Introduction to Development
... Figure 21.12 The effect of the bicoid gene, a maternal effect (egg-polarity) gene Drosophila ...
... Figure 21.12 The effect of the bicoid gene, a maternal effect (egg-polarity) gene Drosophila ...
What is a Gene? - GAURAV KUMAR PAL
... MUTON - It is the smallest unit of DNA which can undergo Mutation. CISTRON - It is the unit of Function. It is the Gene in real sense capable of synthesizing a Polypeptide chain of an ...
... MUTON - It is the smallest unit of DNA which can undergo Mutation. CISTRON - It is the unit of Function. It is the Gene in real sense capable of synthesizing a Polypeptide chain of an ...
Part 1 Microarray Timeseries Analysis with replicates OSM
... The test statistic used for the gene-set-test is the mean of the statistics in the set. If ranks.only is TRUE the only the ranks of the statistics are used. In this case the pvalue is obtained from a Wilcoxon test. If ranks.only is FALSE, then the p-value is obtained by simulation using nsim random ...
... The test statistic used for the gene-set-test is the mean of the statistics in the set. If ranks.only is TRUE the only the ranks of the statistics are used. In this case the pvalue is obtained from a Wilcoxon test. If ranks.only is FALSE, then the p-value is obtained by simulation using nsim random ...
Population Evolution
... Main Points of Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection 1. Over production. Most organisms produce more offspring than can survive. 2. Competition. Organisms compete for food and resources. 3. Variation. There is variation among individuals of a species. 4. Adaptation. Individuals with traits best suite ...
... Main Points of Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection 1. Over production. Most organisms produce more offspring than can survive. 2. Competition. Organisms compete for food and resources. 3. Variation. There is variation among individuals of a species. 4. Adaptation. Individuals with traits best suite ...
Chapter 12-1: DNA
... – Heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes – Homozygous parental phenotypes not seen in F1 offspring ______________________________________: • situation in which both alleles of a gene contribute to the phenotype of the organism; ________________ alleles are expre ...
... – Heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes – Homozygous parental phenotypes not seen in F1 offspring ______________________________________: • situation in which both alleles of a gene contribute to the phenotype of the organism; ________________ alleles are expre ...
Biology
... reproduce successfully – Give examples of mutations affecting an organisms phenotype that would make them more and less successful! ...
... reproduce successfully – Give examples of mutations affecting an organisms phenotype that would make them more and less successful! ...
Mutations and Metabolic Pathways
... discuss what would happen to the DNA base sequence and final protein if an additional nucleotide was inserted into the sequence as an extra, rather than being substituted for another, and ...
... discuss what would happen to the DNA base sequence and final protein if an additional nucleotide was inserted into the sequence as an extra, rather than being substituted for another, and ...
Plasmids by Dr. Ty C.M. Hoffman
... circular chromosome of a bacterium, only much smaller. The bacterial chromosome contains all the genes that code for proteins that are necessary for survival under normal circumstances. Plasmids represent DNA ...
... circular chromosome of a bacterium, only much smaller. The bacterial chromosome contains all the genes that code for proteins that are necessary for survival under normal circumstances. Plasmids represent DNA ...
Slides
... Quantitatively characterize interactions of network elements; Predict the function of genes in biological networks. ...
... Quantitatively characterize interactions of network elements; Predict the function of genes in biological networks. ...
Chapter 15 Chromosomal Basis of Heredity
... 2. Explain why Drosophila melanogaster is a good experimental organism for genetic studies. 3. Explain why linked genes do not assort independently. 4. Distinguish between parental and recombinant phenotypes. 5. Explain how crossing over can unlink genes. 6. Explain how Sturtevant created linkage ma ...
... 2. Explain why Drosophila melanogaster is a good experimental organism for genetic studies. 3. Explain why linked genes do not assort independently. 4. Distinguish between parental and recombinant phenotypes. 5. Explain how crossing over can unlink genes. 6. Explain how Sturtevant created linkage ma ...
2015 Event Materials - Iowa FFA Association
... a. Identify a termination sequence and a proper coding region and put them together. b. Identify a promoter and a proper coding region and put them together. c. Identify a proper promoter and termination region and put them together. 10. Amino acids, referred to as the building blocks of life, each ...
... a. Identify a termination sequence and a proper coding region and put them together. b. Identify a promoter and a proper coding region and put them together. c. Identify a proper promoter and termination region and put them together. 10. Amino acids, referred to as the building blocks of life, each ...
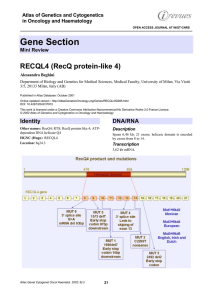
Gene Section RECQL4 (RecQ protein-like 4) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... domain with a potential ATP binding site from aa 502 to 509, and the DEAH box from aa 605 to 608. ...
... domain with a potential ATP binding site from aa 502 to 509, and the DEAH box from aa 605 to 608. ...
Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
... Blue lines: various quantiles (same as before) across all GO class Compare with KS and modified KS (Right column. MIT, PNAS and Nature Gen.) Same data, same permutation!! ...
... Blue lines: various quantiles (same as before) across all GO class Compare with KS and modified KS (Right column. MIT, PNAS and Nature Gen.) Same data, same permutation!! ...
Dihybrid Crosses
... Mendel was experimenting with flowers in the monastery's gardens. He wondered how traits were passed from parent to offspring. He studied the relations between parents and offspring with mathematical symbols. His favorite plants to experiment with were peas. ...
... Mendel was experimenting with flowers in the monastery's gardens. He wondered how traits were passed from parent to offspring. He studied the relations between parents and offspring with mathematical symbols. His favorite plants to experiment with were peas. ...
BIO 208: GENETICS
... 1. What is GFP and from what organism (genus and species) is the GFP gene obtained? 2. A number of colorations proteins have been identified in the snake-licks sea anemone. Which of these proteins is/are fluorescent after UV irradiation an in what part of the anemone body are they located? 3. The fu ...
... 1. What is GFP and from what organism (genus and species) is the GFP gene obtained? 2. A number of colorations proteins have been identified in the snake-licks sea anemone. Which of these proteins is/are fluorescent after UV irradiation an in what part of the anemone body are they located? 3. The fu ...
Genetic Transfer in Bacteria
... surrounding environment. – For example, harmless Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria can be transformed to pneumonia-causing cells. – This occurs when a live nonpathogenic cell takes up a piece of DNA that happened to include the allele for pathogenicity from dead, broken-open pathogenic cells. – The ...
... surrounding environment. – For example, harmless Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria can be transformed to pneumonia-causing cells. – This occurs when a live nonpathogenic cell takes up a piece of DNA that happened to include the allele for pathogenicity from dead, broken-open pathogenic cells. – The ...
S. M. Short and B. P. Lazzaro 3 SI Figure S2 Log2 fold
... values we obtained for these same genes from the microarray experiment (y-axis). All values plotted in this figure can be found in Table S6. For many of the genes we measured, there was more than one independent probeset on the microarray. In these cases, we picked one probeset at random to include ...
... values we obtained for these same genes from the microarray experiment (y-axis). All values plotted in this figure can be found in Table S6. For many of the genes we measured, there was more than one independent probeset on the microarray. In these cases, we picked one probeset at random to include ...
Genetics Unit final
... inherits a normal copy of fathers genes, but the mothers gene may be mutated, and the mother’s overpowers the father’s. ...
... inherits a normal copy of fathers genes, but the mothers gene may be mutated, and the mother’s overpowers the father’s. ...
Cengage Learning
... Probability is a number between 0 and 1 that indicates the likelihood that something will happen (if 0, it never happens; if 1, it always happens). Thus, each new organism has a probability of three chances in four of having at least one dominant allele in the above example. ...
... Probability is a number between 0 and 1 that indicates the likelihood that something will happen (if 0, it never happens; if 1, it always happens). Thus, each new organism has a probability of three chances in four of having at least one dominant allele in the above example. ...
embj201284303-sup-0001-SupportingInformation
... Ion leakage measurement was conducted essentially as described earlier (Heidrich et al, 2011). Leaves of 4-week old plants were infiltrated with Pst DC3000 AvrRpm1 at 108 cfu/ml. Leaf discs were excised at 1, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10 and 22 h post infiltration, washed in water for 30 minutes, and then transfe ...
... Ion leakage measurement was conducted essentially as described earlier (Heidrich et al, 2011). Leaves of 4-week old plants were infiltrated with Pst DC3000 AvrRpm1 at 108 cfu/ml. Leaf discs were excised at 1, 3, 5, 6, 8, 10 and 22 h post infiltration, washed in water for 30 minutes, and then transfe ...
Slide 1
... Plasmid-stimulated transfer Recipient w/o plasmid Plasmid only is transferred Plasmid is integrated in the chromosome both transferred Plasmid w. chromosomal genes ...
... Plasmid-stimulated transfer Recipient w/o plasmid Plasmid only is transferred Plasmid is integrated in the chromosome both transferred Plasmid w. chromosomal genes ...
Genome evolution

Genome evolution is the process by which a genome changes in structure (sequence) or size over time. The study of genome evolution involves multiple fields such as structural analysis of the genome, the study of genomic parasites, gene and ancient genome duplications, polyploidy, and comparative genomics. Genome evolution is a constantly changing and evolving field due to the steadily growing number of sequenced genomes, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, available to the scientific community and the public at large.