The Self-Healing Affect of - Electronic Concepts, Inc.
... the dielectric at this point produce several gases including carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. The pretest clearings as an open section allow these gases to escape. In finished units small clearings do not produce enough gases to damage the capacitor performance. If the larger clearings are not pr ...
... the dielectric at this point produce several gases including carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. The pretest clearings as an open section allow these gases to escape. In finished units small clearings do not produce enough gases to damage the capacitor performance. If the larger clearings are not pr ...
DN303 - Photofl ash Capacitor Charger Has Fast Effi cient Charging
... the relevant waveforms when the output has reached 300V in the circuit of Figure 1a. The peak primary current is limited to 1.4A (typical), while the primary current when the power switch turns on is 480mA (typical). By operating the part in Continuous Conduction Mode (CCM), charge time is minimize ...
... the relevant waveforms when the output has reached 300V in the circuit of Figure 1a. The peak primary current is limited to 1.4A (typical), while the primary current when the power switch turns on is 480mA (typical). By operating the part in Continuous Conduction Mode (CCM), charge time is minimize ...
Product Sheet MKV-E1X-2,5-200
... Rated Urms (V): 2000 Rated voltage UN (V): 2830 Voltage UNDC (V): 4000 Peak voltage Us (V): 6000 Max current (Arms): 34 Peak current (A): 1800 Series resistance (mΩ): 4,3 Thermal resistance (°C/W): 5,4 Self inductance (nH): 145 Diameter (mm): 80 Height (mm): 159 Weight (kg): 850 Creepage between ter ...
... Rated Urms (V): 2000 Rated voltage UN (V): 2830 Voltage UNDC (V): 4000 Peak voltage Us (V): 6000 Max current (Arms): 34 Peak current (A): 1800 Series resistance (mΩ): 4,3 Thermal resistance (°C/W): 5,4 Self inductance (nH): 145 Diameter (mm): 80 Height (mm): 159 Weight (kg): 850 Creepage between ter ...
Product Sheet MKV-E1X-1,4-200
... Rated Urms (V): 2000 Rated voltage UN (V): 2830 Voltage UNDC (V): 4000 Peak voltage Us (V): 6000 Max current (Arms): 35 Peak current (A): 1800 Series resistance (mΩ): 3,1 Thermal resistance (°C/W): 6,9 Self inductance (nH): 125 Diameter (mm): 80 Height (mm): 119 Weight (kg): 650 Creepage between ter ...
... Rated Urms (V): 2000 Rated voltage UN (V): 2830 Voltage UNDC (V): 4000 Peak voltage Us (V): 6000 Max current (Arms): 35 Peak current (A): 1800 Series resistance (mΩ): 3,1 Thermal resistance (°C/W): 6,9 Self inductance (nH): 125 Diameter (mm): 80 Height (mm): 119 Weight (kg): 650 Creepage between ter ...
Product Sheet MKV-D1X-15-75
... Rated Urms (V): 750 Rated voltage UN (V): 1060 Voltage UNDC (V): 1400 Peak voltage Us (V): 2100 Max current (Arms): 31 Peak current (A): 1800 Series resistance (mΩ): 3,5 Thermal resistance (°C/W): 6,8 Self inductance (nH): 120 Diameter (mm): 80 Height (mm): 137 Weight (kg): 820 Creepage between term ...
... Rated Urms (V): 750 Rated voltage UN (V): 1060 Voltage UNDC (V): 1400 Peak voltage Us (V): 2100 Max current (Arms): 31 Peak current (A): 1800 Series resistance (mΩ): 3,5 Thermal resistance (°C/W): 6,8 Self inductance (nH): 120 Diameter (mm): 80 Height (mm): 137 Weight (kg): 820 Creepage between term ...
RC circuit
... The simplest example of a RC circuit consists of a battery, a resistor, and a capacitor. The resistors limit the rate at which charge can flow, and an appreciable amount of time may be required before the capacitors become fully charged. PHY 1161 ...
... The simplest example of a RC circuit consists of a battery, a resistor, and a capacitor. The resistors limit the rate at which charge can flow, and an appreciable amount of time may be required before the capacitors become fully charged. PHY 1161 ...
ECE2262 Electric Circuits Chapter 6: Capacitance and Inductance
... • A capacitor consists of two conductors separated by a non-conductive region. The non-conductive region (orange) is called the dielectric Charge separation in a parallel-plate capacitor causes an internal electric field. • A dielectric reduces the electric field and increases the capacitance. Beca ...
... • A capacitor consists of two conductors separated by a non-conductive region. The non-conductive region (orange) is called the dielectric Charge separation in a parallel-plate capacitor causes an internal electric field. • A dielectric reduces the electric field and increases the capacitance. Beca ...
Charge Sharing by Capacitors
... Thus, we may determine the value of an "unknown" capacitor C1 in terms of a "known" capacitor C2 and measured voltages V1, V2 and V'. In circuit #2, in section IV, we have two capacitors and a power supply connected in series. Circuit #3 is used for charging and reading voltages of the capacitors of ...
... Thus, we may determine the value of an "unknown" capacitor C1 in terms of a "known" capacitor C2 and measured voltages V1, V2 and V'. In circuit #2, in section IV, we have two capacitors and a power supply connected in series. Circuit #3 is used for charging and reading voltages of the capacitors of ...
ppt_ch16
... A voltage rating higher than the potential difference applied provides a safety factor for long life in service. The breakdown rating is lower for ac voltage because of the internal heat produced by continuous charge and discharge. ...
... A voltage rating higher than the potential difference applied provides a safety factor for long life in service. The breakdown rating is lower for ac voltage because of the internal heat produced by continuous charge and discharge. ...
Dissipation Factor and Capacitance Measuring Bridge
... The measuring bridge, type TG-3 MOD, is a stand-alone or a built-in (19”) universal device for measurements of dissipation factor (tan delta), capacitance (C) and power factor in connection with a standard capacitor (Data Sheet 5.31) at voltages of 50 or 60 Hz. The measuring principle is that of a c ...
... The measuring bridge, type TG-3 MOD, is a stand-alone or a built-in (19”) universal device for measurements of dissipation factor (tan delta), capacitance (C) and power factor in connection with a standard capacitor (Data Sheet 5.31) at voltages of 50 or 60 Hz. The measuring principle is that of a c ...
Film Capacitors – Power Factor Correction
... The following applies to all products named in this publication: 1. Some parts of this publication contain statements about the suitability of our products for certain areas of application. These statements are based on our knowledge of typical requirements that are often placed on our products in t ...
... The following applies to all products named in this publication: 1. Some parts of this publication contain statements about the suitability of our products for certain areas of application. These statements are based on our knowledge of typical requirements that are often placed on our products in t ...
Name - Seattle Central College
... In your write up you will show your circuits, describe your procedure and summarize how your most excellent data proves you correct. Please wordprocess all text integrating your circuit diagrams throughout. ...
... In your write up you will show your circuits, describe your procedure and summarize how your most excellent data proves you correct. Please wordprocess all text integrating your circuit diagrams throughout. ...
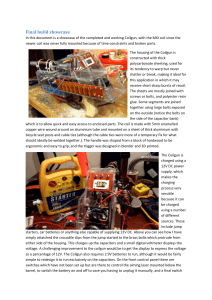
Final build showcase
... which was there so that if needed I could switch between an alternate mode which would use a timing circuit instead of an infrared detection circuit to switch the coil. ...
... which was there so that if needed I could switch between an alternate mode which would use a timing circuit instead of an infrared detection circuit to switch the coil. ...
Design Optimization of Bulk Capacitor
... Bulk Capacitor – Definition / Function Definition Bulk Capacitor is combination of capacitors which have different design purpose. It is called as DC Link, since basic function is filtering of DC flow. Y-Capacitor, X Capacitor and bus bars are located inside Power Inverter under certain Purpose. ...
... Bulk Capacitor – Definition / Function Definition Bulk Capacitor is combination of capacitors which have different design purpose. It is called as DC Link, since basic function is filtering of DC flow. Y-Capacitor, X Capacitor and bus bars are located inside Power Inverter under certain Purpose. ...
Delta Versus Wye Connected Capacitor Banks
... Fusing: Figure one also shows common fusing practices for each of the bank arrangements. The figure shows that the delta connected bank can be protected by placing the fuses inside or outside of the delta. Two fuses per single phase capacitor are required when fusing inside of the delta, but their r ...
... Fusing: Figure one also shows common fusing practices for each of the bank arrangements. The figure shows that the delta connected bank can be protected by placing the fuses inside or outside of the delta. Two fuses per single phase capacitor are required when fusing inside of the delta, but their r ...
HFAN-1.1 Choosing AC-Coupling Capacitors
... cutoff of the AC-coupling network. When NRZ data containing long strings of identical 1’s or 0’s is applied to this high-pass filter, a voltage droop occurs, resulting in low-frequency pattern-dependent jitter (PDJ). This can be understood as illustrated in Figure 1. In order to limit the low-freque ...
... cutoff of the AC-coupling network. When NRZ data containing long strings of identical 1’s or 0’s is applied to this high-pass filter, a voltage droop occurs, resulting in low-frequency pattern-dependent jitter (PDJ). This can be understood as illustrated in Figure 1. In order to limit the low-freque ...
Capacitor
.jpg?width=300)
A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors (plates) separated by a dielectric (i.e. an insulator that can store energy by becoming polarized). The conductors can be thin films, foils or sintered beads of metal or conductive electrolyte, etc. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's charge capacity. A dielectric can be glass, ceramic, plastic film, air, vacuum, paper, mica, oxide layer etc. Capacitors are widely used as parts of electrical circuits in many common electrical devices. Unlike a resistor, an ideal capacitor does not dissipate energy. Instead, a capacitor stores energy in the form of an electrostatic field between its plates.When there is a potential difference across the conductors (e.g., when a capacitor is attached across a battery), an electric field develops across the dielectric, causing positive charge +Q to collect on one plate and negative charge −Q to collect on the other plate. If a battery has been attached to a capacitor for a sufficient amount of time, no current can flow through the capacitor. However, if a time-varying voltage is applied across the leads of the capacitor, a displacement current can flow.An ideal capacitor is characterized by a single constant value, its capacitance. Capacitance is defined as the ratio of the electric charge Q on each conductor to the potential difference V between them. The SI unit of capacitance is the farad (F), which is equal to one coulomb per volt (1 C/V). Typical capacitance values range from about 1 pF (10−12 F) to about 1 mF (10−3 F).The larger the surface area of the ""plates"" (conductors) and the narrower the gap between them, the greater the capacitance is. In practice, the dielectric between the plates passes a small amount of leakage current and also has an electric field strength limit, known as the breakdown voltage. The conductors and leads introduce an undesired inductance and resistance.Capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for blocking direct current while allowing alternating current to pass. In analog filter networks, they smooth the output of power supplies. In resonant circuits they tune radios to particular frequencies. In electric power transmission systems, they stabilize voltage and power flow.