Linked___Genes
... meiosis, there is no change, as the alleles are the same on each. HOWEVER, if there is crossing over in the paternal chromosomes, and the G/g alleles swap places, there will be ...
... meiosis, there is no change, as the alleles are the same on each. HOWEVER, if there is crossing over in the paternal chromosomes, and the G/g alleles swap places, there will be ...
"The Evolutionary Position of the Unique, Tropical Placazoa in the Animal Tree of Life"
... inheritance from one generation to the next, also contain a record of shared ancestry between the organisms that contain them [1]. Because all animal morphology and physiology (with the exception of certain aspects of the immune system) has a heritable molecular basis, and because molecular patterns ...
... inheritance from one generation to the next, also contain a record of shared ancestry between the organisms that contain them [1]. Because all animal morphology and physiology (with the exception of certain aspects of the immune system) has a heritable molecular basis, and because molecular patterns ...
LIMMA
... • logFC - Estimate of the log2-fold-change corresponding to the effect or contrast • AveExpr - Average log2-expression for the probe over all arrays/channels • t - moderated t-statistic • P.Value - Raw p-value • adj.P.Value -Adjusted p-value • B - log odds that the gene is differentially expressed ...
... • logFC - Estimate of the log2-fold-change corresponding to the effect or contrast • AveExpr - Average log2-expression for the probe over all arrays/channels • t - moderated t-statistic • P.Value - Raw p-value • adj.P.Value -Adjusted p-value • B - log odds that the gene is differentially expressed ...
Gene Finding in Prokaryotes
... • GC relative to AT is a distinguishing factor of bacterial genomes • Varies dramatically across species – Serves as a means to identify bacterial species ...
... • GC relative to AT is a distinguishing factor of bacterial genomes • Varies dramatically across species – Serves as a means to identify bacterial species ...
Lecture 15
... am including Background correction along with Normalizing here. • The pros and Cons of normalizing vs not. • What theoretically Normalizing is supposed to do and WHAT it actually does. ...
... am including Background correction along with Normalizing here. • The pros and Cons of normalizing vs not. • What theoretically Normalizing is supposed to do and WHAT it actually does. ...
Integration of chemical-genetic and genetic interaction data links
... • ~6000 annotated genes • 182 genes with significant similarity to human disease genes. • No complete comparison between humans and yeast yet completed but likely many more orthologous genes than this (Carroll et al, 2003). • Many metabolic and signal transduction pathways are conserved ...
... • ~6000 annotated genes • 182 genes with significant similarity to human disease genes. • No complete comparison between humans and yeast yet completed but likely many more orthologous genes than this (Carroll et al, 2003). • Many metabolic and signal transduction pathways are conserved ...
Answers to 14.1 Genetics questions
... pedigree shows the dominant trait of a white hair flock in humans. 22. What is the genotype of anyone with a “white” symbol on the chart? 23. How is it possible to ...
... pedigree shows the dominant trait of a white hair flock in humans. 22. What is the genotype of anyone with a “white” symbol on the chart? 23. How is it possible to ...
Nutrigenomics? Epigenetics? The must-know
... The word ‘nutrigenomics’ is derived from ‘nutri’ meaning food and ‘genomics’ referring to your genes. In other words; ‘your food talking to your genes’. One of the most bioactive nutrigenomic food chemicals is a compound known as ‘sulforaphane’ which is released in abundance from certain forms of br ...
... The word ‘nutrigenomics’ is derived from ‘nutri’ meaning food and ‘genomics’ referring to your genes. In other words; ‘your food talking to your genes’. One of the most bioactive nutrigenomic food chemicals is a compound known as ‘sulforaphane’ which is released in abundance from certain forms of br ...
Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA)
... higher mean expression than DMSO group. Similarly, positive β2 means that the 3-week group has higher mean expression than the 1-day group. ...
... higher mean expression than DMSO group. Similarly, positive β2 means that the 3-week group has higher mean expression than the 1-day group. ...
No Slide Title
... Tissue-specific Regulation of Transcription Regulated transcription depends on: - specific enhancer for gene(s) - enhancer-specific activator proteins - correct interaction between enhancer and activator Tissue-specific regulation requires that the enhancer-specific activator is present only in cel ...
... Tissue-specific Regulation of Transcription Regulated transcription depends on: - specific enhancer for gene(s) - enhancer-specific activator proteins - correct interaction between enhancer and activator Tissue-specific regulation requires that the enhancer-specific activator is present only in cel ...
Gene Tests in Yeast Aid Work on Cancer
... in the journal PLoS Biology, the researchers describe the first fruit of this approach: a drug that shows a promising ability to shrink tumors. Its cancer-fighting ability has been hiding in plain sight since the 1960s, when it was approved to treat fungal infections. Until the new research, no one ...
... in the journal PLoS Biology, the researchers describe the first fruit of this approach: a drug that shows a promising ability to shrink tumors. Its cancer-fighting ability has been hiding in plain sight since the 1960s, when it was approved to treat fungal infections. Until the new research, no one ...
Ch. 5.1 and 5.2
... Colorblindness is controlled by a recessive allele on the X chromosome (XcXc or XcY) If you have the Dominant NORMAL gene, you will see in color. (XCXC or XCY) If you are a girl and have one of each (XCXc) then you are a carrier. You CARRY the gene for colorblindness, but you see in color! Because ...
... Colorblindness is controlled by a recessive allele on the X chromosome (XcXc or XcY) If you have the Dominant NORMAL gene, you will see in color. (XCXC or XCY) If you are a girl and have one of each (XCXc) then you are a carrier. You CARRY the gene for colorblindness, but you see in color! Because ...
Class Schedule
... Don’t print this page…just visit it every time you visit the course web page! Because of the collaborative and discussion/activity-based nature of this class, this course schedule is an “evolving” one! I cannot predict how deeply we will want to explore and discuss the concepts addressed in this c ...
... Don’t print this page…just visit it every time you visit the course web page! Because of the collaborative and discussion/activity-based nature of this class, this course schedule is an “evolving” one! I cannot predict how deeply we will want to explore and discuss the concepts addressed in this c ...
Training error
... caused by active protein A Predictive information is in expression of A minus expression of B Calling signature genes markers for a certain disease is misleading! Naïve Idea: Don’t calculate weights based on single gene scores but optimize over all possible hyperplanes ...
... caused by active protein A Predictive information is in expression of A minus expression of B Calling signature genes markers for a certain disease is misleading! Naïve Idea: Don’t calculate weights based on single gene scores but optimize over all possible hyperplanes ...
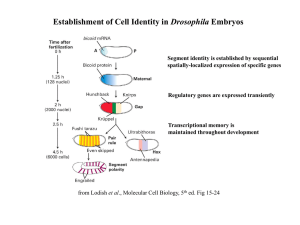
Establishment of Cell Identity in Drosophila Embryos
... Polycomb and Trithorax Complexes Prevents changes in cell identity by preserving transcription patterns Chromatin is altered in a heritable manner ...
... Polycomb and Trithorax Complexes Prevents changes in cell identity by preserving transcription patterns Chromatin is altered in a heritable manner ...
Mol Bio CH1 Sept 13
... -Give a relative position to genes on chromosomes -Could explain much of Darwin’s black box by genes on chrom., inherited by offspring with crossing over, mutation ...
... -Give a relative position to genes on chromosomes -Could explain much of Darwin’s black box by genes on chrom., inherited by offspring with crossing over, mutation ...
Document
... Individual genotypes might operate in ways to restrict development or constrain outcome • Range of reaction principle: • Genotype, or genetic structure, sets the limits on the range of possible phenotypes that a person might display in response to different environments: • Example: Intellectual deve ...
... Individual genotypes might operate in ways to restrict development or constrain outcome • Range of reaction principle: • Genotype, or genetic structure, sets the limits on the range of possible phenotypes that a person might display in response to different environments: • Example: Intellectual deve ...
Genetics - Sakshieducation.com
... 29. A normal-visioned man whose father was colour – blind marries a woman whose father was also colour-blind. They have their first child as a daughter. What are the chances that this child would be colour –blind? ...
... 29. A normal-visioned man whose father was colour – blind marries a woman whose father was also colour-blind. They have their first child as a daughter. What are the chances that this child would be colour –blind? ...
Section 6.4- Traits, Genes, Alleles
... about its’ phenotype. In the previous example, both TT and Tt would be tall, so we don’t care that the alleles are different We only care about the physical appearance when talking about phenotype. ...
... about its’ phenotype. In the previous example, both TT and Tt would be tall, so we don’t care that the alleles are different We only care about the physical appearance when talking about phenotype. ...
Behavioral Genetics
... B. Twin studies have been conducted to assess the influence of heredity on expression of a behavior or constellation of behaviors. 1. Monozygotic (MZ) or identical twins develop from a single fertilized egg that has split to form two embryos early in development. Thus they share the same heredity. 2 ...
... B. Twin studies have been conducted to assess the influence of heredity on expression of a behavior or constellation of behaviors. 1. Monozygotic (MZ) or identical twins develop from a single fertilized egg that has split to form two embryos early in development. Thus they share the same heredity. 2 ...