Genetics Powerpoint - teacher version 2012 no
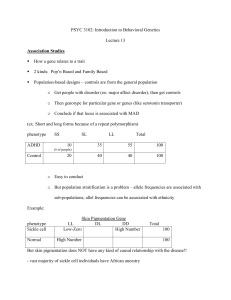
... among people are attributable to genes Heritability is numerical value with a range from 0.0 to 1.0 0 = genes do not contribute at all to individual differences High environmentability 1.0 = genes are the only reason for individual differences High heritability For human behavior, almost all ...
... among people are attributable to genes Heritability is numerical value with a range from 0.0 to 1.0 0 = genes do not contribute at all to individual differences High environmentability 1.0 = genes are the only reason for individual differences High heritability For human behavior, almost all ...
Twin Studies - Solon City Schools
... among people are attributable to genes Heritability is numerical value with a range from 0.0 to 1.0 0 = genes do not contribute at all to individual differences High environmentability 1.0 = genes are the only reason for individual differences High heritability For human behavior, almost all ...
... among people are attributable to genes Heritability is numerical value with a range from 0.0 to 1.0 0 = genes do not contribute at all to individual differences High environmentability 1.0 = genes are the only reason for individual differences High heritability For human behavior, almost all ...
Genetic Diversity of Offspring
... chance of survival if be advantageous to have they are rearranged genes rearrange each at each generation generation? • Only offspring that are • Are you a twin, or do you not diverse are twins know any twins? Do you – Identical twins – Fraternal twins ...
... chance of survival if be advantageous to have they are rearranged genes rearrange each at each generation generation? • Only offspring that are • Are you a twin, or do you not diverse are twins know any twins? Do you – Identical twins – Fraternal twins ...
Haneen`s Presentation
... characteristics and these genes are inherited from our parents. The actual genetic code is known as the genotype. However, you get one gene from each parent for everything, but obviously only one of these can be expressed; so how the genes actually manifest themselves is called the phenotype. ...
... characteristics and these genes are inherited from our parents. The actual genetic code is known as the genotype. However, you get one gene from each parent for everything, but obviously only one of these can be expressed; so how the genes actually manifest themselves is called the phenotype. ...
Bio Chp 15.2 Page 1
... In your textbook, read about population genetics and evolution. Determine if the statement is true. If it is not, rewrite the italicized part to make it true. 1. Adaptations of species are determined by the genes contained in the DNA code. __________________ 2. When Charles Mendel developed the theo ...
... In your textbook, read about population genetics and evolution. Determine if the statement is true. If it is not, rewrite the italicized part to make it true. 1. Adaptations of species are determined by the genes contained in the DNA code. __________________ 2. When Charles Mendel developed the theo ...
Genetics Objectives 22
... and dizygotic twins share 50% of their genetic information. Thus, if monozygotic twins share a trait less than 100% of the time, the trait must be influenced by environmental factors. Similarly, if a trait is more commonly shared between monozygotic twins than dizygotic twins, the trait must be infl ...
... and dizygotic twins share 50% of their genetic information. Thus, if monozygotic twins share a trait less than 100% of the time, the trait must be influenced by environmental factors. Similarly, if a trait is more commonly shared between monozygotic twins than dizygotic twins, the trait must be infl ...
It`s All in the Genes
... fascinating inherited traits in humans, from top to toes. Genes control whether hair is blond, brown, or black, whether or not it has red highlights, and whether it is straight, curly, or kinky. Widow’s peaks, cowlicks, a whorl in the eyebrow, and white forelocks run in families, ...
... fascinating inherited traits in humans, from top to toes. Genes control whether hair is blond, brown, or black, whether or not it has red highlights, and whether it is straight, curly, or kinky. Widow’s peaks, cowlicks, a whorl in the eyebrow, and white forelocks run in families, ...
Genetics: An Introduction
... domestication of animals and plants, selective breeding for good characteristics Sumerian horse breeding records Egyptian data palm breeding ...
... domestication of animals and plants, selective breeding for good characteristics Sumerian horse breeding records Egyptian data palm breeding ...
JHS 2017 Workshop on Return of Genetic Results Glossary ACMG
... for an RNA chain. A gene mutation is a change in the region of DNA that makes up a gene. This change can be as small as a single chemical unit (A, C, G, or T) in the DNA. ...
... for an RNA chain. A gene mutation is a change in the region of DNA that makes up a gene. This change can be as small as a single chemical unit (A, C, G, or T) in the DNA. ...
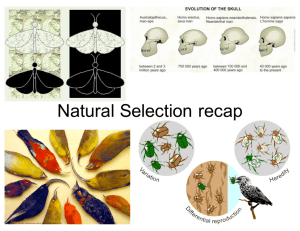
Natural Selection Intro
... organisms an advantage to survival in a specific environment. Natural selection leads to adaptations becoming common • Over many generations populations become adapted to their environment. ...
... organisms an advantage to survival in a specific environment. Natural selection leads to adaptations becoming common • Over many generations populations become adapted to their environment. ...
Ch. 4. Modern Genetics
... To explain why some human traits show a large variety of phenotypes. To explain how environmental factors can alter the effects of a gene. To explain what determines sex and why some sex linked traits are more common in males than in females. To describe how geneticists use pedigrees. ...
... To explain why some human traits show a large variety of phenotypes. To explain how environmental factors can alter the effects of a gene. To explain what determines sex and why some sex linked traits are more common in males than in females. To describe how geneticists use pedigrees. ...
DNA and Gene Expression
... • Heritability measures always refer to degree of variation between individuals in a population • Can not be applied at level of individual • E.g., if heritability index of trait is 0.4 it is incorrect to say that 40% of this trait is from the parents and 60% is from the environment – In clones the ...
... • Heritability measures always refer to degree of variation between individuals in a population • Can not be applied at level of individual • E.g., if heritability index of trait is 0.4 it is incorrect to say that 40% of this trait is from the parents and 60% is from the environment – In clones the ...
chapter_22
... Francis Galton and Karl Pearson (late 1800s): Recognized that continuous traits are statistically correlated between parents and offspring, but could not determine how transmission occurs. ...
... Francis Galton and Karl Pearson (late 1800s): Recognized that continuous traits are statistically correlated between parents and offspring, but could not determine how transmission occurs. ...
The first midterm will consist of 20 four
... mates with a female who is a carrier of this disorder. Give the genotypes, phenotypes, and their expected frequencies among their male and female offspring. (4 points) 3. Answer the following: A. Explain the components of the ACE model and what MZ and DZ twins tell us with respect to this model. (3 ...
... mates with a female who is a carrier of this disorder. Give the genotypes, phenotypes, and their expected frequencies among their male and female offspring. (4 points) 3. Answer the following: A. Explain the components of the ACE model and what MZ and DZ twins tell us with respect to this model. (3 ...
Genetics Pre-assessment Quiz
... GENETIC QUESTIONS – ASSIGNMENT #1 On a separate piece of paper, answer the following questions. 1. Compare and contrast heredity and genetics. 2. State some of the early ideas about how traits were passed from parents to offspring. 3. What is the Cell Theory and how does this theory relate to the st ...
... GENETIC QUESTIONS – ASSIGNMENT #1 On a separate piece of paper, answer the following questions. 1. Compare and contrast heredity and genetics. 2. State some of the early ideas about how traits were passed from parents to offspring. 3. What is the Cell Theory and how does this theory relate to the st ...
WLHS / Biology / Monson Name Date Per READING GUIDE: 17.1
... controlled by 2 alleles: R and r, which follow the rule of simple dominance at a single locus. The condition affects only homozygous recessive individuals. (the heterozygous phenotype shows no symptoms). The population you are studying has a population size of 10,000 and there are 36 individuals aff ...
... controlled by 2 alleles: R and r, which follow the rule of simple dominance at a single locus. The condition affects only homozygous recessive individuals. (the heterozygous phenotype shows no symptoms). The population you are studying has a population size of 10,000 and there are 36 individuals aff ...
READING GUIDE: 17.1 – Genes and Variation (p. 482
... controlled by 2 alleles: R and r, which follow the rule of simple dominance at a single locus. The condition affects only homozygous recessive individuals. (the heterozygous phenotype shows no symptoms). The population you are studying has a population size of 10,000 and there are 36 individuals aff ...
... controlled by 2 alleles: R and r, which follow the rule of simple dominance at a single locus. The condition affects only homozygous recessive individuals. (the heterozygous phenotype shows no symptoms). The population you are studying has a population size of 10,000 and there are 36 individuals aff ...
Human Genetics
... How are traits determined? Traits can be determined predominantly by one gene. Mendelian traits result from variation in alleles of one gene. Traits can be determined by multiple genes. Polygenic traits result from variation in several genes. ...
... How are traits determined? Traits can be determined predominantly by one gene. Mendelian traits result from variation in alleles of one gene. Traits can be determined by multiple genes. Polygenic traits result from variation in several genes. ...
Figures from Chapter 3
... Behavioral Genetics • Genetic/environment cause of trait • Heritability estimates (genetic) • Methods of studying – Experimental and selective breeding – attempt to breed particular traits into animals • Tryon’s maze-bright rats ...
... Behavioral Genetics • Genetic/environment cause of trait • Heritability estimates (genetic) • Methods of studying – Experimental and selective breeding – attempt to breed particular traits into animals • Tryon’s maze-bright rats ...
Behavior Genetics and Evolutionary Psychology
... similarities can be found between strangers. Researchers point out that differences between fraternal twins are greater than identical twins. ...
... similarities can be found between strangers. Researchers point out that differences between fraternal twins are greater than identical twins. ...
Behavioural genetics

Behavioural genetics, also commonly referred to as behaviour genetics, is the field of study that examines the role of genetic and environmental influences on animal (including human) behaviour. Often associated with the ""nature versus nurture"" debate, behavioural genetics is highly interdisciplinary, involving contributions from biology, neuroscience, genetics, epigenetics, ethology, psychology, and statistics. Behavioural geneticists study the inheritance of behavioural traits. In humans, this information is often gathered through the use of the twin study or adoption study. In animal studies, breeding, transgenesis, and gene knockout techniques are common. Psychiatric genetics is a closely related field.