Genetics - FAQ`s - El Camino College
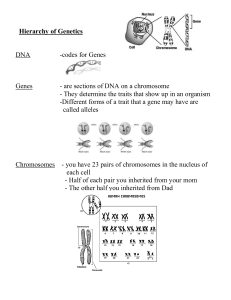
... primary carrier of genetic (hereditary) information. It’s made up of nucleic acids, which consist of phosphates, sugars and four chemical bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine). WHAT IS A CHROMOSOME? A threadlike structure found in the nucleus of the cell that contains the hereditary materi ...
... primary carrier of genetic (hereditary) information. It’s made up of nucleic acids, which consist of phosphates, sugars and four chemical bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine). WHAT IS A CHROMOSOME? A threadlike structure found in the nucleus of the cell that contains the hereditary materi ...
MODULE 7: REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION DURING
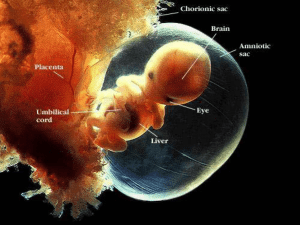
... Discuss the importance of DNA methylation during early vertebrate development Discuss the importance of Wnt signaling during mammalian development Comment on: Hedgehog and the role of retinoid acid in mammalian development What are embryonic stem cells? Where are they present in a mammalian embryo? ...
... Discuss the importance of DNA methylation during early vertebrate development Discuss the importance of Wnt signaling during mammalian development Comment on: Hedgehog and the role of retinoid acid in mammalian development What are embryonic stem cells? Where are they present in a mammalian embryo? ...
Human Genome Project - College Heights Secondary School
... • Consider ethical, legal, and social issues associated with this research ...
... • Consider ethical, legal, and social issues associated with this research ...
sex-linked traits: traits controlled by genes located on thr sex
... SEX-LINKED TRAITS: TRAITS CONTROLLED BY GENES LOCATED ON THR SEX CHROMOSOMES. X = FEMALE SEX CHROMOSOME Y = MALE SEX CHROMOSOME (SMALLER THAN X AND DOES NOT CONTAIN AS MANY GENES) Objectives: 1) Define through example sex-linked traits and polygenic inheritance. 2) Identify other factors that might ...
... SEX-LINKED TRAITS: TRAITS CONTROLLED BY GENES LOCATED ON THR SEX CHROMOSOMES. X = FEMALE SEX CHROMOSOME Y = MALE SEX CHROMOSOME (SMALLER THAN X AND DOES NOT CONTAIN AS MANY GENES) Objectives: 1) Define through example sex-linked traits and polygenic inheritance. 2) Identify other factors that might ...
Genes - Bill Nye
... 1. You get your genes from your _____________________. 2. Your body is made of ______________. 3. DNA is shaped like a _____________________________. 4. ____________ is the chemical genes are made of. 5. _________________ of genes are joined together to make a chromosome. 6. If you uncoil chromosome ...
... 1. You get your genes from your _____________________. 2. Your body is made of ______________. 3. DNA is shaped like a _____________________________. 4. ____________ is the chemical genes are made of. 5. _________________ of genes are joined together to make a chromosome. 6. If you uncoil chromosome ...
The modern synthesis
... One of the key assumptions of the theory of natural selection. How does that work? Genes! ...
... One of the key assumptions of the theory of natural selection. How does that work? Genes! ...
Natural Selection on the Olfactory Receptor Gene Family in
... Human have more than 1000 OR genes, and about 40% have intact (non-mutated) coding region : functional 68 to 72% for apes Comparing the variations at the OR genes with at intergenic region (a stretch of DNA sequences located between clusters of genes that contain few or no genes) ...
... Human have more than 1000 OR genes, and about 40% have intact (non-mutated) coding region : functional 68 to 72% for apes Comparing the variations at the OR genes with at intergenic region (a stretch of DNA sequences located between clusters of genes that contain few or no genes) ...
Control of Gene Express in Prokaryotes
... • Regulation of enzyme activityfeedback inhibition • Regulation of gene expression ...
... • Regulation of enzyme activityfeedback inhibition • Regulation of gene expression ...
Slide 1
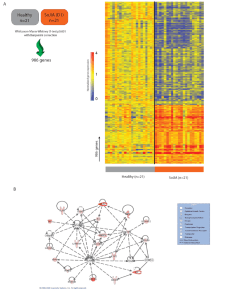
... Non parametric testing (Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney U-test; p<0.01 for class comparisons with Benjamini correction; p<0.05 for modular analyses with no multiple testing corrections) was used to rank genes based on their ability to discriminate among pre-specified groups of patients. 9,477 genes passing th ...
... Non parametric testing (Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney U-test; p<0.01 for class comparisons with Benjamini correction; p<0.05 for modular analyses with no multiple testing corrections) was used to rank genes based on their ability to discriminate among pre-specified groups of patients. 9,477 genes passing th ...
NOVA – Cracking the Code of Life
... 3. About what percentage of the genes in a banana are also in a human? ____ Why is this figure so high? ...
... 3. About what percentage of the genes in a banana are also in a human? ____ Why is this figure so high? ...
Bill Nye - Genetics (worksheet)
... 11) Rosalind Franklin died of ovarian cancer, most likely due to exposure to _______________. ...
... 11) Rosalind Franklin died of ovarian cancer, most likely due to exposure to _______________. ...
With the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have
... Since the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have access to more information than ever before about our genetic make-up. The human genome contains 3 billion base pairs of DNA, encoding an estimated 25,000 genes, which are the basic units of heredity. This course addresses questions such ...
... Since the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have access to more information than ever before about our genetic make-up. The human genome contains 3 billion base pairs of DNA, encoding an estimated 25,000 genes, which are the basic units of heredity. This course addresses questions such ...
Extensions of the Plaid Model for Two-Way Clustering of Microarray Data
... biological process. Art Owen and I introduced the plaid model as a form of cluster analysis in which genes and samples may belong to one, more than one, or no clusters. The clusters are two-sided reflecting the fact that groups of genes may be co-regulated in some experimental samples and not others ...
... biological process. Art Owen and I introduced the plaid model as a form of cluster analysis in which genes and samples may belong to one, more than one, or no clusters. The clusters are two-sided reflecting the fact that groups of genes may be co-regulated in some experimental samples and not others ...