Evaluates: MAX15015A/MAX15015B MAX15015A Evaluation Kit General Description Features
... greater than 4.1V by selecting resistors R2 and R3. To reconfigure the converter’s turn-on threshold, use the following equation: ⎡ VEN _ SW ...
... greater than 4.1V by selecting resistors R2 and R3. To reconfigure the converter’s turn-on threshold, use the following equation: ⎡ VEN _ SW ...
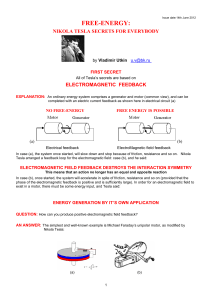
Free-Energy
... The next step is to move to this "bait" to one side of the circuit, close to the source of the charges which is the Ground. At this small separation, breakdown occurs and the inherent parasitic capacitance of the circuit will be instantly recharged with energy flowing into the circuit from outside. ...
... The next step is to move to this "bait" to one side of the circuit, close to the source of the charges which is the Ground. At this small separation, breakdown occurs and the inherent parasitic capacitance of the circuit will be instantly recharged with energy flowing into the circuit from outside. ...
NCP1562-100WGEVB NCP1562 100 W 48 V DC-DC Converter Evaluation Board
... dc−dc converter. This IC operates from an input supply up to 150 V, thus covering the input voltages usually found in telecom, datacom and 42 V automotive systems. One can also note that the NCP1562 can be used in mains related applications (e.g. desktop, server, flat TVs) as it can be supplied by a ...
... dc−dc converter. This IC operates from an input supply up to 150 V, thus covering the input voltages usually found in telecom, datacom and 42 V automotive systems. One can also note that the NCP1562 can be used in mains related applications (e.g. desktop, server, flat TVs) as it can be supplied by a ...
L5_Overview
... Of importance is the transient behavior of the inverter and the speed at which we are able to drive such an inverter. We assume a step is applied to the input of the inverter. As shown below the pmos is off and the nmos initially starts in saturation. As the load capacitor discharges then Vout decre ...
... Of importance is the transient behavior of the inverter and the speed at which we are able to drive such an inverter. We assume a step is applied to the input of the inverter. As shown below the pmos is off and the nmos initially starts in saturation. As the load capacitor discharges then Vout decre ...
Step-Down DC-to-DC Controller ADP1821 FEATURES
... The capacitor is charged through a diode from PVCC when the low-side MOSFET is on. Connect a 0.1 μF or greater ceramic capacitor from BST to SW and a Schottky diode from PVCC to BST to power the high-side gate driver. High-Side Gate Driver Output. Connect DH to the gate of the external high-side, N- ...
... The capacitor is charged through a diode from PVCC when the low-side MOSFET is on. Connect a 0.1 μF or greater ceramic capacitor from BST to SW and a Schottky diode from PVCC to BST to power the high-side gate driver. High-Side Gate Driver Output. Connect DH to the gate of the external high-side, N- ...
Voltage profile - Mon`s group Sydney
... Ф output = Ф 1 + Ф 2 depending on the position of moving coil. ...
... Ф output = Ф 1 + Ф 2 depending on the position of moving coil. ...
FAN23SV65 TinyBuck™ 15 A Integrated Synchronous Buck Regulator F AN2
... The FAN23SV65 TinyBuck™ is a highly efficient integrated synchronous buck regulator. The regulator is capable of operating with an input range from 7 V to 24 V and supporting up to 15 A continuous load currents. The device can operate from a 5 V rail (±10%) if VIN, PVIN, and PVCC are connected toget ...
... The FAN23SV65 TinyBuck™ is a highly efficient integrated synchronous buck regulator. The regulator is capable of operating with an input range from 7 V to 24 V and supporting up to 15 A continuous load currents. The device can operate from a 5 V rail (±10%) if VIN, PVIN, and PVCC are connected toget ...
NCP1612GEVB 160-W, Wide Mains, PFC Stage Driven by the NCP1612 Evaluation Board
... is proportional to the difference between 2.5 V reference and the FFcontrol voltage. This delay is maximum when the FFcontrol voltage is 0.75 V (about 45 ms) so that a nearly 20 kHz operation is obtained. Below this 0.75 V level, the circuit skips cycles. ...
... is proportional to the difference between 2.5 V reference and the FFcontrol voltage. This delay is maximum when the FFcontrol voltage is 0.75 V (about 45 ms) so that a nearly 20 kHz operation is obtained. Below this 0.75 V level, the circuit skips cycles. ...
Axopatch 200B Amplifier Brochure
... inputs are provided to permit multiple command sources (for cell capacitance experiments, current clamp, etc.). In addition, the Axopatch 200B Amplifier includes series resistance compensation in current clamp mode that allows for correction (similar to the Bridge Balance control of other amplifiers ...
... inputs are provided to permit multiple command sources (for cell capacitance experiments, current clamp, etc.). In addition, the Axopatch 200B Amplifier includes series resistance compensation in current clamp mode that allows for correction (similar to the Bridge Balance control of other amplifiers ...
AP65550 Description Pin Assignments
... Figure 4 shows the over current protection (OCP) scheme of AP65550. In each switching cycle, the inductor current is sensed by monitoring the low-side MOSFET in the OFF period. When the voltage between GND pin and SW pin is smaller than the over current trip level, the OCP will be triggered and the ...
... Figure 4 shows the over current protection (OCP) scheme of AP65550. In each switching cycle, the inductor current is sensed by monitoring the low-side MOSFET in the OFF period. When the voltage between GND pin and SW pin is smaller than the over current trip level, the OCP will be triggered and the ...
AP1534 PWM CONTROL 2A STEP-DOWN CONVERTER Description
... AP1534 consists of step-down switching regulator with PWM control. These devices include a reference voltage source, oscillation circuit, error amplifier, internal PMOS. ...
... AP1534 consists of step-down switching regulator with PWM control. These devices include a reference voltage source, oscillation circuit, error amplifier, internal PMOS. ...
A New Building Block to Light the Way to Rapid Ballast
... is voltage between the drain and source of the external lowside half-bridge MOSFET when LO turns-on, then the system is operating too close to, or, on the capacitive side of, resonance. The result is non-ZVS capacitive-mode switching that causes high peak currents to flow in the half-bridge MOSFETs ...
... is voltage between the drain and source of the external lowside half-bridge MOSFET when LO turns-on, then the system is operating too close to, or, on the capacitive side of, resonance. The result is non-ZVS capacitive-mode switching that causes high peak currents to flow in the half-bridge MOSFETs ...
FlowCAD AN PSpice AutoConvergence
... In a few cases PSpice cannot find a solution to the nonlinear circuit equations. This is generally called a “convergence problem” because the symptom is that the Newton-Raphson repeating series cannot converge onto a consistent set of voltages and currents. If you use the transient analysis, and it ...
... In a few cases PSpice cannot find a solution to the nonlinear circuit equations. This is generally called a “convergence problem” because the symptom is that the Newton-Raphson repeating series cannot converge onto a consistent set of voltages and currents. If you use the transient analysis, and it ...
TransGuard® Application Notes
... required by the EMC Directive, proper selection of voltage suppressor devices is critical. The proper selection is a function of the performance of the device under transient conditions. An ideal transient voltage suppressor would reach its “clamping voltage” in zero time. Under the conditions impos ...
... required by the EMC Directive, proper selection of voltage suppressor devices is critical. The proper selection is a function of the performance of the device under transient conditions. An ideal transient voltage suppressor would reach its “clamping voltage” in zero time. Under the conditions impos ...
LNK454/456-458/460 LinkSwitch-PL Family
... blocks, a passive damper, an active damper and a bleeder. The drawback of these blocks is increased power dissipation and therefore reduced efficiency of the supply. In this design, the values selected allow flicker-free operation with a single lamp connected to a single dimmer at high-line. For fli ...
... blocks, a passive damper, an active damper and a bleeder. The drawback of these blocks is increased power dissipation and therefore reduced efficiency of the supply. In this design, the values selected allow flicker-free operation with a single lamp connected to a single dimmer at high-line. For fli ...
1783 Basic AC Circuits
... Partial Mastery: The student demonstrates basic but inconsistent performance of fundamental knowledge and skills characterized by errors and/or omissions. Performance needs further development and supervision. ...
... Partial Mastery: The student demonstrates basic but inconsistent performance of fundamental knowledge and skills characterized by errors and/or omissions. Performance needs further development and supervision. ...
RT6254A, RT6254B - Richtek Technology
... of capacitors change as temperature, bias voltage, and operating frequency change. For example the capacitance value of a capacitor decreases as the dc bias across the capacitor increases. Several ceramic capacitors may be paralleled to meet the RMS current, size, and height requirements of the appl ...
... of capacitors change as temperature, bias voltage, and operating frequency change. For example the capacitance value of a capacitor decreases as the dc bias across the capacitor increases. Several ceramic capacitors may be paralleled to meet the RMS current, size, and height requirements of the appl ...
R-MAG®Medium Voltage Tank Vacuum Magnetic
... actuator assembly. The armature is held there by the force developed by the magnet. When the top coil is energized, the magnetic flux generated is in the same direction as the magnet assembly. The armature is drawn into the coil and brought into contact with the upper plate. In this position, the co ...
... actuator assembly. The armature is held there by the force developed by the magnet. When the top coil is energized, the magnetic flux generated is in the same direction as the magnet assembly. The armature is drawn into the coil and brought into contact with the upper plate. In this position, the co ...
SWIFT Designer power supply design program
... when external compensation is used. If the operating frequency is not one of the default values, the actual nominal frequency is shown in the calculated value. Ripple voltage, efficiency, and loop response calculations are shown at full load and nominal input voltage. Efficiency may be viewed at any ...
... when external compensation is used. If the operating frequency is not one of the default values, the actual nominal frequency is shown in the calculated value. Ripple voltage, efficiency, and loop response calculations are shown at full load and nominal input voltage. Efficiency may be viewed at any ...
Understanding Electronics Components
... and gnd. To get the optimal performance (high amplification, low distortion, low noise, etc) , it is necessary to "set" the transistor's operating point. Details on the operating point will be provided in chapter 4; for now, let's just say that DC voltage between node C and gnd should be approximate ...
... and gnd. To get the optimal performance (high amplification, low distortion, low noise, etc) , it is necessary to "set" the transistor's operating point. Details on the operating point will be provided in chapter 4; for now, let's just say that DC voltage between node C and gnd should be approximate ...
Capacitor
.jpg?width=300)
A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors (plates) separated by a dielectric (i.e. an insulator that can store energy by becoming polarized). The conductors can be thin films, foils or sintered beads of metal or conductive electrolyte, etc. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's charge capacity. A dielectric can be glass, ceramic, plastic film, air, vacuum, paper, mica, oxide layer etc. Capacitors are widely used as parts of electrical circuits in many common electrical devices. Unlike a resistor, an ideal capacitor does not dissipate energy. Instead, a capacitor stores energy in the form of an electrostatic field between its plates.When there is a potential difference across the conductors (e.g., when a capacitor is attached across a battery), an electric field develops across the dielectric, causing positive charge +Q to collect on one plate and negative charge −Q to collect on the other plate. If a battery has been attached to a capacitor for a sufficient amount of time, no current can flow through the capacitor. However, if a time-varying voltage is applied across the leads of the capacitor, a displacement current can flow.An ideal capacitor is characterized by a single constant value, its capacitance. Capacitance is defined as the ratio of the electric charge Q on each conductor to the potential difference V between them. The SI unit of capacitance is the farad (F), which is equal to one coulomb per volt (1 C/V). Typical capacitance values range from about 1 pF (10−12 F) to about 1 mF (10−3 F).The larger the surface area of the ""plates"" (conductors) and the narrower the gap between them, the greater the capacitance is. In practice, the dielectric between the plates passes a small amount of leakage current and also has an electric field strength limit, known as the breakdown voltage. The conductors and leads introduce an undesired inductance and resistance.Capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for blocking direct current while allowing alternating current to pass. In analog filter networks, they smooth the output of power supplies. In resonant circuits they tune radios to particular frequencies. In electric power transmission systems, they stabilize voltage and power flow.