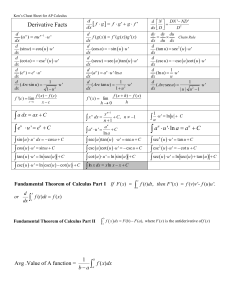
Ken`s Cheat Sheet 2014 Version 11 by 17
... For a limit to exist, the left and right hand limits must agree (be equal) V R r dx ...
... For a limit to exist, the left and right hand limits must agree (be equal) V R r dx ...
Section 17.3 - Gordon State College
... • A simple curve is a curve that does not intersect itself anywhere between its endpoints. • A simply-connected region in the plane is a connected region D such that every simple closed curve in D encloses only points that are in D. Intuitively speaking, a simply-connected regions contains no holes ...
... • A simple curve is a curve that does not intersect itself anywhere between its endpoints. • A simply-connected region in the plane is a connected region D such that every simple closed curve in D encloses only points that are in D. Intuitively speaking, a simply-connected regions contains no holes ...
Math 170 Calculus w/Analytic Geometry I Fall 2015
... Calculate the linear approximation of a given function and maximum error. Apply Newton’s method to find approximations to zeros Solve problems of related rates Find critical numbers and understand their role in finding relative extrema Test for concavity Use intercepts, asymptotes, relative extrema, ...
... Calculate the linear approximation of a given function and maximum error. Apply Newton’s method to find approximations to zeros Solve problems of related rates Find critical numbers and understand their role in finding relative extrema Test for concavity Use intercepts, asymptotes, relative extrema, ...
ma 166* analytic geometry and calculus ii
... COORDINATING FACULTY: S.K. Yeung, Chair, Calculus Committee ...
... COORDINATING FACULTY: S.K. Yeung, Chair, Calculus Committee ...
File
... continuous function f with an interval [a, b] as its domain takes values f(a) and f(b) at each end of the interval, then it also takes any value between f(a) and f(b) at some point within the interval. This has two important specializations: If a continuous function has values of opposite sign insid ...
... continuous function f with an interval [a, b] as its domain takes values f(a) and f(b) at each end of the interval, then it also takes any value between f(a) and f(b) at some point within the interval. This has two important specializations: If a continuous function has values of opposite sign insid ...
[Write on board:
... Because L(f,P) is a lower bound for the set of upper sums, it must be less than the greatest lower bound for this set; i.e., L(f,P) U(f). But P is arbitrary in this discussion, meaning that U(f) is an upper bound on the set of lower sums. From the definition of the supremum we get L(f) U(f) as d ...
... Because L(f,P) is a lower bound for the set of upper sums, it must be less than the greatest lower bound for this set; i.e., L(f,P) U(f). But P is arbitrary in this discussion, meaning that U(f) is an upper bound on the set of lower sums. From the definition of the supremum we get L(f) U(f) as d ...
∞ ∞ lnx sinx x =1 Local minimum
... 1. Read the problem carefully. Ask yourself: What is the unknown? What are the given quantities? What are the given conditions? In most cases it is useful to draw a diagram to better understand the problem. 2. Introduce the variables: Assign a variable to the quantity that is to be maximized or mini ...
... 1. Read the problem carefully. Ask yourself: What is the unknown? What are the given quantities? What are the given conditions? In most cases it is useful to draw a diagram to better understand the problem. 2. Introduce the variables: Assign a variable to the quantity that is to be maximized or mini ...
SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS MATHEMATICS FOR PART I
... 1. This module covers basic material on integration and will be mainly revision for you. Read the introductory sentence to section 8.7 on p.622. Then study section 8.7.1 on defining an integral as a limit, up to and including Example 8.37. You should note that areas above the x-axis are positive whe ...
... 1. This module covers basic material on integration and will be mainly revision for you. Read the introductory sentence to section 8.7 on p.622. Then study section 8.7.1 on defining an integral as a limit, up to and including Example 8.37. You should note that areas above the x-axis are positive whe ...
Functions and Their Limits Domain, Image, Range Increasing and Decreasing Functions 1-to-1, Onto
... (Every element in B is mapped to by at most one element of A.) ...
... (Every element in B is mapped to by at most one element of A.) ...
5.4 Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Herbst - Spring
... • Set up the equation to find the area of the ...
... • Set up the equation to find the area of the ...