Vector impedance meter
... Constant current mode- lower range (X1, X10, X100) - unknown component connected across the input of the differential amplifier. Current depends on range of impedance switch. - Transresistance amplifier converts current through into voltage. (Op-Amp) ...
... Constant current mode- lower range (X1, X10, X100) - unknown component connected across the input of the differential amplifier. Current depends on range of impedance switch. - Transresistance amplifier converts current through into voltage. (Op-Amp) ...
Major causes of transient overvoltages
... Limit the cable length Add load if possible Change switching strategy – switch at transformer terminals instead of at cable source side • Use YY grounded transformers supplied from cables – long cable runs may need three single-phase transformer in YY grounded bank ...
... Limit the cable length Add load if possible Change switching strategy – switch at transformer terminals instead of at cable source side • Use YY grounded transformers supplied from cables – long cable runs may need three single-phase transformer in YY grounded bank ...
How to make electrolytic capacitors at home
... It's important to that there be nothing on the aluminum to start with. For the foil all you can do Spiral rolled plates in is take it straight off the roll, cut it and put it in the container with minimal handling. For the a container. soda can aluminum you'll have to sand off all paint and also san ...
... It's important to that there be nothing on the aluminum to start with. For the foil all you can do Spiral rolled plates in is take it straight off the roll, cut it and put it in the container with minimal handling. For the a container. soda can aluminum you'll have to sand off all paint and also san ...
company name - Schneider Electric
... compensation, highly fluctuating cyclical load compensation) may require special data collection which is not typically available form general power metering devices. Evaluation of the load characteristics with respect to harmonic content (both voltage and current) becomes a main factor in proper ca ...
... compensation, highly fluctuating cyclical load compensation) may require special data collection which is not typically available form general power metering devices. Evaluation of the load characteristics with respect to harmonic content (both voltage and current) becomes a main factor in proper ca ...
18. REASONING The electric potential at a distance r from a point
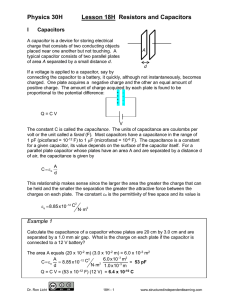
... 46. REASONING Equation 19.10 gives the capacitance as C = 0A/d, where is the dielectric constant, and A and d are, respectively, the plate area and separation. Other things being equal, the capacitor with the larger plate area has the greater capacitance. The diameter of the circle equals the l ...
... 46. REASONING Equation 19.10 gives the capacitance as C = 0A/d, where is the dielectric constant, and A and d are, respectively, the plate area and separation. Other things being equal, the capacitor with the larger plate area has the greater capacitance. The diameter of the circle equals the l ...
Power Conditioning Glossary
... the point where the device turns on and conducts current. Similar in operation to MOVs but do not degrade with use. Very reliable as long as they are used strictly within their ratings. Brown out: A sustained under-voltage condition which is low enough to cause equipment malfunction. Most equipment ...
... the point where the device turns on and conducts current. Similar in operation to MOVs but do not degrade with use. Very reliable as long as they are used strictly within their ratings. Brown out: A sustained under-voltage condition which is low enough to cause equipment malfunction. Most equipment ...
PHYSICA
... importance for the experiment to measure e, we report here on a cryogenic capacitance bridge u s i n g a SET e l e c t r o m e t e r to determine the capacitance ratio of two fused silica capacitors in a dilution refrigerator. Fig. 1 shows our capacitance bridge circuit for m e a s u r i n g the two ...
... importance for the experiment to measure e, we report here on a cryogenic capacitance bridge u s i n g a SET e l e c t r o m e t e r to determine the capacitance ratio of two fused silica capacitors in a dilution refrigerator. Fig. 1 shows our capacitance bridge circuit for m e a s u r i n g the two ...
Press Release: Power factor correction
... offer PFC values of between 5 kvar (50 Hz) and 33 kvar (60 Hz) at capacitance values of between 3 x 11 and 3 x 55 µF. Thanks to their compact design with diameters of only 116 and 136 mm at insertion heights of 164 and 200 mm, these capacitors are particularly useful for designing space-saving PFC s ...
... offer PFC values of between 5 kvar (50 Hz) and 33 kvar (60 Hz) at capacitance values of between 3 x 11 and 3 x 55 µF. Thanks to their compact design with diameters of only 116 and 136 mm at insertion heights of 164 and 200 mm, these capacitors are particularly useful for designing space-saving PFC s ...
Word - Structured Independent Learning
... Just as resistors can be placed in series or parallel in a circuit, so can capacitors. Rather than deriving the relations for capacitors in series and in parallel, the following rules are given. (For a derivation of the rules you are referred to Giancoli, 1st Edition, pp. 424-425.) The rules for pot ...
... Just as resistors can be placed in series or parallel in a circuit, so can capacitors. Rather than deriving the relations for capacitors in series and in parallel, the following rules are given. (For a derivation of the rules you are referred to Giancoli, 1st Edition, pp. 424-425.) The rules for pot ...
A2 Unit G485: Fields, particles and frontiers of physics
... (ii) V = Q/C = 40 × 10−6/(14 × 10−6) = 2.9 V (iii) Q = 10 × 10−6 × 2.9 = 2.9 × 10−5 C Examiner comments: (b) These calculations could do with some explanations. (i) When they are connected, all the positive charge remains on the top two plates and all the negative charge is on the bottom plates. The ...
... (ii) V = Q/C = 40 × 10−6/(14 × 10−6) = 2.9 V (iii) Q = 10 × 10−6 × 2.9 = 2.9 × 10−5 C Examiner comments: (b) These calculations could do with some explanations. (i) When they are connected, all the positive charge remains on the top two plates and all the negative charge is on the bottom plates. The ...
Capacitor
.jpg?width=300)
A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors (plates) separated by a dielectric (i.e. an insulator that can store energy by becoming polarized). The conductors can be thin films, foils or sintered beads of metal or conductive electrolyte, etc. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's charge capacity. A dielectric can be glass, ceramic, plastic film, air, vacuum, paper, mica, oxide layer etc. Capacitors are widely used as parts of electrical circuits in many common electrical devices. Unlike a resistor, an ideal capacitor does not dissipate energy. Instead, a capacitor stores energy in the form of an electrostatic field between its plates.When there is a potential difference across the conductors (e.g., when a capacitor is attached across a battery), an electric field develops across the dielectric, causing positive charge +Q to collect on one plate and negative charge −Q to collect on the other plate. If a battery has been attached to a capacitor for a sufficient amount of time, no current can flow through the capacitor. However, if a time-varying voltage is applied across the leads of the capacitor, a displacement current can flow.An ideal capacitor is characterized by a single constant value, its capacitance. Capacitance is defined as the ratio of the electric charge Q on each conductor to the potential difference V between them. The SI unit of capacitance is the farad (F), which is equal to one coulomb per volt (1 C/V). Typical capacitance values range from about 1 pF (10−12 F) to about 1 mF (10−3 F).The larger the surface area of the ""plates"" (conductors) and the narrower the gap between them, the greater the capacitance is. In practice, the dielectric between the plates passes a small amount of leakage current and also has an electric field strength limit, known as the breakdown voltage. The conductors and leads introduce an undesired inductance and resistance.Capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for blocking direct current while allowing alternating current to pass. In analog filter networks, they smooth the output of power supplies. In resonant circuits they tune radios to particular frequencies. In electric power transmission systems, they stabilize voltage and power flow.