Ch. 23 Series and Parallel Circuits
... – Describe both a series connection and a parallel connection and state the important characteristics of each – Calculate current, voltage drops, and equivalent resistance for devices connected in series and in parallel – Describe a voltage divider and solve problems involving one ...
... – Describe both a series connection and a parallel connection and state the important characteristics of each – Calculate current, voltage drops, and equivalent resistance for devices connected in series and in parallel – Describe a voltage divider and solve problems involving one ...
2nd Order Circuits
... in the circuit before and after a step function transition. In steady state (t < to and t = ∞s), replace energy storage devices. ...
... in the circuit before and after a step function transition. In steady state (t < to and t = ∞s), replace energy storage devices. ...
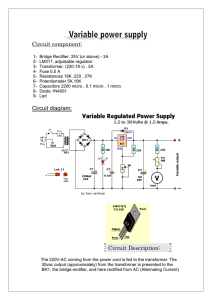
Circuit component
... provide a fixed reference voltage of 1.2 volt across the external resistor R2. (This resistor is usually around 240 ohms, but 220 ohms will work fine without any problems). Because of this the voltage at the output can never decrease below 1.2 volts, but as the potentiometer (P1) increases in resist ...
... provide a fixed reference voltage of 1.2 volt across the external resistor R2. (This resistor is usually around 240 ohms, but 220 ohms will work fine without any problems). Because of this the voltage at the output can never decrease below 1.2 volts, but as the potentiometer (P1) increases in resist ...
RC Circuits - University of Utah Physics
... through a resistor. • Learn how to build a simple resistor and capacitor from “everyday materials”. ...
... through a resistor. • Learn how to build a simple resistor and capacitor from “everyday materials”. ...
Tutorial4 clamper circuit
... short time constant, so they act as a differentiator network. This results in a brief pulse of voltage across R1 at each leading edge of the square wave input. Capacitor C2 and resistor R2 are sized to provide a long time constant, so as to form an integrator network. This time-averages the brief pu ...
... short time constant, so they act as a differentiator network. This results in a brief pulse of voltage across R1 at each leading edge of the square wave input. Capacitor C2 and resistor R2 are sized to provide a long time constant, so as to form an integrator network. This time-averages the brief pu ...
DC1664 - LTC3109EUF Evaluation Kit Quick Start Guide
... Demonstration Circuit 1664A featuring the LTC3109 is a highly integrated DC/DC converter optimized for harvesting and managing energy from extremely low input voltage sources such as thermoelectric generators (TEG). Its unique, proprietary auto-polarity topology allows it to operate from input volta ...
... Demonstration Circuit 1664A featuring the LTC3109 is a highly integrated DC/DC converter optimized for harvesting and managing energy from extremely low input voltage sources such as thermoelectric generators (TEG). Its unique, proprietary auto-polarity topology allows it to operate from input volta ...
DATASHEET HS208 SUPERCAPACITOR Features
... A traditional capacitor stores energy in the electric field created by charge separation. The electric field normally exists in a dielectric which becomes polarised. The capacitance is proportional to the permittivity of the dielectric and the area of the plates, and inversely proportional to the se ...
... A traditional capacitor stores energy in the electric field created by charge separation. The electric field normally exists in a dielectric which becomes polarised. The capacitance is proportional to the permittivity of the dielectric and the area of the plates, and inversely proportional to the se ...
Fixed capacitor bank 12kV spec
... or higher than 1,43 times the capacitor bank nominal current. The inductance value is calculated so that the peak inrush current value is lower than 100 times the nominal current of the capacitor bank, as per IEC recommendation. 4.8 Connections The connection supports are made of porcelain or epoxy ...
... or higher than 1,43 times the capacitor bank nominal current. The inductance value is calculated so that the peak inrush current value is lower than 100 times the nominal current of the capacitor bank, as per IEC recommendation. 4.8 Connections The connection supports are made of porcelain or epoxy ...
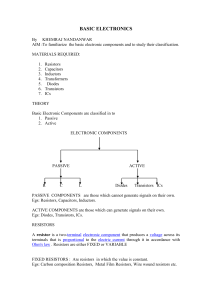
1.basic electronics
... Carbon composition resistors consist of a solid cylindrical resistive element with embedded wire leads or metal end caps to which the lead wires are attached. The body of the resistor is protected with paint or plastic The resistive element is made from a mixture of finely ground (powdered) carbon a ...
... Carbon composition resistors consist of a solid cylindrical resistive element with embedded wire leads or metal end caps to which the lead wires are attached. The body of the resistor is protected with paint or plastic The resistive element is made from a mixture of finely ground (powdered) carbon a ...
Chapter 33 - University of Utah Physics
... This expression illustrates that we cannot simply add the resistance and reactances in a circuit. We must account for the applied voltage and current being out of phase, with the phase angle f between the current and voltage being f 5 tan 21 a ...
... This expression illustrates that we cannot simply add the resistance and reactances in a circuit. We must account for the applied voltage and current being out of phase, with the phase angle f between the current and voltage being f 5 tan 21 a ...
TAIYO YUDEN Announces: Cylinder Type Lithium Ion Capacitor
... of power transmission, by adding the use of wireless communication functions and real -time clock functions. For this reason, a longer life is required, and a large current must be supplied during wireless communication as compared to the batteries that have been used as power supplies for backup w ...
... of power transmission, by adding the use of wireless communication functions and real -time clock functions. For this reason, a longer life is required, and a large current must be supplied during wireless communication as compared to the batteries that have been used as power supplies for backup w ...
LEP 4.2.03 Capacitance of metal spheres and of a spherical
... spherical conductors is shown in Fig.1. Fig.2 only shows the part of the experimental set-up which must be modified in order to determine the capacitance of a spherical capacitor. The spherical conductor (d = 2 cm) held on a barrel base and insulated against the latter is connected by means of the h ...
... spherical conductors is shown in Fig.1. Fig.2 only shows the part of the experimental set-up which must be modified in order to determine the capacitance of a spherical capacitor. The spherical conductor (d = 2 cm) held on a barrel base and insulated against the latter is connected by means of the h ...
SOT-723 Plastic-Encapsulate Diodes 5V0AT7 CESDLC
... ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Ta= 25°C unless otherwise noted, VF = 0.9 V Max. @ IF = 10mA for all types) ...
... ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (Ta= 25°C unless otherwise noted, VF = 0.9 V Max. @ IF = 10mA for all types) ...
Phys 201
... Electric Field-Strength or Intensity Field patterns of lines of force Field-strength due to point charge; Flux from a point charge Gauss's Theorem Field due to charged sphere and plane conductor Electrostatic shielding Electric potential Potential difference due to a point charge ...
... Electric Field-Strength or Intensity Field patterns of lines of force Field-strength due to point charge; Flux from a point charge Gauss's Theorem Field due to charged sphere and plane conductor Electrostatic shielding Electric potential Potential difference due to a point charge ...
2006-04 CARTS-US Capacitor Considerations for Power
... (DSC), the Sony Cyber Shot U10 contains 169 multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCC)5, while at typical cell phone, the Sony-Ericsson S0505i contains 386 MLCC.6 These numbers change with model and time, but, in general, they increase with increasing device complexity as the trend toward convergence in f ...
... (DSC), the Sony Cyber Shot U10 contains 169 multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCC)5, while at typical cell phone, the Sony-Ericsson S0505i contains 386 MLCC.6 These numbers change with model and time, but, in general, they increase with increasing device complexity as the trend toward convergence in f ...
Capacitor
.jpg?width=300)
A capacitor (originally known as a condenser) is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store electrical energy temporarily in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors (plates) separated by a dielectric (i.e. an insulator that can store energy by becoming polarized). The conductors can be thin films, foils or sintered beads of metal or conductive electrolyte, etc. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's charge capacity. A dielectric can be glass, ceramic, plastic film, air, vacuum, paper, mica, oxide layer etc. Capacitors are widely used as parts of electrical circuits in many common electrical devices. Unlike a resistor, an ideal capacitor does not dissipate energy. Instead, a capacitor stores energy in the form of an electrostatic field between its plates.When there is a potential difference across the conductors (e.g., when a capacitor is attached across a battery), an electric field develops across the dielectric, causing positive charge +Q to collect on one plate and negative charge −Q to collect on the other plate. If a battery has been attached to a capacitor for a sufficient amount of time, no current can flow through the capacitor. However, if a time-varying voltage is applied across the leads of the capacitor, a displacement current can flow.An ideal capacitor is characterized by a single constant value, its capacitance. Capacitance is defined as the ratio of the electric charge Q on each conductor to the potential difference V between them. The SI unit of capacitance is the farad (F), which is equal to one coulomb per volt (1 C/V). Typical capacitance values range from about 1 pF (10−12 F) to about 1 mF (10−3 F).The larger the surface area of the ""plates"" (conductors) and the narrower the gap between them, the greater the capacitance is. In practice, the dielectric between the plates passes a small amount of leakage current and also has an electric field strength limit, known as the breakdown voltage. The conductors and leads introduce an undesired inductance and resistance.Capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for blocking direct current while allowing alternating current to pass. In analog filter networks, they smooth the output of power supplies. In resonant circuits they tune radios to particular frequencies. In electric power transmission systems, they stabilize voltage and power flow.