Genetic Improvement and Crossbreeding in Meat Goats
... grandsons of certain individual sires and sire lines will tend to produce offspring that do well or fail to make the grade in local environments. That informal information circulates among breeders and can be used in knowing which lines of breeding tend to be most useful. Pedigree information is cri ...
... grandsons of certain individual sires and sire lines will tend to produce offspring that do well or fail to make the grade in local environments. That informal information circulates among breeders and can be used in knowing which lines of breeding tend to be most useful. Pedigree information is cri ...
chapt21_HumanBiology14e_lecture
... • What is codominance? • What is incomplete dominance? • What do you think about preimplantation genetic testing? ...
... • What is codominance? • What is incomplete dominance? • What do you think about preimplantation genetic testing? ...
Quantitative Genetics
... brother, mother, grandfather, two uncles, two cousins and an aunt all started and ran their own companies and say they cannot imagine any other livelihood. Why are so many people in the same clan hooked? Some of them have a theory. They believe that somewhere in their chromosomes lurks an actual ent ...
... brother, mother, grandfather, two uncles, two cousins and an aunt all started and ran their own companies and say they cannot imagine any other livelihood. Why are so many people in the same clan hooked? Some of them have a theory. They believe that somewhere in their chromosomes lurks an actual ent ...
SNP Analysis (GAW15 data)
... major regions of linkage on chromosomes 2, 4, 7, 10 and 11. LOD scores remained positive in all family groups. On chromosomes 2, 7, and 11 the LOD scores from the families with one or more parents typed were higher, while on chromosomes 4 and 10, the LOD scores were higher for the set of families wi ...
... major regions of linkage on chromosomes 2, 4, 7, 10 and 11. LOD scores remained positive in all family groups. On chromosomes 2, 7, and 11 the LOD scores from the families with one or more parents typed were higher, while on chromosomes 4 and 10, the LOD scores were higher for the set of families wi ...
The influence of insects and hummingbirds on the
... and gene flow among populations, as well as other complex evolutionary forces acting outside the domain of the focal interacting species, may often lead to variable patterns of adaptation and maladaptation across populations (Gomulkiewicz et al. 2000, Nuismer et al. 2003, Rudgers and Strauss 2004). ...
... and gene flow among populations, as well as other complex evolutionary forces acting outside the domain of the focal interacting species, may often lead to variable patterns of adaptation and maladaptation across populations (Gomulkiewicz et al. 2000, Nuismer et al. 2003, Rudgers and Strauss 2004). ...
An Empirical Test for Branch-Specific Positive Selection
... length and dN/dS ratio. Parameters were varied across a range of values observed in alignments of 175 transcription factor (TF) genes that were sequenced in 12 primate species. The ML method largely lacks the power to detect positive selection that has occurred since the most recent common ancestor ...
... length and dN/dS ratio. Parameters were varied across a range of values observed in alignments of 175 transcription factor (TF) genes that were sequenced in 12 primate species. The ML method largely lacks the power to detect positive selection that has occurred since the most recent common ancestor ...
Reebop Ratios - West Branch Schools
... on this variation. • Darwin knew that in order for his idea to be valid, a mechanism for preserving and inheriting variation had to exist. ...
... on this variation. • Darwin knew that in order for his idea to be valid, a mechanism for preserving and inheriting variation had to exist. ...
apbio ch 14 study guide
... o Peas have a short generation time; each mating produces many offspring. o Mendel was able to strictly control the matings of his pea plants. o Each pea plant has male (stamens) and female (carpal) sexual organs. o In nature, pea plants typically self-fertilize, fertilizing ova with the sperm nucle ...
... o Peas have a short generation time; each mating produces many offspring. o Mendel was able to strictly control the matings of his pea plants. o Each pea plant has male (stamens) and female (carpal) sexual organs. o In nature, pea plants typically self-fertilize, fertilizing ova with the sperm nucle ...
THE EFFECT OF INBREEDING ON THE VARIATION DUE TO
... the point of view of the change of gene frequency in the several lines. Starting from a population with a given gene frequency, the frequencies in the lines, as inbreeding progresses, gradually scatter further and further from the original value due to sampling (the phenomenon which in discussions o ...
... the point of view of the change of gene frequency in the several lines. Starting from a population with a given gene frequency, the frequencies in the lines, as inbreeding progresses, gradually scatter further and further from the original value due to sampling (the phenomenon which in discussions o ...
Genetics and statistical association between lethal alleles and
... balanced lethal system located at the pericentric region of chromosome six, and present two varieties: BLS1 1:1, with two lethal alleles; and BLS1 3:1, with only one lethal allele. The results obtained about the grain yield are compared with that corresponding to different kinds of public lines: N28 ...
... balanced lethal system located at the pericentric region of chromosome six, and present two varieties: BLS1 1:1, with two lethal alleles; and BLS1 3:1, with only one lethal allele. The results obtained about the grain yield are compared with that corresponding to different kinds of public lines: N28 ...
Highly Specialized Highly Specialized
... Science Park. The company has been in operation for over 10 years and has been at the forefront of Diagnostic healthcare in the region. It was established to bring a paradigm shift in the diagnostic industry in the MENA region through adoption of innovative technologies and exceptional customer serv ...
... Science Park. The company has been in operation for over 10 years and has been at the forefront of Diagnostic healthcare in the region. It was established to bring a paradigm shift in the diagnostic industry in the MENA region through adoption of innovative technologies and exceptional customer serv ...
Lost along the way: the significance of evolution in reverse
... underlying genetics of these systems. Here, we discuss several examples of systems that have investigated not only phenotypic, but also the genetic, molecular and developmental mechanisms of evolution in reverse to illustrate the similarities and disparities between different forms of reversibility. ...
... underlying genetics of these systems. Here, we discuss several examples of systems that have investigated not only phenotypic, but also the genetic, molecular and developmental mechanisms of evolution in reverse to illustrate the similarities and disparities between different forms of reversibility. ...
Proportionality between variances in gene expression induced by
... reflects the structural robustness of the phenotype, i.e., the rigidity of the phenotype against changes induced by genetic mutations, whereas the latter reflects the robustness of the phenotype against the stochasticity encountered during the developmental process or that induced by environmental c ...
... reflects the structural robustness of the phenotype, i.e., the rigidity of the phenotype against changes induced by genetic mutations, whereas the latter reflects the robustness of the phenotype against the stochasticity encountered during the developmental process or that induced by environmental c ...
Fetal Hemoglobin Levels in Sickle Cell Disease and
... reticulocytes is the major variable contributing to differences in Hb F levels. The broad distribution of Hb F levels in normal adults and in anemic SS individuals suggests that more than one genetic factor may control Hb F production. Several point mutations in the promoter regions of the two gamma ...
... reticulocytes is the major variable contributing to differences in Hb F levels. The broad distribution of Hb F levels in normal adults and in anemic SS individuals suggests that more than one genetic factor may control Hb F production. Several point mutations in the promoter regions of the two gamma ...
View presentation
... In this paper, they impose the constraint that short selling is not allowed. Hence, for the case of two assets, when the portfolio weight of a certain asset is greater than 1, it is truncated to 1, and the other portfolio weight is set equal to 0. This approach, which may yield suboptimal result ...
... In this paper, they impose the constraint that short selling is not allowed. Hence, for the case of two assets, when the portfolio weight of a certain asset is greater than 1, it is truncated to 1, and the other portfolio weight is set equal to 0. This approach, which may yield suboptimal result ...
homolog of the agouti gene
... majority of metaphases in the proximal long arm of chromosome 20 (Fig. 3). Specific FISH signals were not seen on any of the other chromosomes. According to the banding pattern of 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)-stained metaphase chromosomes, the FISH signals for the agouti gene could be assign ...
... majority of metaphases in the proximal long arm of chromosome 20 (Fig. 3). Specific FISH signals were not seen on any of the other chromosomes. According to the banding pattern of 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI)-stained metaphase chromosomes, the FISH signals for the agouti gene could be assign ...
Seed and Sieve of Odd Composite Numbers with Applications In
... Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 13, Number 2 (2017), pp. 493-517 ...
... Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics. ISSN 0973-1768 Volume 13, Number 2 (2017), pp. 493-517 ...
EvolutionChapter11
... • Selection always acts for a particular phenotypic trait, but results in selection of the genes that code for this trait ...
... • Selection always acts for a particular phenotypic trait, but results in selection of the genes that code for this trait ...
EvolutionReview
... A: What is Genetic Drift is a random change in allele frequencies when a sample is removed from the original population- either directly via founder effect, or indirectly in bottleneck effect? S2C06 Jeopardy Review ...
... A: What is Genetic Drift is a random change in allele frequencies when a sample is removed from the original population- either directly via founder effect, or indirectly in bottleneck effect? S2C06 Jeopardy Review ...
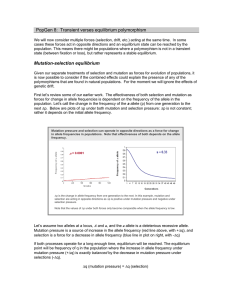
PopGen 8: Transient verses equilibrium polymorphism Mutation
... and selection pressure sufficiently large; i.e., Nes >> 1, otherwise beneficial alleles will lost occasionally due to change alone. This means that in real populations, that have finite population sizes, maladaptive alleles can be fixed. The upper limit of the fitness consequences of such alleles wi ...
... and selection pressure sufficiently large; i.e., Nes >> 1, otherwise beneficial alleles will lost occasionally due to change alone. This means that in real populations, that have finite population sizes, maladaptive alleles can be fixed. The upper limit of the fitness consequences of such alleles wi ...
You Light Up My Life
... Homozygous for an allele that specifies a heatsensitive version of an enzyme in melaninproducing pathway • Melanin is produced in cooler areas of body ...
... Homozygous for an allele that specifies a heatsensitive version of an enzyme in melaninproducing pathway • Melanin is produced in cooler areas of body ...
Ch. 7: Presentation Slides
... • Tandem duplications = repeated segments are adjacent • Tandem duplications often result from unequal crossing-over due to mispairing of homologous chromosomes during meiotic recombination ...
... • Tandem duplications = repeated segments are adjacent • Tandem duplications often result from unequal crossing-over due to mispairing of homologous chromosomes during meiotic recombination ...
single nucleotide polymorphisms and suicidal behaviour
... impaired in suicide victims by the altered function of the enzymes involved in the degradation of neurotransmitters. Catecholamine degradation is regulated with the activity of the enzyme catehol-O-methyltransferase (COMT), which catalyses the transfer of a methyl group to catecholamines and degrade ...
... impaired in suicide victims by the altered function of the enzymes involved in the degradation of neurotransmitters. Catecholamine degradation is regulated with the activity of the enzyme catehol-O-methyltransferase (COMT), which catalyses the transfer of a methyl group to catecholamines and degrade ...
Microdeletions on the long arm of the Y chromosome
... treated with ICSI. In effect, this approach treats the disorder with little knowledge of the possible consequences for the patient and/or their potential children.4 There is evidence that some cases of male infertility have an underlying genetic basis.6 Furthermore, severe male-factor infertility ha ...
... treated with ICSI. In effect, this approach treats the disorder with little knowledge of the possible consequences for the patient and/or their potential children.4 There is evidence that some cases of male infertility have an underlying genetic basis.6 Furthermore, severe male-factor infertility ha ...
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.