No Slide Title
... The angular momentum of a particle confined to a plane can be represented by a vector of length |ml| units along the z-axis and with an orientation that indicates the direction of motion of the particle. The direction is given by the right-hand screw rule. ...
... The angular momentum of a particle confined to a plane can be represented by a vector of length |ml| units along the z-axis and with an orientation that indicates the direction of motion of the particle. The direction is given by the right-hand screw rule. ...
Which is it: Dark Matter or Modified Gravity?
... within the clusters, derived from observations by the CFHT and smoothed to show the location of most of the galaxies, is colored orange. ...
... within the clusters, derived from observations by the CFHT and smoothed to show the location of most of the galaxies, is colored orange. ...
13-QuantumMechanics
... 3. The wave function must be twice differentiable. This means that it and its derivative must be continuous. (An exception to this rule occurs when V is infinite.) 4. In order to normalize a wave function, it must approach zero as x approaches infinity. ...
... 3. The wave function must be twice differentiable. This means that it and its derivative must be continuous. (An exception to this rule occurs when V is infinite.) 4. In order to normalize a wave function, it must approach zero as x approaches infinity. ...
PPT - LSU Physics & Astronomy
... loss in order to maximize the extraction of the available phase information in an interferometer. Our approach optimizes over the entire available input Hilbert space with no constraints, other than fixed total initial photon number. ...
... loss in order to maximize the extraction of the available phase information in an interferometer. Our approach optimizes over the entire available input Hilbert space with no constraints, other than fixed total initial photon number. ...
Slide 1
... Data are sent in weak pulses of photons. The physical behavior of the particles themselves gives the receiver the encryption key. If a third party interrupts the data stream, the encryption key is rendered useless and both parties are alerted. The encryption key isn’t in the message, it is t ...
... Data are sent in weak pulses of photons. The physical behavior of the particles themselves gives the receiver the encryption key. If a third party interrupts the data stream, the encryption key is rendered useless and both parties are alerted. The encryption key isn’t in the message, it is t ...
A universal alphabet and rewrite system
... However, when we first conceive of the real ‘numbers’, they are not numbers at all. They are not related to anything concerned with counting, because counting does not yet exist. The set of reals (ℜ) is simply one of things unspecified. Our startingpoint must be non-specific, and could be anything. ...
... However, when we first conceive of the real ‘numbers’, they are not numbers at all. They are not related to anything concerned with counting, because counting does not yet exist. The set of reals (ℜ) is simply one of things unspecified. Our startingpoint must be non-specific, and could be anything. ...
WHAT CAN THOMISTIC PHILOSOPHY OF NATURE CONTRIBUTE
... To date physicists do not know why mathematics is working in physics. Only the fact that it does work is well known. Working means that physicists more or less successfully ‘apply’ mathematical expressions to natural processes, wherefore these expressions are called ‘laws of nature’. The application ...
... To date physicists do not know why mathematics is working in physics. Only the fact that it does work is well known. Working means that physicists more or less successfully ‘apply’ mathematical expressions to natural processes, wherefore these expressions are called ‘laws of nature’. The application ...
Dynamical Generation of the Gauge Hierarchy in SUSY
... Q~ and Q6 is not generated even in the presence of instanton effects and hence there is no transition matrix between Ha and fia. We note that this is consistent with the result by Affieck, Dine and Seiberg. 18 ) The GUT unification of three gauge coupling constants of SU(3)c x SU(2)L x U(l)y is achi ...
... Q~ and Q6 is not generated even in the presence of instanton effects and hence there is no transition matrix between Ha and fia. We note that this is consistent with the result by Affieck, Dine and Seiberg. 18 ) The GUT unification of three gauge coupling constants of SU(3)c x SU(2)L x U(l)y is achi ...
Deviations from exponential law and Van Hove`s “2t” limit
... The purpose of this paper is to consider the e ects that arise when the coupling constant is small but nonvanishing. This will enable us to give general estimates for deviations from exponential behavior. The paper is organized as follows. We shall rst look, in Section 2, at a simple system: we sum ...
... The purpose of this paper is to consider the e ects that arise when the coupling constant is small but nonvanishing. This will enable us to give general estimates for deviations from exponential behavior. The paper is organized as follows. We shall rst look, in Section 2, at a simple system: we sum ...
ECE692_2_1008
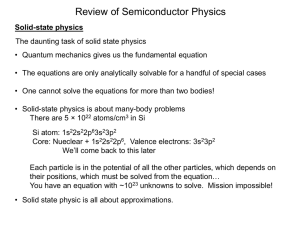
... The daunting task of solid state physics • Quantum mechanics gives us the fundamental equation • The equations are only analytically solvable for a handful of special cases • One cannot solve the equations for more than two bodies! • Solid-state physics is about many-body problems There are 5 × 1022 ...
... The daunting task of solid state physics • Quantum mechanics gives us the fundamental equation • The equations are only analytically solvable for a handful of special cases • One cannot solve the equations for more than two bodies! • Solid-state physics is about many-body problems There are 5 × 1022 ...
Charge sensing in intrinsic silicon quantum dots
... Due to variation in the coupling of the QD to the leads, a modulation of the peak height is observed for the QD conductance over the gate range shown in Fig. 2共b兲. This variation in peak amplitude for the QD gives an excellent demonstration of the benefits of an electrometer as a probe of the charge ...
... Due to variation in the coupling of the QD to the leads, a modulation of the peak height is observed for the QD conductance over the gate range shown in Fig. 2共b兲. This variation in peak amplitude for the QD gives an excellent demonstration of the benefits of an electrometer as a probe of the charge ...
Renormalization group

In theoretical physics, the renormalization group (RG) refers to a mathematical apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different distance scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in the underlying force laws (codified in a quantum field theory) as the energy scale at which physical processes occur varies, energy/momentum and resolution distance scales being effectively conjugate under the uncertainty principle (cf. Compton wavelength).A change in scale is called a ""scale transformation"". The renormalization group is intimately related to ""scale invariance"" and ""conformal invariance"", symmetries in which a system appears the same at all scales (so-called self-similarity). (However, note that scale transformations are included in conformal transformations, in general: the latter including additional symmetry generators associated with special conformal transformations.)As the scale varies, it is as if one is changing the magnifying power of a notional microscope viewing the system. In so-called renormalizable theories, the system at one scale will generally be seen to consist of self-similar copies of itself when viewed at a smaller scale, with different parameters describing the components of the system. The components, or fundamental variables, may relate to atoms, elementary particles, atomic spins, etc. The parameters of the theory typically describe the interactions of the components. These may be variable ""couplings"" which measure the strength of various forces, or mass parameters themselves. The components themselves may appear to be composed of more of the self-same components as one goes to shorter distances.For example, in quantum electrodynamics (QED), an electron appears to be composed of electrons, positrons (anti-electrons) and photons, as one views it at higher resolution, at very short distances. The electron at such short distances has a slightly different electric charge than does the ""dressed electron"" seen at large distances, and this change, or ""running,"" in the value of the electric charge is determined by the renormalization group equation.