5. Complex Pedigrees
... Example: Blood group O in pedigree Fig. 4.5A ABO blood groups A is dominant to O AA and AO = A blood type OO = O blood type Type O blood is common in population 2. Penetrance: probability that a person who has genotype will show the character. But dominant traits show different degrees of penetrance ...
... Example: Blood group O in pedigree Fig. 4.5A ABO blood groups A is dominant to O AA and AO = A blood type OO = O blood type Type O blood is common in population 2. Penetrance: probability that a person who has genotype will show the character. But dominant traits show different degrees of penetrance ...
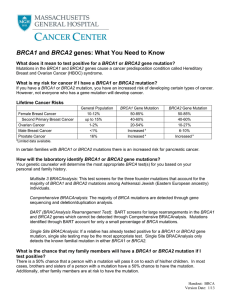
BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes: What You Need to Know
... BART (BRACAnalysis Rearrangement Test): BART screens for large rearrangements in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes which cannot be detected through Comprehensive BRACAnalysis. Mutations identified through BART account for only a small percentage of BRCA mutations. Single Site BRACAnalysis: If a relative has ...
... BART (BRACAnalysis Rearrangement Test): BART screens for large rearrangements in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes which cannot be detected through Comprehensive BRACAnalysis. Mutations identified through BART account for only a small percentage of BRCA mutations. Single Site BRACAnalysis: If a relative has ...
The Ubiquitous Nature of Epistasis in Determining Susceptibility to
... all transcriptional complexes. The third group is comprised of proteins that interact with activators and repressors to enhance their effects. As discussed by Martinez [2002], it is cooperative protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions that are critical for the regulation of transcription by pro ...
... all transcriptional complexes. The third group is comprised of proteins that interact with activators and repressors to enhance their effects. As discussed by Martinez [2002], it is cooperative protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions that are critical for the regulation of transcription by pro ...
Unit 1: Part I: Understanding Biological inheritance
... I describe the key features? I relate them to real life? I provide examples? I solve example problems? ...
... I describe the key features? I relate them to real life? I provide examples? I solve example problems? ...
(1) Quantitative traits and sequence variation Lecture objectives
... Often encoded by single genes ...
... Often encoded by single genes ...
13.3 Mutations
... The effects of mutations on genes vary widely. Some have little or no effect; and some produce beneficial variations. Some negatively disrupt gene function. ...
... The effects of mutations on genes vary widely. Some have little or no effect; and some produce beneficial variations. Some negatively disrupt gene function. ...
Annotating Gene List From Literature
... Biologists often need to understand the commonalities of a list of genes (e.g. whether they are involved in the same pathway). These genes typically come from clustering results in microarray expression Given a list of gene names, is there any automatic way to find the common themes from literature ...
... Biologists often need to understand the commonalities of a list of genes (e.g. whether they are involved in the same pathway). These genes typically come from clustering results in microarray expression Given a list of gene names, is there any automatic way to find the common themes from literature ...
13.3 Mutations
... The effects of mutations on genes vary widely. Some have little or no effect; and some produce beneficial variations. Some negatively disrupt gene function. ...
... The effects of mutations on genes vary widely. Some have little or no effect; and some produce beneficial variations. Some negatively disrupt gene function. ...
Les 10 Deliterious Genes ppt
... • Such genes will not be strongly selected against, because an organism’s fitness is determined by the genes it leaves in the next generation and not its life span. • Often, a fetus with homozygous dominant deleterious genes, such as Huntington’s, will not survive. ...
... • Such genes will not be strongly selected against, because an organism’s fitness is determined by the genes it leaves in the next generation and not its life span. • Often, a fetus with homozygous dominant deleterious genes, such as Huntington’s, will not survive. ...
Chapter 23 EVOLUTION AND GENETIC VARIATION
... • Traits controlled by two or more genes • Each gene of a polygenic trait has two or more alleles • As a result one polygenic trait can have many possible genotypes and phenotypes Ex.) height ...
... • Traits controlled by two or more genes • Each gene of a polygenic trait has two or more alleles • As a result one polygenic trait can have many possible genotypes and phenotypes Ex.) height ...
Warm-Up 5/2 and 5/3
... • We saw how natural selection impacts the frequency of alleles for a SINGLE gene trait • What about polygenic traits, where individuals have more than two genes for a trait? ...
... • We saw how natural selection impacts the frequency of alleles for a SINGLE gene trait • What about polygenic traits, where individuals have more than two genes for a trait? ...
Ch 23 Evolution of Populations Guided Rdg
... 19. In the human eye, the retina is behind the nerves that form the optic nerve. Where the optic nerve leaves the eye, there is a hole, which results in a blind spot. It would be far better for the human eye to not have such a blind spot. How can it be that natural selection, the process that leads ...
... 19. In the human eye, the retina is behind the nerves that form the optic nerve. Where the optic nerve leaves the eye, there is a hole, which results in a blind spot. It would be far better for the human eye to not have such a blind spot. How can it be that natural selection, the process that leads ...
Genetics
... Usually heteroplasmic (phenotypic expression: reduced penetrance, variable expression, pleiotropy) ...
... Usually heteroplasmic (phenotypic expression: reduced penetrance, variable expression, pleiotropy) ...
Bio290-08-Week 9
... Chapter 15: Mutations • Mutations generate genetic variants • These variants are then subject to recombination ...
... Chapter 15: Mutations • Mutations generate genetic variants • These variants are then subject to recombination ...
Honors Biology
... effect of point mutations on DNA : why is the order of amino acids important in protein structure?, what can happen in point mutations top affect that order? 2. Mendelian genetics associated terms: be able to define genotype, phenotype, homozygous, heterozygous, alleles, etc. one trait crosses ...
... effect of point mutations on DNA : why is the order of amino acids important in protein structure?, what can happen in point mutations top affect that order? 2. Mendelian genetics associated terms: be able to define genotype, phenotype, homozygous, heterozygous, alleles, etc. one trait crosses ...
A Common Voice: Marketing Argentine Wines in the U.S.
... Low BCAA may affect neurocognitive phenotypes Mutations in the genes encoding components of the BCKDC result in increased BCAA levels and MSUD. In contrast, mutations in the BCKDK, which phosphorylates and activates the BCKDC, have been recently associated with decreased BCAA levels and a phenotype ...
... Low BCAA may affect neurocognitive phenotypes Mutations in the genes encoding components of the BCKDC result in increased BCAA levels and MSUD. In contrast, mutations in the BCKDK, which phosphorylates and activates the BCKDC, have been recently associated with decreased BCAA levels and a phenotype ...
Microevolution
... reproduction eliminates variation. Sexual reproduction does not eliminate the frequency of alleles in a population. This idea have become known as the “Hardy-Weinberg ...
... reproduction eliminates variation. Sexual reproduction does not eliminate the frequency of alleles in a population. This idea have become known as the “Hardy-Weinberg ...
The Major Transitions in Evolution
... • Occasionally the mutant reverts phenotypically during somatic development, correlating with demethylation of Lcyc and restoration of gene expression. • It is surprising that the first natural morphological mutant to be characterized should trace to methylation, given the rarity of this mutational ...
... • Occasionally the mutant reverts phenotypically during somatic development, correlating with demethylation of Lcyc and restoration of gene expression. • It is surprising that the first natural morphological mutant to be characterized should trace to methylation, given the rarity of this mutational ...
blood12618insidebloodcombined 2075..2083
... With the limited sample size of this study, it is difficult to disentangle the genes’ individual effects from that of the multiple hit combinations. What are the implications? We tend to simplify the impact of prognostic factors or gene mutations into single dimensions such as presence or absence. It ...
... With the limited sample size of this study, it is difficult to disentangle the genes’ individual effects from that of the multiple hit combinations. What are the implications? We tend to simplify the impact of prognostic factors or gene mutations into single dimensions such as presence or absence. It ...
Chapter 12 PowerPoint
... Genetic Traits and Disorders Genetic disorders – diseases or debilitating condition that has a genetic basis ...
... Genetic Traits and Disorders Genetic disorders – diseases or debilitating condition that has a genetic basis ...
Document
... • The genes are inherit from both parents but the offspring’s phenotype is determined not by its own phenotype but by the genotype of the mother. • The substances present in the cytoplasm of an egg are pivotal in early development. Example: shell coiling of the snail Limnaea peregra. ...
... • The genes are inherit from both parents but the offspring’s phenotype is determined not by its own phenotype but by the genotype of the mother. • The substances present in the cytoplasm of an egg are pivotal in early development. Example: shell coiling of the snail Limnaea peregra. ...
Mendelian Genetics
... – A dihybrid cross involving epistasis will not yield the typical 9:3:3:1 ratio ...
... – A dihybrid cross involving epistasis will not yield the typical 9:3:3:1 ratio ...
Epistasis

Epistasis is a phenomenon that consists of the effect of one gene being dependent on the presence of one or more 'modifier genes' (genetic background). Similarly, epistatic mutations have different effects in combination than individually. It was originally a concept from genetics but is now used in biochemistry, population genetics, computational biology and evolutionary biology. It arises due to interactions, either between genes, or within them leading to non-additive effects. Epistasis has a large influence on the shape of evolutionary landscapes which leads to profound consequences for evolution and evolvability of traits.