Chapter 16
... • Gene flow can increase variation within a population by introducing novel alleles produced by mutation in another population • Continued gene flow decreases diversity among populations, causing gene pools to become similar • Gene flow among populations can prevent speciation from occurring • Genet ...
... • Gene flow can increase variation within a population by introducing novel alleles produced by mutation in another population • Continued gene flow decreases diversity among populations, causing gene pools to become similar • Gene flow among populations can prevent speciation from occurring • Genet ...
Ch.11 Heredity
... 1. I can develop and use a model to show and describe the effects of structural changes to genes. 2. I can use and develop a Punnett Square to show genetic variations. 3. I can explain ways in which humans have influenced the inheritance of traits. 4. Explain how some genetic variations increase org ...
... 1. I can develop and use a model to show and describe the effects of structural changes to genes. 2. I can use and develop a Punnett Square to show genetic variations. 3. I can explain ways in which humans have influenced the inheritance of traits. 4. Explain how some genetic variations increase org ...
Module 5 - Valencia College
... the same species. There is no agreement on how many differences it takes to make a race. Any one race does not have exclusive possession of any particular variant of any gene or genes. The differences among individuals and within a population are generally greater than the differences among po ...
... the same species. There is no agreement on how many differences it takes to make a race. Any one race does not have exclusive possession of any particular variant of any gene or genes. The differences among individuals and within a population are generally greater than the differences among po ...
Genetic Drift
... Gene flow also drives some species to extinction. Nonnative species can threaten native plants and animals with extinction by hybridization if they have advantageous allele. Interbreeding between the species can cause a 'swamping' of the rarer species' gene pool, creating hybrids that supplan ...
... Gene flow also drives some species to extinction. Nonnative species can threaten native plants and animals with extinction by hybridization if they have advantageous allele. Interbreeding between the species can cause a 'swamping' of the rarer species' gene pool, creating hybrids that supplan ...
What are 3 major limitations of using the chimpanzee genome for
... Comment in no more than a half page on the final paragraph of the paper: explain why you agree or disagre. “Finally, the genomic rearrangements, duplications, gene-specific expansions, and measurements of the impact of natural selection presented here have revealed the rich and heterogeneous genomic ...
... Comment in no more than a half page on the final paragraph of the paper: explain why you agree or disagre. “Finally, the genomic rearrangements, duplications, gene-specific expansions, and measurements of the impact of natural selection presented here have revealed the rich and heterogeneous genomic ...
The making of the Fittest: Natural Selection and Adaptation
... Dramatic changes in traits can occur through mutations in a small number of genes, or even a single gene. Different environments can provide different selective pressures on an organism’s morphology. In the stickleback, pelvic spines provide a selective advantage in environments with large predatory ...
... Dramatic changes in traits can occur through mutations in a small number of genes, or even a single gene. Different environments can provide different selective pressures on an organism’s morphology. In the stickleback, pelvic spines provide a selective advantage in environments with large predatory ...
Part 1B Population and Community Dynamics - Science
... Change the frequency of q2 to a decimal. Take the square root of the value of q2 to find the value of q. Subtract q from 1.00 to find the value of p. Find the value of 2pq. Multiply the population size (N) by the frequency of the ...
... Change the frequency of q2 to a decimal. Take the square root of the value of q2 to find the value of q. Subtract q from 1.00 to find the value of p. Find the value of 2pq. Multiply the population size (N) by the frequency of the ...
Genetic Disorders - Michigan Department of Education Technology
... B4.2A Show that when mutations occur in sex cells, they can be passed on to offspring (inherited mutations), but if they occur in other cells, they can be passed on to descendant cells only (noninherited mutations). B4.2D Predict the consequences that changes in the DNA composition of particular ge ...
... B4.2A Show that when mutations occur in sex cells, they can be passed on to offspring (inherited mutations), but if they occur in other cells, they can be passed on to descendant cells only (noninherited mutations). B4.2D Predict the consequences that changes in the DNA composition of particular ge ...
How Are Traits Passed From Generation to Generation
... Gene- a segment of DNA that contains genetic information for making a protein Genotype- The genes in an allele pair Heterozygous- Having two different alleles of a gene pair Homologous chromosomes- a pair of chromosomes that carry corresponding genes for the same traits Homozygous- Having identical ...
... Gene- a segment of DNA that contains genetic information for making a protein Genotype- The genes in an allele pair Heterozygous- Having two different alleles of a gene pair Homologous chromosomes- a pair of chromosomes that carry corresponding genes for the same traits Homozygous- Having identical ...
Syllabus PNS0130 Evolution – effects on genes, individuals and
... Schools "Organism Biology" and "Ecology - basics and applications", but will be open for all interested PhD students/researchers. Objective: After the course, students are expected to be able to review the nature of population genetic and evolutionary processes and discuss their impact on genes, ind ...
... Schools "Organism Biology" and "Ecology - basics and applications", but will be open for all interested PhD students/researchers. Objective: After the course, students are expected to be able to review the nature of population genetic and evolutionary processes and discuss their impact on genes, ind ...
Genetic Drift
... alleles are created. After being shuffled in various combinations with the rest of the gene pool, these provide the raw material on which natural selection can act. ...
... alleles are created. After being shuffled in various combinations with the rest of the gene pool, these provide the raw material on which natural selection can act. ...
Purposeful Population Genetics
... • 3. Gene Flow – occurs when a population gains or loses alleles due to migration (either in or out) • -can bring neighboring populations together to one ...
... • 3. Gene Flow – occurs when a population gains or loses alleles due to migration (either in or out) • -can bring neighboring populations together to one ...
the evolution of populations
... makes to the gene pool of the next generation, relative to the contributions of other individuals. ¢ Natural selection is the only evolutionary mechanism that continually leads to adaptive ...
... makes to the gene pool of the next generation, relative to the contributions of other individuals. ¢ Natural selection is the only evolutionary mechanism that continually leads to adaptive ...
Notes 9.4 – DISRUPTING HWE EQUILIBRIUM
... Evolution: change in population’s genetic material (alleles) over time Genotype frequencies stay the same over time as long as certain conditions are met: ...
... Evolution: change in population’s genetic material (alleles) over time Genotype frequencies stay the same over time as long as certain conditions are met: ...
Genetic Epidemiology Lecture 13
... 1. Determination of familial aggregation 2. Determination of evidence of familial aggregation discrimination between environmental/cultural and genetic factors that may contribute to the mutation clustering 3. Determination of genetic factors and their identification ...
... 1. Determination of familial aggregation 2. Determination of evidence of familial aggregation discrimination between environmental/cultural and genetic factors that may contribute to the mutation clustering 3. Determination of genetic factors and their identification ...
Big Idea 1
... Evolution is a change in the genetic makeup of a population over time, with natural selection its major driving mechanism. Darwin’s theory, which is supported by evidence from many scientific disciplines, states that inheritable variations occur in individuals in a population. Due to competition for ...
... Evolution is a change in the genetic makeup of a population over time, with natural selection its major driving mechanism. Darwin’s theory, which is supported by evidence from many scientific disciplines, states that inheritable variations occur in individuals in a population. Due to competition for ...
Ch 023 evolupop
... 5 Agents of Microevolution 1. Genetic Drift: changes in the gene pool of a small population ...
... 5 Agents of Microevolution 1. Genetic Drift: changes in the gene pool of a small population ...
Lecture 3 Human Genetics
... Many human disorders, conditions and predispositions are multigenic Twin studies where identical twins are raised together or raised apart Look at complex behaviors and ask if they are genetic or environment Answer: For almost every single behavior…..it’s a little of both “Heritability” or the frac ...
... Many human disorders, conditions and predispositions are multigenic Twin studies where identical twins are raised together or raised apart Look at complex behaviors and ask if they are genetic or environment Answer: For almost every single behavior…..it’s a little of both “Heritability” or the frac ...
Lecture Chpt. 24 Evolutn Show 4 Variatn
... the most important effects of genetic drift: it reduces the amount of genetic variation in a population. And with less genetic variation, there is less for natural selection to work with. If the green gene drifts out of the population, and the population ends up in a situation where it would be adv ...
... the most important effects of genetic drift: it reduces the amount of genetic variation in a population. And with less genetic variation, there is less for natural selection to work with. If the green gene drifts out of the population, and the population ends up in a situation where it would be adv ...
How is DNA packed in the nucleus?
... The average gene consists of 3000 bases, but sizes vary greatly, with the largest known human gene being dystrophin at 2.4 million bases. ...
... The average gene consists of 3000 bases, but sizes vary greatly, with the largest known human gene being dystrophin at 2.4 million bases. ...
Human Genetic Disorders
... genetic disorders like PKU, Sickle-cell Anemia, and TaySachs Disease. 2. Karyotyping: A greatly enlarged photograph of chromosomes is viewed and examined to see if there are any abnormalities in number or structure. 3. Amniocentesis: A technique in which a small sample of amniotic fluid is taken fro ...
... genetic disorders like PKU, Sickle-cell Anemia, and TaySachs Disease. 2. Karyotyping: A greatly enlarged photograph of chromosomes is viewed and examined to see if there are any abnormalities in number or structure. 3. Amniocentesis: A technique in which a small sample of amniotic fluid is taken fro ...
Genetics and Behavior Principles of Gene Action and Heredity
... • Behavioral geneticists study how genes and environment combine to influence organism’s development – Variations in environment can have large effects on development of phenotype – Gene-environment interaction is a two-way process – Genetic factors play a role in the environments that individuals i ...
... • Behavioral geneticists study how genes and environment combine to influence organism’s development – Variations in environment can have large effects on development of phenotype – Gene-environment interaction is a two-way process – Genetic factors play a role in the environments that individuals i ...
population genetics
... Mutation changes DNA sequence changes amino acid sequence changes protein’s: ...
... Mutation changes DNA sequence changes amino acid sequence changes protein’s: ...
Evolution
... each locus, but the offspring will differ from both parents in traits for which there was more than one allele Genome The complete range of genes present in a species There are over 25,000 different genes in the human genome. ...
... each locus, but the offspring will differ from both parents in traits for which there was more than one allele Genome The complete range of genes present in a species There are over 25,000 different genes in the human genome. ...
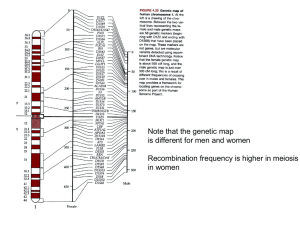
Human genetic variation

Human genetic variation is the genetic differences both within and among populations. There may be multiple variants of any given gene in the human population (genes), leading to polymorphism. Many genes are not polymorphic, meaning that only a single allele is present in the population: the gene is then said to be fixed. On average, in terms of DNA sequence all humans are 99.9% similar to any other humans.No two humans are genetically identical. Even monozygotic twins, who develop from one zygote, have infrequent genetic differences due to mutations occurring during development and gene copy-number variation. Differences between individuals, even closely related individuals, are the key to techniques such as genetic fingerprinting. Alleles occur at different frequencies in different human populations, with populations that are more geographically and ancestrally remote tending to differ more.Causes of differences between individuals include the exchange of genes during meiosis and various mutational events. There are at least two reasons why genetic variation exists between populations. Natural selection may confer an adaptive advantage to individuals in a specific environment if an allele provides a competitive advantage. Alleles under selection are likely to occur only in those geographic regions where they confer an advantage. The second main cause of genetic variation is due to the high degree of neutrality of most mutations. Most mutations do not appear to have any selective effect one way or the other on the organism. The main cause is genetic drift, this is the effect of random changes in the gene pool. In humans, founder effect and past small population size (increasing the likelihood of genetic drift) may have had an important influence in neutral differences between populations. The theory that humans recently migrated out of Africa supports this.The study of human genetic variation has both evolutionary significance and medical applications. It can help scientists understand ancient human population migrations as well as how different human groups are biologically related to one another. For medicine, study of human genetic variation may be important because some disease-causing alleles occur more often in people from specific geographic regions. New findings show that each human has on average 60 new mutations compared to their parents.Apart from mutations, many genes that may have aided humans in ancient times plague humans today. For example, it is suspected that genes that allow humans to more efficiently process food are those that make people susceptible to obesity and diabetes today.