Singularity of the time-energy uncertainty in adiabatic perturbation
... field. Its quantum trajectory is shown to be a cycloid on the Bloch sphere, traced by a point on a rolling circle, of a radius determined by the angular speed of the magnetic field, along the adiabatic path of the instantaneous eigenstate. We find the two basic geometric quantities, the distance and ...
... field. Its quantum trajectory is shown to be a cycloid on the Bloch sphere, traced by a point on a rolling circle, of a radius determined by the angular speed of the magnetic field, along the adiabatic path of the instantaneous eigenstate. We find the two basic geometric quantities, the distance and ...
the transcendental meditation technique and quantum physics
... mood. Moreover, from the existence of the pure consciousness state, the scientist interested in studying consciousness learns two important facts. First, it becomes evident that conscious awareness does not depend on thought content; it can exist by itself ( 10). Second, it is seen that consciousnes ...
... mood. Moreover, from the existence of the pure consciousness state, the scientist interested in studying consciousness learns two important facts. First, it becomes evident that conscious awareness does not depend on thought content; it can exist by itself ( 10). Second, it is seen that consciousnes ...
Detecting a many-body mobility edge with quantum
... the antiferromagnetic XXZ model in a random field [6, 7, 16, 17, 20], and the random-bond Ising model in a transverse field [19], among others. These models have the common feature that, when not protected from disorder by an energy gap, the ground state is localized for any arbitrary disorder stren ...
... the antiferromagnetic XXZ model in a random field [6, 7, 16, 17, 20], and the random-bond Ising model in a transverse field [19], among others. These models have the common feature that, when not protected from disorder by an energy gap, the ground state is localized for any arbitrary disorder stren ...
ap physics 1
... as vectors and classify as positive or negative depending upon whether they give rise to or correspond to counterclockwise or clockwise rotation with respect to an axis. (EK 4.D.1) 6. TSW calculate the change in angular momentum given by the product of the average torque and the time interval during ...
... as vectors and classify as positive or negative depending upon whether they give rise to or correspond to counterclockwise or clockwise rotation with respect to an axis. (EK 4.D.1) 6. TSW calculate the change in angular momentum given by the product of the average torque and the time interval during ...
The modal nature of structures in ontic structural realism
... physical relations among objects that are nothing but what stands in these relations, that is, do not possess an intrinsic identity over and above the relations in which they stand (Esfeld 2004, Esfeld & Lam 2008, Floridi 2008). This position takes notably the entangled states of elementary quantum ...
... physical relations among objects that are nothing but what stands in these relations, that is, do not possess an intrinsic identity over and above the relations in which they stand (Esfeld 2004, Esfeld & Lam 2008, Floridi 2008). This position takes notably the entangled states of elementary quantum ...
Entanglement Theory and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
... thus a full analogy to the second law of thermodynamics. While operationally well motivated, the set of LOCC operations is not such a class. The following choice of quantum operations represents a key insight that is crucial for establishing reversibility in entanglement theory. As we are concerned ...
... thus a full analogy to the second law of thermodynamics. While operationally well motivated, the set of LOCC operations is not such a class. The following choice of quantum operations represents a key insight that is crucial for establishing reversibility in entanglement theory. As we are concerned ...
Qualitative individuation in permutation
... By now the philosophy literature on permutation invariance and related issues in quantum mechanics is formidable, and a variety of construals of permutation invariance have been well articulated.1 The purpose of this article is to expound and advocate a construal according to which permutation invar ...
... By now the philosophy literature on permutation invariance and related issues in quantum mechanics is formidable, and a variety of construals of permutation invariance have been well articulated.1 The purpose of this article is to expound and advocate a construal according to which permutation invar ...
TOPICS IN QUANTUM NANOSTRUCTURE PHYSICS: SPIN-ORBIT EFFECTS AND FAR-INFRARED RESPONSE TEMES DE F´
... Because of their particular topology, quantum ring (QR) systems exhibit unique physical phenomena that make them very interesting from both a purely theoretical and a technological point of view. In this sense they allow, for example, the observation of Aharonov-Bohm oscillations [Aha59] and related ...
... Because of their particular topology, quantum ring (QR) systems exhibit unique physical phenomena that make them very interesting from both a purely theoretical and a technological point of view. In this sense they allow, for example, the observation of Aharonov-Bohm oscillations [Aha59] and related ...
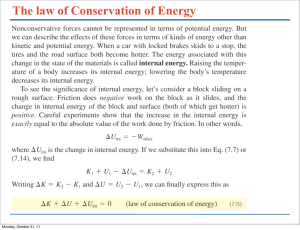
The law of Conservation of Energy
... The two ramps shown are both frictionless. The heights y1 and y2 are the same for each ramp. A block of mass m is released from rest at the left-hand end of each ramp. Which block arrives at the righthand end with the greater speed? ...
... The two ramps shown are both frictionless. The heights y1 and y2 are the same for each ramp. A block of mass m is released from rest at the left-hand end of each ramp. Which block arrives at the righthand end with the greater speed? ...
From a few to many electrons in quantum dots under strong
... Due to the growing interest in solid-state nanostructures, driven by basic research and potential technological considerations, two-dimensional 共2D兲 N-electron semiconductor quantum dots 共QDs兲 in field-free conditions and under applied magnetic fields 共B兲 have been extensively studied in the last fe ...
... Due to the growing interest in solid-state nanostructures, driven by basic research and potential technological considerations, two-dimensional 共2D兲 N-electron semiconductor quantum dots 共QDs兲 in field-free conditions and under applied magnetic fields 共B兲 have been extensively studied in the last fe ...
Underdetermination as a Path to Ontic Structural Realism 1
... (P2) If that’s the case, then we should expect our best theories to describe what those facts are (call this an “individuality profile”). (P3) But our best theories fail to say how objects are individuated, or even whether they are individuals at all: they fail to specify an individuality profile. I ...
... (P2) If that’s the case, then we should expect our best theories to describe what those facts are (call this an “individuality profile”). (P3) But our best theories fail to say how objects are individuated, or even whether they are individuals at all: they fail to specify an individuality profile. I ...
Department of Physics, Chemistry and Biology Master’s Thesis
... same spin cannot be on the same site. It means a site can accommodate zero, one or two electrons with opposite spin. Its Hamiltonian has two terms: a kinetic term allowing tunneling of particles between sites and a potential term consisting of the on-site interaction. If the particles in the system ...
... same spin cannot be on the same site. It means a site can accommodate zero, one or two electrons with opposite spin. Its Hamiltonian has two terms: a kinetic term allowing tunneling of particles between sites and a potential term consisting of the on-site interaction. If the particles in the system ...
Two-gluon rapidity correlations of strong colour
... Figure 2: Rapidity dependence of the saturation scale Q s (a) and the widths (b) of uGD of proton (red dash-point and solid lines) and nucleus (blue dash-point and solid lines). Where the initial saturation scales for proton and nucleus are Q2s0 = 0.168 GeV2 and 0.504 GeV2 , respectively. ...
... Figure 2: Rapidity dependence of the saturation scale Q s (a) and the widths (b) of uGD of proton (red dash-point and solid lines) and nucleus (blue dash-point and solid lines). Where the initial saturation scales for proton and nucleus are Q2s0 = 0.168 GeV2 and 0.504 GeV2 , respectively. ...
Renormalization group

In theoretical physics, the renormalization group (RG) refers to a mathematical apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different distance scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in the underlying force laws (codified in a quantum field theory) as the energy scale at which physical processes occur varies, energy/momentum and resolution distance scales being effectively conjugate under the uncertainty principle (cf. Compton wavelength).A change in scale is called a ""scale transformation"". The renormalization group is intimately related to ""scale invariance"" and ""conformal invariance"", symmetries in which a system appears the same at all scales (so-called self-similarity). (However, note that scale transformations are included in conformal transformations, in general: the latter including additional symmetry generators associated with special conformal transformations.)As the scale varies, it is as if one is changing the magnifying power of a notional microscope viewing the system. In so-called renormalizable theories, the system at one scale will generally be seen to consist of self-similar copies of itself when viewed at a smaller scale, with different parameters describing the components of the system. The components, or fundamental variables, may relate to atoms, elementary particles, atomic spins, etc. The parameters of the theory typically describe the interactions of the components. These may be variable ""couplings"" which measure the strength of various forces, or mass parameters themselves. The components themselves may appear to be composed of more of the self-same components as one goes to shorter distances.For example, in quantum electrodynamics (QED), an electron appears to be composed of electrons, positrons (anti-electrons) and photons, as one views it at higher resolution, at very short distances. The electron at such short distances has a slightly different electric charge than does the ""dressed electron"" seen at large distances, and this change, or ""running,"" in the value of the electric charge is determined by the renormalization group equation.