Enter the weird world of the imagination!
... different types of cells in different parts of your body.You can only see human cells by looking at them down a microscope, which makes them look much bigger than they really are. Inside each cell there is something called a nucleus – this is where the chromosomes are found. Chromosomes look like lo ...
... different types of cells in different parts of your body.You can only see human cells by looking at them down a microscope, which makes them look much bigger than they really are. Inside each cell there is something called a nucleus – this is where the chromosomes are found. Chromosomes look like lo ...
Genetics Challenge Name 1. The abbreviation for deoxyribonucleic
... 8. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ are rod-shaped structures found in the nucleus of every cell in an organism. ...
... 8. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ are rod-shaped structures found in the nucleus of every cell in an organism. ...
Additional information
... Brief Description of Research: We aim to decipher the complex pathways that control transcription and how cells maintain their transcriptional state via chromatin. These are central basic questions for many biological systems, including cancer and other human diseases. We use yeast as a model organi ...
... Brief Description of Research: We aim to decipher the complex pathways that control transcription and how cells maintain their transcriptional state via chromatin. These are central basic questions for many biological systems, including cancer and other human diseases. We use yeast as a model organi ...
No Slide Title
... Why V1rb and V1ra Genes? Figure 1a • One region of chromosome 6 has a cluster of 23 Vr1, – 16 functional genes, – 7 pseudogenes, ...
... Why V1rb and V1ra Genes? Figure 1a • One region of chromosome 6 has a cluster of 23 Vr1, – 16 functional genes, – 7 pseudogenes, ...
Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q
... traits, such as a red and white flower making a pink flower is an example of______________. ...
... traits, such as a red and white flower making a pink flower is an example of______________. ...
Steps to follow to obtain data required for using the
... “choose database pull down” menu, please select “ENSEMBL 53 GENES (SANGER UK)” option. Another pull down menu, “choose database” appears. Please select a genes set of interest (reference genome) as shown below. ...
... “choose database pull down” menu, please select “ENSEMBL 53 GENES (SANGER UK)” option. Another pull down menu, “choose database” appears. Please select a genes set of interest (reference genome) as shown below. ...
The role of complex genetic variation of immune system genes in
... Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified multiple regions of the genome associated with respiratory health and disease and amongst these, one of the strongest signals of association is in the Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) region gene cluster on chromosome 6 which encodes proteins with ...
... Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified multiple regions of the genome associated with respiratory health and disease and amongst these, one of the strongest signals of association is in the Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) region gene cluster on chromosome 6 which encodes proteins with ...
LECT37 regul
... Q: Of this number how many are protein-encoding components? A: Roughly 1.5 percent Q: Have all of the genes been identified? A: No, we are not even close Q: What is left to do? A: Gene products, i.e., functional mRNAs and proteins, need to be identified, non-coding regulatory sequences need to be un ...
... Q: Of this number how many are protein-encoding components? A: Roughly 1.5 percent Q: Have all of the genes been identified? A: No, we are not even close Q: What is left to do? A: Gene products, i.e., functional mRNAs and proteins, need to be identified, non-coding regulatory sequences need to be un ...
Development and Apoptosis
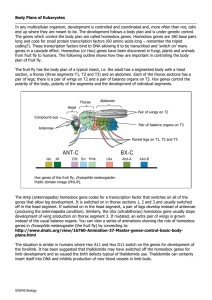
... Body Plans of Eukaryotes In any multicellular organism, development is controlled and coordinated and, more often than not, cells end up where they are meant to be. The development follows a body plan and is under genetic control. The genes which control the body plan are called homeobox genes. Home ...
... Body Plans of Eukaryotes In any multicellular organism, development is controlled and coordinated and, more often than not, cells end up where they are meant to be. The development follows a body plan and is under genetic control. The genes which control the body plan are called homeobox genes. Home ...
Genetics in the New Millennium: From Plants to People
... Rapid growth (of plant) Lower tooth decay (in people) Altered fatty acid profiles for industrial oils Longer shelf life (plant and products) ...
... Rapid growth (of plant) Lower tooth decay (in people) Altered fatty acid profiles for industrial oils Longer shelf life (plant and products) ...
Bioinformatics and the Language of DNA A. Tozeren
... Each and every cell in the body has the same book of life ...
... Each and every cell in the body has the same book of life ...
The Human Genome
... Pedigree Chart—shows relationships within a family; can be used to determine how a trait is passed from one generation to the next ...
... Pedigree Chart—shows relationships within a family; can be used to determine how a trait is passed from one generation to the next ...
2 Sex chromosomes
... • How many autosomes do humans have? How many sex chromosomes? • 44 autosomes (22 pairs) • 2 Sex chromosomes (1 pair) ...
... • How many autosomes do humans have? How many sex chromosomes? • 44 autosomes (22 pairs) • 2 Sex chromosomes (1 pair) ...
Chapter 4: Modern Genetics
... "good" genes for other attributes. Genetically impoverished individuals. ...
... "good" genes for other attributes. Genetically impoverished individuals. ...
doc
... A. Two nearly identical genomes were used, but the origin of replication was miscalled in one. B. One massive genome inversion, involving half of the genome C. One round of whole genome duplication, so that every gene is present in one of the two genomes twice and only once in the other D. These gen ...
... A. Two nearly identical genomes were used, but the origin of replication was miscalled in one. B. One massive genome inversion, involving half of the genome C. One round of whole genome duplication, so that every gene is present in one of the two genomes twice and only once in the other D. These gen ...
the maternal grandsire - Weimaraner Club of America
... each parent. Each chromosome pairs off with a corresponding chromosome of the other parent, and in each chromosome there are thousands of genes, which contain the protein codes that determine every physical trait. Within a pair of chromosomes will be pairs of genes from each parent that determine va ...
... each parent. Each chromosome pairs off with a corresponding chromosome of the other parent, and in each chromosome there are thousands of genes, which contain the protein codes that determine every physical trait. Within a pair of chromosomes will be pairs of genes from each parent that determine va ...
Developmental Biology 8/e - Florida International University
... A mutation in a particular enhancer can delete its particular stripe and no other. The placement of the stripes can be altered by deleting the gap genes that regulate them. ...
... A mutation in a particular enhancer can delete its particular stripe and no other. The placement of the stripes can be altered by deleting the gap genes that regulate them. ...
Evolucijska genomika 2
... Gene numbers do not increase as much as expected with complexity: - worm and fly gene numbers (12-14,000) are only about twice those of yeast (6,000) and P. aeruginosa (5,500) - mammalian (human, mouse) gene numbers (~30,000) are only about twice those of invertebrates. Phenotypic variation in m ...
... Gene numbers do not increase as much as expected with complexity: - worm and fly gene numbers (12-14,000) are only about twice those of yeast (6,000) and P. aeruginosa (5,500) - mammalian (human, mouse) gene numbers (~30,000) are only about twice those of invertebrates. Phenotypic variation in m ...
BB30055: Genes and genomes
... signal transduction and immune function) However, only 3 cases where a combination of 3 domain types shared by human & yeast proteins. e.g carbomyl-phosphate synthase (involved in the first 3 steps of de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis) has 7 domain types, which occurs once in human and yeast but twice ...
... signal transduction and immune function) However, only 3 cases where a combination of 3 domain types shared by human & yeast proteins. e.g carbomyl-phosphate synthase (involved in the first 3 steps of de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis) has 7 domain types, which occurs once in human and yeast but twice ...
What is really out there?
... “We found that the improvement of a plant variety through the acquisition of a new desired trait, using either mutagenesis or transgenesis, may cause stress and thus lead to an altered expression of untargeted genes. In all of the cases studied, the observed alteration was more extensive in mutageni ...
... “We found that the improvement of a plant variety through the acquisition of a new desired trait, using either mutagenesis or transgenesis, may cause stress and thus lead to an altered expression of untargeted genes. In all of the cases studied, the observed alteration was more extensive in mutageni ...
Nedchromosnotes2jan2014NED 20 KB
... condition refer to what? Important terms you need to and should know but I do not have time to redefine because they should be hardwired by now are haploid, diploid, nucleosome, chromatin, histone, centromere, telomere, homologues, chromatids. Bacterial genomes = 4.6 Mb = 4.6 x 10^6 bp Human genome ...
... condition refer to what? Important terms you need to and should know but I do not have time to redefine because they should be hardwired by now are haploid, diploid, nucleosome, chromatin, histone, centromere, telomere, homologues, chromatids. Bacterial genomes = 4.6 Mb = 4.6 x 10^6 bp Human genome ...