Review PPT
... • BOD low demand B. Pollution enters stream C. Decomposition Zone • DECOMPOSITION increases to break down pollution • OXYGEN decreases as it is used up by decomposers D. Septic zone – DEAD ZONE - Hypoxic • dissolved oxygen levels are very low and very few species can survive E. Recovery Zone • Waste ...
... • BOD low demand B. Pollution enters stream C. Decomposition Zone • DECOMPOSITION increases to break down pollution • OXYGEN decreases as it is used up by decomposers D. Septic zone – DEAD ZONE - Hypoxic • dissolved oxygen levels are very low and very few species can survive E. Recovery Zone • Waste ...
Water Resources and Pollution
... incinerated or treated for harmful bacteria, toxic metals and then can be applied as fertilizer • Require industries to remove toxic and hazardous waste before reaching municiapl sewage treatment plant (E’town requires this) • Use natural and artificial wetland systems to treat sewage: water pumped ...
... incinerated or treated for harmful bacteria, toxic metals and then can be applied as fertilizer • Require industries to remove toxic and hazardous waste before reaching municiapl sewage treatment plant (E’town requires this) • Use natural and artificial wetland systems to treat sewage: water pumped ...
MUTAG ny Multi Phostrip
... Not only phosphorus, but also nitrogen and excess sludge represent an economic and environmental problem at municipal wastewater treatment plants. Specific return flow loads on plants by process water from sludge dewatering facilities can be put at 5-20% total phosphorus, 15-25% total nitrogen, and ...
... Not only phosphorus, but also nitrogen and excess sludge represent an economic and environmental problem at municipal wastewater treatment plants. Specific return flow loads on plants by process water from sludge dewatering facilities can be put at 5-20% total phosphorus, 15-25% total nitrogen, and ...
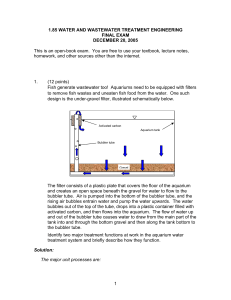
1.85 water and wastewater treatment engineering final exam
... Anoxic = low in oxygen such that nitrate is also used as an electron acceptor. ...
... Anoxic = low in oxygen such that nitrate is also used as an electron acceptor. ...
15_FynnM, Waste Water Treatment Comparison Method
... IN ORDER TO BE IN THE BEST POSITION TO UTILIZE THE WASTEWATER AS FOOD TWO TYPES OF GROWTH ENVIRONMENTS SUSPENDED GROWTH ENVIRONMENT FIXED GROWTH ENVIRONMENTS ...
... IN ORDER TO BE IN THE BEST POSITION TO UTILIZE THE WASTEWATER AS FOOD TWO TYPES OF GROWTH ENVIRONMENTS SUSPENDED GROWTH ENVIRONMENT FIXED GROWTH ENVIRONMENTS ...
From photosynthesis to wastewater treatment: exploitation of gas
... in real and synthetic wastewater were carried out in order to investigate their growth and their nutrient removal capacity under continuous light and under day/night cycle conditions. Five conditions were studied in order to compare the growth of these microorganisms and their capacity of degrading ...
... in real and synthetic wastewater were carried out in order to investigate their growth and their nutrient removal capacity under continuous light and under day/night cycle conditions. Five conditions were studied in order to compare the growth of these microorganisms and their capacity of degrading ...
Slide 1
... gravity. This primary wastewater flows out to the next stage of treatment. Scrapers collect the solid matter that remains (called "primary sludge"). A surface skimmer collects scum or grease floating on top of the basins. ...
... gravity. This primary wastewater flows out to the next stage of treatment. Scrapers collect the solid matter that remains (called "primary sludge"). A surface skimmer collects scum or grease floating on top of the basins. ...
Environmental Engineering - Pollution: Types, Sources and
... • 250 g are dissolved solids such as Ca, Na • 125 g are insoluable solids that will settle out in ...
... • 250 g are dissolved solids such as Ca, Na • 125 g are insoluable solids that will settle out in ...
BIOLOGICAL TREATMENT Objective
... The microorganisms responsible for treatment are maintained suspension by appropriate mixing methods. Attached – growth processes : The microorganisms are attached to some inert medium, such as rock, slag or specially designed ceramic or plastic materials. (also called Fixed-film processes) ...
... The microorganisms responsible for treatment are maintained suspension by appropriate mixing methods. Attached – growth processes : The microorganisms are attached to some inert medium, such as rock, slag or specially designed ceramic or plastic materials. (also called Fixed-film processes) ...
Environmental Technology 1
... If residence time is excessive (> 2hr) the risk in secondary clarifier is that denitrification takes place, generating N2 microbubbles which can float sludge flocs. What we obviously want to avoid is sludge loss into the receiving water body we actually wanted to protect in the first place. On site ...
... If residence time is excessive (> 2hr) the risk in secondary clarifier is that denitrification takes place, generating N2 microbubbles which can float sludge flocs. What we obviously want to avoid is sludge loss into the receiving water body we actually wanted to protect in the first place. On site ...
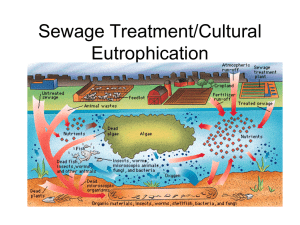
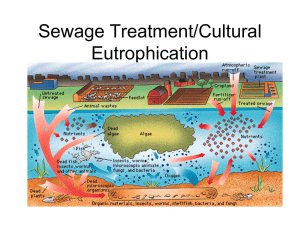
Sewage Treatment/Cultural Eutrophication
... Grit and sand, which would damage pumps, are also removed by settling tanks and disposed of in a similar way. ...
... Grit and sand, which would damage pumps, are also removed by settling tanks and disposed of in a similar way. ...
File
... Grit and sand, which would damage pumps, are also removed by settling tanks and disposed of in a similar way. ...
... Grit and sand, which would damage pumps, are also removed by settling tanks and disposed of in a similar way. ...
Secondary treatment
Secondary treatment is a treatment process for wastewater (or sewage) to achieve a certain degree of effluent quality by using a sewage treatment plant with physical phase separation to remove settleable solids and a biological process to remove dissolved and suspended organic compounds. After this kind of treatment, the wastewater may be called as secondary-treated wastewater.Secondary treatment is the portion of a sewage treatment sequence removing dissolved and colloidal compounds measured as biochemical oxygen demand (BOD). Secondary treatment is traditionally applied to the liquid portion of sewage after primary treatment has removed settleable solids and floating material. Secondary treatment is typically performed by indigenous, aquatic microorganisms in a managed aerobic habitat. Bacteria and protozoa consume biodegradable soluble organic contaminants (e.g. sugars, fats, and organic short-chain carbon molecules from human waste, food waste, soaps and detergent) while reproducing to form cells of biological solids. Biological oxidation processes are sensitive to temperature and, between 0 °C and 40 °C, the rate of biological reactions increase with temperature. Most surface aerated vessels operate at between 4 °C and 32 °C.