AP Biology - Genetic Practice Problems Choose the answer which
... that were heterozygous at both loci (5.) none of the above 32. Huntington's disease is an example of a genetic disorder caused by (1.) late-acting lethal dominant allele (2.) a nonlethal dominant allele (3.) a late-acting recessive allele (4.) homozygous recessive alleles (5.) multiple alleles 33. S ...
... that were heterozygous at both loci (5.) none of the above 32. Huntington's disease is an example of a genetic disorder caused by (1.) late-acting lethal dominant allele (2.) a nonlethal dominant allele (3.) a late-acting recessive allele (4.) homozygous recessive alleles (5.) multiple alleles 33. S ...
Genetic Crosses
... • Extra-nuclear genes are present as small circles of DNA in mitochondria and chloroplasts (both of which reproduce by themselves passing on their genes) • Since, pollen does not contain these organelles and mitochondria are in the tail of the sperm, only the head joins with the egg, this means that ...
... • Extra-nuclear genes are present as small circles of DNA in mitochondria and chloroplasts (both of which reproduce by themselves passing on their genes) • Since, pollen does not contain these organelles and mitochondria are in the tail of the sperm, only the head joins with the egg, this means that ...
HEREDITY
... bag. This represents their first offspring. Begin a chart to record the genotype and phenotype of this offspring. Place the beads back in their original bags. 6. Shake the bags to mix the alleles and repeat the mating process from Step 5. Record the results as before. Repeat until you have produced 2 ...
... bag. This represents their first offspring. Begin a chart to record the genotype and phenotype of this offspring. Place the beads back in their original bags. 6. Shake the bags to mix the alleles and repeat the mating process from Step 5. Record the results as before. Repeat until you have produced 2 ...
Genetic Variation & Evolution
... Mutation: mostly point mutations (other mutations are possible) Sexual Reproduction: crossing over, independent assortment Diploidy: recessive alleles can be hidden (from natural selection) but stay around ...
... Mutation: mostly point mutations (other mutations are possible) Sexual Reproduction: crossing over, independent assortment Diploidy: recessive alleles can be hidden (from natural selection) but stay around ...
Genetics Study Guide- Be sure to review the chapters and your
... 2. What are the differences between mitosis and meiosis? ...
... 2. What are the differences between mitosis and meiosis? ...
VII. Natural Selection - Effingham County Schools
... will reproduce and pass those traits down to their offspring. B. Predator that can beat the competition for food will survive and pass on their dominant traits to their offspring ...
... will reproduce and pass those traits down to their offspring. B. Predator that can beat the competition for food will survive and pass on their dominant traits to their offspring ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs), randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPDs), and short tandem repeats (STRs), which are also known as microsatellites. The alleles at microsatellite markers differ in the number of replications of short (1–6 base pairs) sequences of DNA. In compariso ...
... restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs), randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPDs), and short tandem repeats (STRs), which are also known as microsatellites. The alleles at microsatellite markers differ in the number of replications of short (1–6 base pairs) sequences of DNA. In compariso ...
8-3 notes
... C. Both parents must be considered when calculating probability D. To find probability, multiply the separate probabilities of the two events ...
... C. Both parents must be considered when calculating probability D. To find probability, multiply the separate probabilities of the two events ...
Mendel and Heredity
... • The P generation was ½ purple & ½ white. • In the F1 generation one trait disappeared in all of the plants. (All purple, no white) • In the F2 generation the white trait reappeared in ¼ of the plants. • The ratio of purple to white flowers was ...
... • The P generation was ½ purple & ½ white. • In the F1 generation one trait disappeared in all of the plants. (All purple, no white) • In the F2 generation the white trait reappeared in ¼ of the plants. • The ratio of purple to white flowers was ...
Ch. 08 Mendel and Heredity
... • The P generation was ½ purple & ½ white. • In the F1 generation one trait disappeared in all of the plants. (All purple, no white) • In the F2 generation the white trait reappeared in ¼ of the plants. • The ratio of purple to white flowers was ...
... • The P generation was ½ purple & ½ white. • In the F1 generation one trait disappeared in all of the plants. (All purple, no white) • In the F2 generation the white trait reappeared in ¼ of the plants. • The ratio of purple to white flowers was ...
3327 Syllabus - Kennesaw State University | College of Science and
... must get a prior approval from the instructor before you can take make-up exams. In case of illness, you must hand in a copy of your doctor’s note to the instructor. Withdraw Policy: The last day to withdraw without academic penalty is March 12, 2012. Enrolment Policy: Only those students who are en ...
... must get a prior approval from the instructor before you can take make-up exams. In case of illness, you must hand in a copy of your doctor’s note to the instructor. Withdraw Policy: The last day to withdraw without academic penalty is March 12, 2012. Enrolment Policy: Only those students who are en ...
Heredity
... From his experiments, Mendel concluded that biological inheritance was determined by factors that are passed down from one generation to the next. Today, scientists call these factors GENES Since sexual reproducing organisms have two parents, then they have two forms of the same gene – one from each ...
... From his experiments, Mendel concluded that biological inheritance was determined by factors that are passed down from one generation to the next. Today, scientists call these factors GENES Since sexual reproducing organisms have two parents, then they have two forms of the same gene – one from each ...
13 Genetics Part 1
... applies to dihybrid cross. Illustrate an example of dihybrid cross. Discuss how a testcross is performed to determine the genotype of an organism. ...
... applies to dihybrid cross. Illustrate an example of dihybrid cross. Discuss how a testcross is performed to determine the genotype of an organism. ...
Principals of General Zoology (Zoo-103)
... Understand the definition and branches of genetics. Understand the key features of chromosome and gene. Describe the key steps in the cell cycle. Describe the relationship between mitosis and meiosis in both ...
... Understand the definition and branches of genetics. Understand the key features of chromosome and gene. Describe the key steps in the cell cycle. Describe the relationship between mitosis and meiosis in both ...
Genetics Since Mendle
... Polygenic Inheritance 1. Poly is a prefix meaning more than one. 2. Polygenic inheritance occurs when a group of gene pairs act together to produce a trait. 3. Eye color, height, hair color, and skin color are examples of polygenic inheritance. ...
... Polygenic Inheritance 1. Poly is a prefix meaning more than one. 2. Polygenic inheritance occurs when a group of gene pairs act together to produce a trait. 3. Eye color, height, hair color, and skin color are examples of polygenic inheritance. ...
Linkage with Dragon Genetics
... eggs produced by the heterozygous (WwHh) mother dragon and the sperm produced by the homozygous (wwhh) father dragon. Considering both the wing and horn genes, what different genotypes of eggs could the heterozygous mother dragon produce? Use the figure below to answer this question. Notice that, in ...
... eggs produced by the heterozygous (WwHh) mother dragon and the sperm produced by the homozygous (wwhh) father dragon. Considering both the wing and horn genes, what different genotypes of eggs could the heterozygous mother dragon produce? Use the figure below to answer this question. Notice that, in ...
8. Conservation genetics
... – If heterozygosity itself is good, then individual heterozygosity and fitness should correlate • However, this phenomenon could be caused for example by population structure or partial inbreeding • Enzyme gene heterozygosity: only rarely heterozygosity-fitness correlation, which could not be explai ...
... – If heterozygosity itself is good, then individual heterozygosity and fitness should correlate • However, this phenomenon could be caused for example by population structure or partial inbreeding • Enzyme gene heterozygosity: only rarely heterozygosity-fitness correlation, which could not be explai ...
Variation Within a Population
... In organisms that reproduce _____________, ____________________ mutation in producing of alleles _________________ is more important than ___________ the genetic differences that make adaptation possible ...
... In organisms that reproduce _____________, ____________________ mutation in producing of alleles _________________ is more important than ___________ the genetic differences that make adaptation possible ...
Document
... Phenotype – a physical trait that shows as a result of an organism’s particular genotype Genotype – the genetic makeup of an organism for a trait; alleles in a gene pair Punnett square – a tool for predicting possible offspring Probability – the mathematical chance that an event will occur ...
... Phenotype – a physical trait that shows as a result of an organism’s particular genotype Genotype – the genetic makeup of an organism for a trait; alleles in a gene pair Punnett square – a tool for predicting possible offspring Probability – the mathematical chance that an event will occur ...
Unit 5 - Notes
... What are the four possible blood types? _______ Is albinism dominant or recessive? _________ If two people are both heterozygous for sickle cell trait, what is the chance they they will have a child with sickle cell disease? ...
... What are the four possible blood types? _______ Is albinism dominant or recessive? _________ If two people are both heterozygous for sickle cell trait, what is the chance they they will have a child with sickle cell disease? ...
Genetics in Everyday Life
... family of Queen Victoria. She was a carrier, and a number of her children and grandchildren were either affected by the condition or carriers themselves. Other examples of X-linked conditions include red-green colour blindness and fragile Xsyndrome. Section 6: Genetic Conditions There are many genet ...
... family of Queen Victoria. She was a carrier, and a number of her children and grandchildren were either affected by the condition or carriers themselves. Other examples of X-linked conditions include red-green colour blindness and fragile Xsyndrome. Section 6: Genetic Conditions There are many genet ...
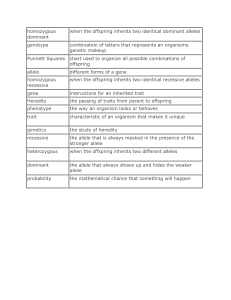
homozygous dominant when the offspring inherits two identical
... the allele that is always masked in the presence of the stronger allele ...
... the allele that is always masked in the presence of the stronger allele ...