Isolation, Characterization and Complementation
... Anaerobic cultures of Escherichia coli K12 reduce nitrite rapidly to ammonia (Cole, 1978). The most active of the three enzymes involved in this reaction is an NADH-dependent nitrite reductase (EC 1 .6.6.4) which, in a typical wild-type strain, contributes about 75 % to the overall rate of nitrite r ...
... Anaerobic cultures of Escherichia coli K12 reduce nitrite rapidly to ammonia (Cole, 1978). The most active of the three enzymes involved in this reaction is an NADH-dependent nitrite reductase (EC 1 .6.6.4) which, in a typical wild-type strain, contributes about 75 % to the overall rate of nitrite r ...
Substitution of Serine Caused by a Recessive Lethal Suppressor in Yeast
... systematically characterized with respect to their ability to suppress nutritional mutants and cycl mutants which contain defined UAA (ochre) and UAG (amber) mutations. In addition, the efficiencies of suppression have been determined from the levels of iso-l-cytochrome c in suppressed cycl mutants. ...
... systematically characterized with respect to their ability to suppress nutritional mutants and cycl mutants which contain defined UAA (ochre) and UAG (amber) mutations. In addition, the efficiencies of suppression have been determined from the levels of iso-l-cytochrome c in suppressed cycl mutants. ...
Identification of One BOCR Mutation and Five NF1 Mutations in Male
... We studied six male patients with NF1 and CPT from five unrelated families. Two patients (A2-II:1 and A3-II:2) were sporadic cases whose first-degree relatives neither presented NF1 nor CPT, whereas the others inherited NF1 from one of their parents. In these families (A1, A4, A5), the genetic trans ...
... We studied six male patients with NF1 and CPT from five unrelated families. Two patients (A2-II:1 and A3-II:2) were sporadic cases whose first-degree relatives neither presented NF1 nor CPT, whereas the others inherited NF1 from one of their parents. In these families (A1, A4, A5), the genetic trans ...
Involvement of HLS1 in Sugar and Auxin
... mutation. However, sugar repression of HLS1 was less than that for RBCS. One explanation for the effects of the hls1 mutation on sugar-responsive gene expression is that hls1 cells incorporate more sugars than wild-type cells. We tested this possibility with plants grown on different concentration o ...
... mutation. However, sugar repression of HLS1 was less than that for RBCS. One explanation for the effects of the hls1 mutation on sugar-responsive gene expression is that hls1 cells incorporate more sugars than wild-type cells. We tested this possibility with plants grown on different concentration o ...
Lab #7
... usually used are homogametic for females (because they can only give Xs to their gametes) and heterogametic for males (because they can give gametes with either Xs or Ys). In addition to determining the sex of the individual, some genes for other traits are carried on the sex chromosomes, primarily ...
... usually used are homogametic for females (because they can only give Xs to their gametes) and heterogametic for males (because they can give gametes with either Xs or Ys). In addition to determining the sex of the individual, some genes for other traits are carried on the sex chromosomes, primarily ...
The Jumping SHOX Gene—Crossover in the Pseudoautosomal
... pseudoautosomal. The SHOX gene in the normal situation is present in two functional copies. In fact, one might consider PAR1 as a very small extra pair of autosomes (11), except that segregation in autosomes is independent of sex. Here we describe three families in which an abnormality in PAR1 segre ...
... pseudoautosomal. The SHOX gene in the normal situation is present in two functional copies. In fact, one might consider PAR1 as a very small extra pair of autosomes (11), except that segregation in autosomes is independent of sex. Here we describe three families in which an abnormality in PAR1 segre ...
Lab 7
... used are homogametic for females (because they can only give Xs to their gametes) and heterogametic for males (because they can give gametes with either Xs or Ys). In addition to determining the sex of the individual, some genes for other traits are carried on the sex chromosomes, primarily on the X ...
... used are homogametic for females (because they can only give Xs to their gametes) and heterogametic for males (because they can give gametes with either Xs or Ys). In addition to determining the sex of the individual, some genes for other traits are carried on the sex chromosomes, primarily on the X ...
basic of the genetic
... • GENOTYPE = complex of all hereditary information of organism (all genes) • PHENOTYPE = complex of visible outward signs and characters, outer demonstration of the genotype • ALLELE = one form of the gene • HOMOZYGOUS = organism, which from perspective of selected gene includes couple of alleles wi ...
... • GENOTYPE = complex of all hereditary information of organism (all genes) • PHENOTYPE = complex of visible outward signs and characters, outer demonstration of the genotype • ALLELE = one form of the gene • HOMOZYGOUS = organism, which from perspective of selected gene includes couple of alleles wi ...
Functional and ecological impacts of horizontal gene transfer in
... cases of HGT in bacteria were drug-resistance genes [1], and the movement of other kinds of genes related to virulence led to the concept of mobile ‘pathogenecity islands’ [48]. In both case, the practical advantage to mobility, both to the pathogen and the genes themselves, are obvious and their ra ...
... cases of HGT in bacteria were drug-resistance genes [1], and the movement of other kinds of genes related to virulence led to the concept of mobile ‘pathogenecity islands’ [48]. In both case, the practical advantage to mobility, both to the pathogen and the genes themselves, are obvious and their ra ...
The genetic basis of inherited anomalies of the teeth: Part 1: Clinical
... Paediatric Dentistry Department, Paris 7 University, AP-HP, Hôtel-Dieu e Garancière, Paris, France INSERM, UMRS 872, Molecular Oral Physiopathology, University Denis-Diderot Paris 7, Cordeliers Research Center, University Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris, France ...
... Paediatric Dentistry Department, Paris 7 University, AP-HP, Hôtel-Dieu e Garancière, Paris, France INSERM, UMRS 872, Molecular Oral Physiopathology, University Denis-Diderot Paris 7, Cordeliers Research Center, University Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris, France ...
Estimates of Selection and Gene Flow From Measures of
... Gene flow also causes gametic correlations (linkage disequilibria) between genes that differ across hybrid zones. Correlations are stronger when the hybrid zone is narrow, and rise to a maximum roughly equal to s. Thus cline width and gametic correlations combine to give estimates of gene flow and s ...
... Gene flow also causes gametic correlations (linkage disequilibria) between genes that differ across hybrid zones. Correlations are stronger when the hybrid zone is narrow, and rise to a maximum roughly equal to s. Thus cline width and gametic correlations combine to give estimates of gene flow and s ...
Genetics and Heredity
... Pattern Baldness In Humans: A Sex Influenced Trait Baldness is an autosomal trait and is apparently influenced by sex hormones after people reach 30 years of age or older. In men the gene is dominant, while in women it is recessive. A man needs only one allele (B) for the baldness trait to be expre ...
... Pattern Baldness In Humans: A Sex Influenced Trait Baldness is an autosomal trait and is apparently influenced by sex hormones after people reach 30 years of age or older. In men the gene is dominant, while in women it is recessive. A man needs only one allele (B) for the baldness trait to be expre ...
PDF
... Protein extracts from 2⫻106 untreated, 10 mM DTT-treated or eIF2α RNAitreated S2 cells, or from 30 μl 2- to 4-hour w1118 or wol1 germline clone embryos were prepared as described (Lilja et al., 2007). Proteins (7 μg) were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to PVDF membrane (GE Healthcare), and incub ...
... Protein extracts from 2⫻106 untreated, 10 mM DTT-treated or eIF2α RNAitreated S2 cells, or from 30 μl 2- to 4-hour w1118 or wol1 germline clone embryos were prepared as described (Lilja et al., 2007). Proteins (7 μg) were separated by SDS-PAGE, transferred to PVDF membrane (GE Healthcare), and incub ...
Vegetative incompatibility in filamentous fungi: Podospora and
... between unlike individuals, and by limiting the horizontal transfer of deleterious genetic elements like mycoviruses, senescence plasmids or transposons [5,6]. It has been shown, however, that such cytoplasmic elements can sometimes be transmitted horizontally, even between incompatible isolates (fo ...
... between unlike individuals, and by limiting the horizontal transfer of deleterious genetic elements like mycoviruses, senescence plasmids or transposons [5,6]. It has been shown, however, that such cytoplasmic elements can sometimes be transmitted horizontally, even between incompatible isolates (fo ...
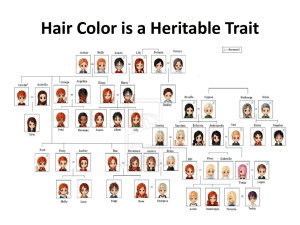
Hair Color is a Heritable Trait
... • Ignoring G*E interactions deflates h2 (MDD is not very heritable) ...
... • Ignoring G*E interactions deflates h2 (MDD is not very heritable) ...
Genetics Tutorial
... individual can pass on genetic information to its offspring. In order to avoid doubling the number of chromosomes in each generation, cells must be created that carry only one set of chromosomes (haploid or 1n). ...
... individual can pass on genetic information to its offspring. In order to avoid doubling the number of chromosomes in each generation, cells must be created that carry only one set of chromosomes (haploid or 1n). ...
chapter 5 powerpoint
... • Enamel hypoplasis is an autosomal dominant disorder that results in holes and cracks around the crowns of baby teeth. Some individuals are apparently unaffected but transmit the trait to their offspring. Individuals with the trait also vary in the number of teeth affected. This trait is an example ...
... • Enamel hypoplasis is an autosomal dominant disorder that results in holes and cracks around the crowns of baby teeth. Some individuals are apparently unaffected but transmit the trait to their offspring. Individuals with the trait also vary in the number of teeth affected. This trait is an example ...
Epistasis

Epistasis is a phenomenon that consists of the effect of one gene being dependent on the presence of one or more 'modifier genes' (genetic background). Similarly, epistatic mutations have different effects in combination than individually. It was originally a concept from genetics but is now used in biochemistry, population genetics, computational biology and evolutionary biology. It arises due to interactions, either between genes, or within them leading to non-additive effects. Epistasis has a large influence on the shape of evolutionary landscapes which leads to profound consequences for evolution and evolvability of traits.