang-Mills (or non-Abelian) gauge fields. The quantisation of such fields leads to the important prediction that at high-energy the strength of the gauge c ...
... the electric charge at high energies, a result known as asymptotic freedom. The standard model of particle physics is based in part on quantised Yang-Mills (or non-Abelian) gauge fields. The quantisation of such fields leads to the important prediction that at high-energy the strength of the gauge c ...
1. Introduction - Departamento de Fisica/UFPB
... Only whole atoms are react with one another. The first atomic model (W. Prout, 1815) assumed that the atoms of all elements are put together out of hydrogen atoms. As a heuristic principle this hypothesis finally led to a scheme for ordering the elements based on their chemical properties, thQperiod ...
... Only whole atoms are react with one another. The first atomic model (W. Prout, 1815) assumed that the atoms of all elements are put together out of hydrogen atoms. As a heuristic principle this hypothesis finally led to a scheme for ordering the elements based on their chemical properties, thQperiod ...
Chapter 9d Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
... The s shell in each bracket is always filled first, although it can lose one or both of its electrons as the other shells in the bracket fill up. Apart from the brackets (parenthesis and braces), there are no deviations from the indicated order of filling. ...
... The s shell in each bracket is always filled first, although it can lose one or both of its electrons as the other shells in the bracket fill up. Apart from the brackets (parenthesis and braces), there are no deviations from the indicated order of filling. ...
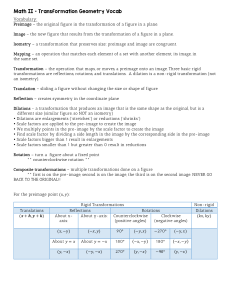
Math II – Transformation Geometry Vocab
... Transformation – the operation that maps, or moves, a preimage onto an image. Three basic rigid transformations are reflections, rotations, and translations. A dilation is a non-rigid transformation (not an isometry). Translation – sliding a figure without changing the size or shape of figure Reflec ...
... Transformation – the operation that maps, or moves, a preimage onto an image. Three basic rigid transformations are reflections, rotations, and translations. A dilation is a non-rigid transformation (not an isometry). Translation – sliding a figure without changing the size or shape of figure Reflec ...
QUANTUM DOTS
... The tunnel barrier between dots can be high or low by setting a gate voltage. In the case of the high barrier potential the tunnelling is forbidden between dots (no evolution in time). In the low barrier potential spins will be subject to a transient Heisenberg coupling (Hubbard model). The equation ...
... The tunnel barrier between dots can be high or low by setting a gate voltage. In the case of the high barrier potential the tunnelling is forbidden between dots (no evolution in time). In the low barrier potential spins will be subject to a transient Heisenberg coupling (Hubbard model). The equation ...
Renormalization group

In theoretical physics, the renormalization group (RG) refers to a mathematical apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different distance scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in the underlying force laws (codified in a quantum field theory) as the energy scale at which physical processes occur varies, energy/momentum and resolution distance scales being effectively conjugate under the uncertainty principle (cf. Compton wavelength).A change in scale is called a ""scale transformation"". The renormalization group is intimately related to ""scale invariance"" and ""conformal invariance"", symmetries in which a system appears the same at all scales (so-called self-similarity). (However, note that scale transformations are included in conformal transformations, in general: the latter including additional symmetry generators associated with special conformal transformations.)As the scale varies, it is as if one is changing the magnifying power of a notional microscope viewing the system. In so-called renormalizable theories, the system at one scale will generally be seen to consist of self-similar copies of itself when viewed at a smaller scale, with different parameters describing the components of the system. The components, or fundamental variables, may relate to atoms, elementary particles, atomic spins, etc. The parameters of the theory typically describe the interactions of the components. These may be variable ""couplings"" which measure the strength of various forces, or mass parameters themselves. The components themselves may appear to be composed of more of the self-same components as one goes to shorter distances.For example, in quantum electrodynamics (QED), an electron appears to be composed of electrons, positrons (anti-electrons) and photons, as one views it at higher resolution, at very short distances. The electron at such short distances has a slightly different electric charge than does the ""dressed electron"" seen at large distances, and this change, or ""running,"" in the value of the electric charge is determined by the renormalization group equation.